Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
- 3.1 The Inca Empire: A Geographical Overview
- 3.2 The Inca Map: A Window into the Past
- 3.3 Types of Inca Maps
- 3.4 The Importance of the Inca Map
- 3.5 The Inca Map: A Legacy of Knowledge
- 3.6 FAQs about the Inca Map
- 3.7 Tips for Understanding the Inca Map
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Legacy of Knowledge
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration

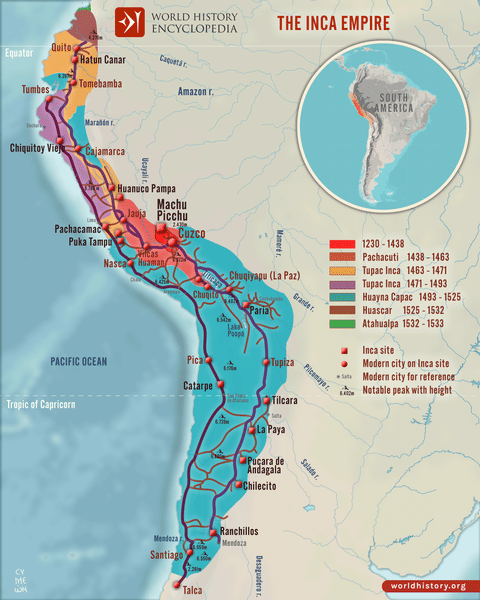
The Inca Empire, a civilization that once spanned vast swathes of South America, continues to captivate historians and travelers alike. Understanding the geographical extent of this remarkable civilization requires examining the Inca map, a vital tool for comprehending its political, social, and economic structures.
The Inca Empire: A Geographical Overview
The Inca Empire, also known as the Tawantinsuyu, meaning "the four parts," encompassed a diverse landscape stretching from present-day southern Colombia to central Chile, encompassing parts of modern-day Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, and Argentina. This vast territory encompassed the Andes Mountains, the Amazon rainforest, and the coastal deserts, presenting a unique challenge for the Inca in terms of administration and resource management.
The Inca Map: A Window into the Past
The Inca map, more accurately described as a collection of diverse cartographic representations, provides valuable insights into the organization and functioning of the empire. These maps, often created on fabric, leather, or knotted strings (quipu), were not mere geographical representations but rather served as complex systems of knowledge, recording information about:
- Administrative Divisions: The Inca Empire was divided into four quarters, each with its own administrative center and governor. The Inca map clearly depicts these divisions, highlighting the intricate network of governance that held the empire together.
- Road Network: The Inca constructed an extensive road system, known as the Qhapaq Ñan, connecting different regions of the empire. The map reveals the strategic placement of these roads, facilitating communication, trade, and military movements.
- Resource Distribution: The Inca map also provides information about the distribution of resources across the empire. This includes agricultural land, mineral deposits, and animal resources, illustrating the complex system of resource management employed by the Inca.
- Cultural and Religious Sites: The map often highlights important cultural and religious sites, such as temples, palaces, and sacred mountains, revealing the significance of these locations within the Inca worldview.
Types of Inca Maps
While the exact nature of Inca maps remains a subject of ongoing research, several types have been identified:
- Quipu: These knotted strings were used to record numerical data, including population counts, tribute payments, and agricultural yields. While not strictly maps, they provide valuable insights into the Inca’s understanding of geography and resource management.
- Fabric Maps: These maps, often woven into textiles, depicted geographical features and administrative divisions. They were often used for teaching purposes and as visual representations of the empire’s structure.
- Leather Maps: These maps, made from animal hides, were often used for ceremonial purposes and to depict specific regions or routes.
- Sand Maps: These ephemeral maps, drawn in the sand, were used for temporary purposes, such as planning military campaigns or navigating unfamiliar terrain.
The Importance of the Inca Map
The Inca map, despite its fragmentary nature, offers invaluable insights into the Inca civilization, highlighting its:
- Sophisticated Administration: The map reveals the complex system of governance that allowed the Inca to effectively manage a vast and diverse empire.
- Advanced Infrastructure: The map showcases the impressive road network, connecting different regions and facilitating trade and communication.
- Resource Management: The map demonstrates the Inca’s ability to manage resources effectively, ensuring food security and economic stability.
- Cultural Understanding: The map provides a glimpse into the Inca worldview, highlighting the significance of sacred sites and cultural practices.
The Inca Map: A Legacy of Knowledge
The Inca map, though often lost to time, serves as a powerful reminder of the ingenuity and complexity of the Inca civilization. It offers a glimpse into the intricate tapestry of their world, revealing their sophisticated understanding of geography, administration, and resource management.
FAQs about the Inca Map
Q: What is the Inca map?
A: The Inca map refers to a collection of diverse cartographic representations used by the Inca to record and understand their world. These maps were created on various materials, including fabric, leather, and knotted strings (quipu).
Q: What information did the Inca map contain?
A: The Inca map provided information about administrative divisions, road networks, resource distribution, and cultural and religious sites. It also included numerical data recorded using quipu.
Q: How were the Inca maps created?
A: The methods of map creation varied. Quipu involved knotting strings to represent numerical data, while fabric maps were woven to depict geographical features. Leather maps were often used for ceremonial purposes.
Q: What is the significance of the Inca map?
A: The Inca map provides invaluable insights into the organization, administration, and resource management of the Inca Empire. It also reveals their understanding of geography and their cultural beliefs.
Q: Where can I find examples of Inca maps?
A: While many Inca maps have been lost, some examples can be found in museums and archives around the world. The Museo Nacional de Antropología y Arqueología in Lima, Peru, houses a collection of Inca artifacts, including quipu and fabric maps.
Tips for Understanding the Inca Map
- Research the different types of Inca maps: Understanding the different materials and methods used in map creation is crucial for interpreting their meaning.
- Examine the context: Consider the purpose and function of the map, as well as the time period and location in which it was created.
- Consult with experts: Seek guidance from archaeologists, historians, and anthropologists specializing in Inca studies.
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and databases offer information about Inca maps and their interpretation.
- Visit museums and archives: Immerse yourself in the world of Inca cartography by visiting museums and archives that house collections of Inca artifacts.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Knowledge
The Inca map, though often fragmented and lost to time, serves as a testament to the ingenuity and complexity of the Inca civilization. It provides a window into their understanding of geography, administration, and resource management, revealing the intricate tapestry of their world. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich history and cultural legacy of the Inca Empire.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!