Unveiling the Tapestry of Latin America: A Geographical Journey
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Latin America: A Geographical Journey
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Latin America: A Geographical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Latin America: A Geographical Journey

Latin America, a vibrant and diverse region stretching from the northern reaches of Mexico to the southern tip of Chile, presents a captivating tapestry of geography, culture, and history. Understanding its intricate geographical landscape is crucial for appreciating its unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces. This comprehensive exploration delves into the diverse features of Latin America’s geographical map, highlighting its significance for understanding the region’s past, present, and future.
The Geographic Tapestry: A Diverse Landscape
Latin America’s geographical map is a testament to the dynamic forces that shaped the Earth. From towering mountain ranges to sprawling rainforests, from arid deserts to fertile plains, the region boasts a remarkable array of landscapes.
-
Mountains and Plateaus: The majestic Andes Mountains, the world’s longest mountain range, form the spine of western South America. Their towering peaks, including Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside Asia, have profoundly influenced the region’s climate, biodiversity, and human settlements. Beyond the Andes, other significant mountain ranges like the Sierra Madre in Mexico and the Guiana Highlands in Venezuela further contribute to the region’s varied topography.
-
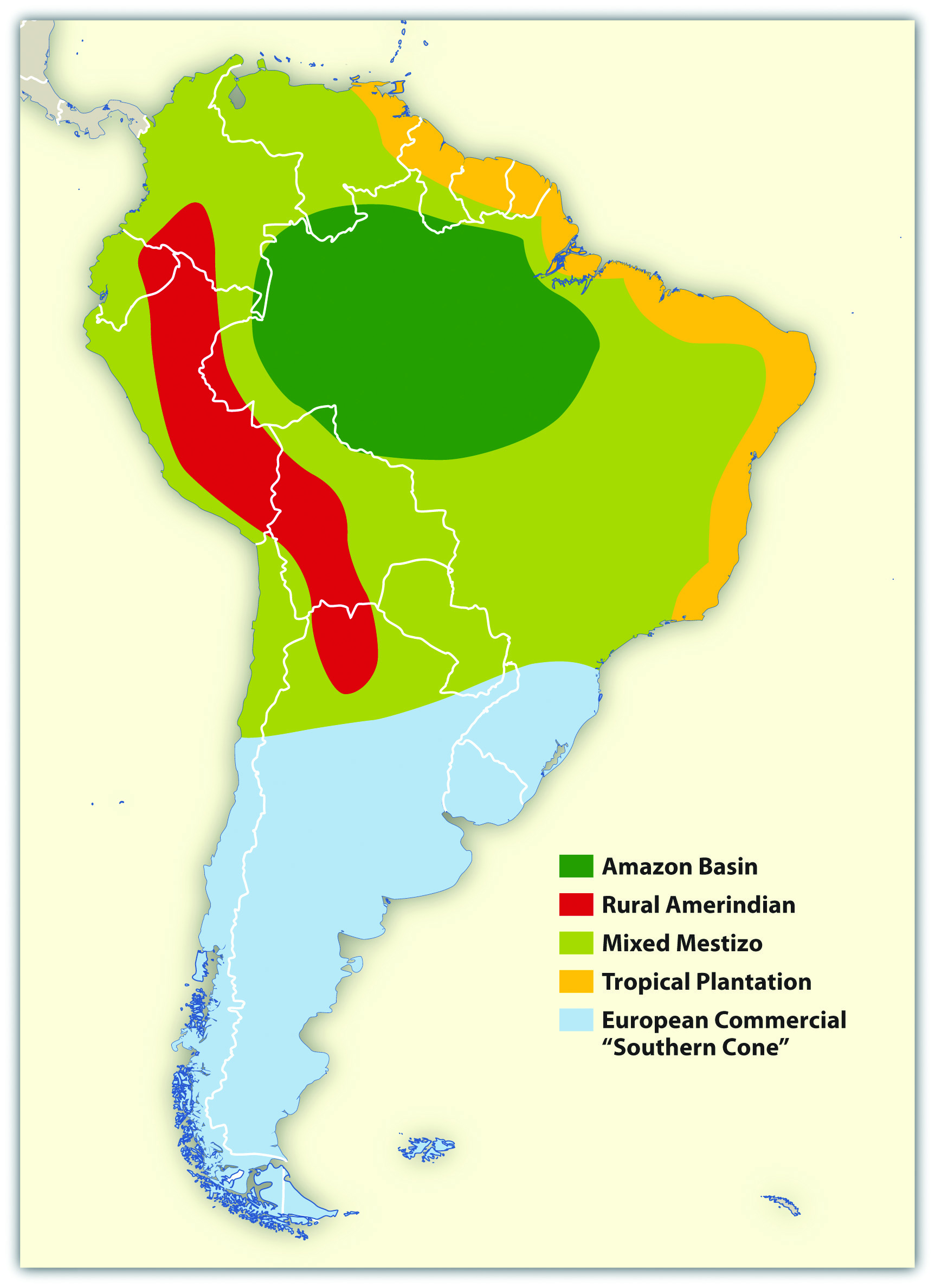
Vast Plains and Lowlands: The vast plains of the Pampas in Argentina and the Llanos in Venezuela are fertile agricultural regions, while the Amazon Basin, the world’s largest rainforest, is a treasure trove of biodiversity. These lowlands are characterized by their flat terrain, rich soils, and significant river systems.
-
Coastal Zones and Islands: Latin America’s extensive coastlines offer a diverse range of ecosystems, from the bustling port cities of the Caribbean to the pristine beaches of the Pacific coast. The region’s numerous islands, including the Caribbean islands, the Galapagos Islands, and the Falkland Islands, boast unique flora and fauna, showcasing the region’s rich biodiversity.
-
Deserts and Semi-Arid Regions: The Atacama Desert in Chile, one of the driest places on Earth, starkly contrasts with the lush rainforests of the Amazon. The region also includes semi-arid areas like the Chaco in Argentina and the Caatinga in Brazil, characterized by seasonal rainfall and distinctive vegetation.
The Influence of Geography: Shaping History and Culture
Latin America’s geographical features have profoundly influenced its history, culture, and development.
-
The Impact of Mountains: The Andes Mountains have acted as a natural barrier, isolating communities and fostering distinct cultural identities. Their rugged terrain also posed significant challenges for transportation and communication, impacting the region’s economic development.
-
The Significance of Rivers: Major river systems like the Amazon, the Orinoco, and the Paraná have served as vital transportation routes and sources of sustenance. They have also played a crucial role in shaping the region’s agricultural practices and its cultural identity.
-
The Influence of Climate: Latin America’s diverse climate zones have fostered a rich variety of agricultural products, from coffee and cocoa in the tropics to grapes and wine in the temperate regions. However, climate variability, including droughts and floods, poses challenges to agriculture and sustainable development.
-
The Role of Coastal Zones: The region’s extensive coastlines have been gateways for trade and migration, facilitating cultural exchange and economic development. However, coastal areas are vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise and coastal erosion.
The Benefits of Understanding Latin America’s Geography
A thorough understanding of Latin America’s geographical landscape offers several significant benefits:
-
Informed Policymaking: Understanding the region’s geographical features is crucial for developing effective policies related to agriculture, transportation, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
-
Sustainable Development: Recognizing the unique environmental challenges and opportunities presented by different geographical regions can guide sustainable development practices, ensuring the long-term well-being of the region’s ecosystems and communities.
-
Cultural Appreciation: Appreciating the interplay between geography, culture, and history allows for a deeper understanding and appreciation of the region’s diverse cultural heritage.
-
International Cooperation: Understanding the geographical challenges and opportunities facing Latin America is essential for promoting international cooperation in areas like climate change adaptation, disaster relief, and economic development.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into Latin America’s Geography
Q: What are the major geographical regions of Latin America?
A: Latin America can be broadly divided into:
- Central America: Comprises countries between Mexico and Colombia, including Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
- Caribbean: Includes islands and island nations in the Caribbean Sea, such as Cuba, Dominican Republic, Haiti, Puerto Rico, and the smaller islands of the Lesser Antilles.
- South America: Comprises the continent south of Central America, including Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela.
Q: What are the most important geographical features of Latin America?
A: The most significant geographical features of Latin America include:
- The Andes Mountains: The longest mountain range in the world, forming the backbone of western South America.
- The Amazon Basin: The world’s largest rainforest, covering a vast area in South America.
- The Pampas: Fertile plains in Argentina, known for their agricultural productivity.
- The Atacama Desert: One of the driest places on Earth, located in northern Chile.
Q: How does geography influence the culture of Latin America?
A: Geography has played a crucial role in shaping the cultural diversity of Latin America:
- Mountainous regions: Often isolated, leading to the development of unique cultural traditions and languages.
- Coastal regions: Influenced by maritime cultures and trade, resulting in a blend of indigenous and European influences.
- Tropical regions: Characterized by vibrant music, dance, and cuisine, reflecting the region’s rich biodiversity and natural resources.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing Latin America?
A: Latin America faces several environmental challenges:
- Deforestation: The rapid loss of forests, particularly in the Amazon, threatens biodiversity and contributes to climate change.
- Climate Change: Impacts like sea-level rise, extreme weather events, and droughts pose significant risks to the region’s ecosystems and communities.
- Pollution: Air and water pollution, particularly in urban areas, is a major health concern.
- Resource Depletion: Overexploitation of natural resources, such as oil and minerals, can lead to environmental degradation.
Tips for Exploring Latin America’s Geography:
- Utilize Maps and Atlases: Refer to detailed maps and atlases to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s geographical features.
- Read Books and Articles: Explore books, articles, and online resources dedicated to the geography of Latin America.
- Watch Documentaries: Documentaries can offer captivating visual insights into the region’s diverse landscapes and ecosystems.
- Travel and Experience: The best way to truly understand Latin America’s geography is to experience it firsthand.
Conclusion: A Journey of Discovery
Latin America’s geographical map is a testament to the planet’s dynamic forces and the resilience of its people. From towering mountains to sprawling rainforests, from arid deserts to fertile plains, the region’s diverse landscapes have shaped its history, culture, and development. By understanding the complexities of Latin America’s geography, we can better appreciate the region’s unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces. Through continued exploration and understanding, we can contribute to the sustainable development and well-being of this vibrant and dynamic region.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Latin America: A Geographical Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!