Unveiling the Taj Mahal: A Journey Through Maps and History
Related Articles: Unveiling the Taj Mahal: A Journey Through Maps and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Taj Mahal: A Journey Through Maps and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Taj Mahal: A Journey Through Maps and History

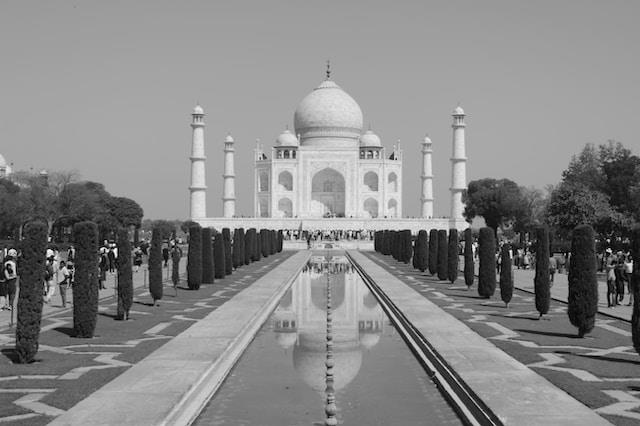
The Taj Mahal, an ivory-white marble mausoleum, stands as a testament to love and architectural brilliance. Situated in the Indian city of Agra, this UNESCO World Heritage site draws millions of visitors each year, captivated by its ethereal beauty and rich history. Understanding the Taj Mahal’s location and its place within the broader Indian landscape requires a deep dive into maps, unraveling the layers of history and geography that have shaped this iconic monument.
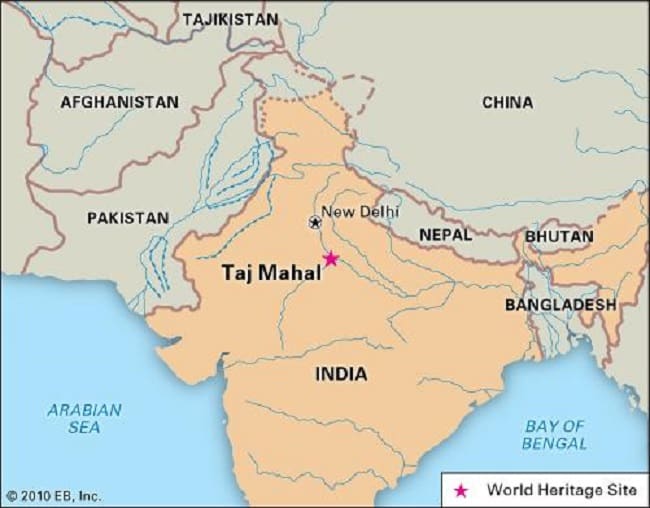
A Geographical Tapestry: The Taj Mahal on the Map
The Taj Mahal’s location is a crucial aspect of its significance. Situated on the south bank of the Yamuna River in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, it occupies a strategic position within the Indo-Gangetic Plain, a fertile region that has been a cradle of civilization for millennia.
Map 1: India: The Taj Mahal’s Context
- National Perspective: The Taj Mahal is located in the northern part of India, within the state of Uttar Pradesh. This state is known for its historical significance, housing several other UNESCO World Heritage sites like the Red Fort in Delhi and the Khajuraho temples.
- Regional Perspective: Agra, the city where the Taj Mahal stands, is strategically located on the Grand Trunk Road, an ancient trade route that connected the Indian subcontinent to Central Asia. This location contributed to the city’s economic and cultural importance, making it a suitable site for such a monumental structure.
Map 2: Agra: The City of the Taj Mahal
- Urban Landscape: The Taj Mahal is situated within the city of Agra, a bustling metropolis with a rich history. The monument is prominently placed on the Yamuna River’s banks, offering a breathtaking view of the surrounding city.
- Local Context: The Taj Mahal is not isolated; it is part of a larger complex that includes the Taj Mahal Gardens, the mosque, and the guest house. These elements are carefully arranged around the mausoleum, creating a harmonious balance between architecture and nature.
A Historical Journey: Tracing the Taj Mahal’s Roots
The Taj Mahal’s story is intricately woven with the history of the Mughal Empire. Constructed between 1632 and 1653, it was commissioned by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal. The monument embodies the Mughal architectural style, a fusion of Persian, Indian, and Islamic influences, resulting in a unique aesthetic.
Map 3: The Mughal Empire: A Realm of Grandeur
- Imperial Context: The Taj Mahal’s construction was a testament to the Mughal Empire’s power and wealth. During this period, the empire controlled vast territories across the Indian subcontinent, fostering a flourishing cultural and artistic scene.
- Trade Routes and Cultural Exchange: The Mughal Empire’s extensive trade routes facilitated the exchange of ideas and artistic practices. This exchange played a significant role in shaping the Taj Mahal’s architectural design, incorporating elements from diverse cultures.
Map 4: The Taj Mahal Complex: A Symphony of Architecture
- Detailed Layout: The Taj Mahal complex is a masterpiece of Mughal architecture, meticulously planned and executed. It encompasses the mausoleum, the mosque, the guest house, and the surrounding gardens, each element contributing to the overall aesthetic and symbolism.
- Symbolic Significance: The Taj Mahal’s design reflects the Mughal belief in paradise, with its symmetrical layout, intricate floral motifs, and use of water reflecting the concept of eternal life.
The Taj Mahal’s Enduring Legacy
The Taj Mahal’s influence extends far beyond its physical presence. It has become a symbol of love, beauty, and architectural excellence, recognized globally as a masterpiece of human creativity. Its enduring legacy is rooted in its historical context, artistic significance, and the enduring power of human emotion.
Understanding the Taj Mahal’s Importance Through Maps
Maps are not just tools for navigation; they offer a unique lens through which to understand the Taj Mahal’s significance. They help us visualize its location within the broader Indian landscape, tracing its historical roots and unraveling the cultural and architectural influences that shaped its creation.
Benefits of Using Maps to Explore the Taj Mahal
- Contextual Understanding: Maps provide a framework for understanding the Taj Mahal’s place within the larger historical and geographical context.
- Visual Representation: Maps offer a visual representation of the Taj Mahal’s location, its relationship to the surrounding city, and its architectural layout.
- Historical Insights: Maps help trace the Taj Mahal’s historical journey, connecting its construction to the Mughal Empire’s reign and the cultural exchange that shaped its design.
- Enhanced Appreciation: By understanding the Taj Mahal’s location and its historical context, visitors can develop a deeper appreciation for its significance and beauty.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Taj Mahal and Its Location
Q: Where is the Taj Mahal located?
A: The Taj Mahal is located in the city of Agra, in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. It sits on the south bank of the Yamuna River.
Q: Why is the Taj Mahal so important?
A: The Taj Mahal is a UNESCO World Heritage site, recognized for its architectural brilliance, historical significance, and enduring legacy as a symbol of love and beauty.
Q: What is the historical significance of the Taj Mahal?
A: The Taj Mahal was commissioned by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his beloved wife Mumtaz Mahal, reflecting the Mughal Empire’s power, wealth, and artistic achievements.
Q: What are the key architectural features of the Taj Mahal?
A: The Taj Mahal is characterized by its white marble construction, symmetrical layout, intricate floral motifs, and the use of water reflecting the concept of eternal life.
Q: How can maps help us understand the Taj Mahal?
A: Maps provide a visual representation of the Taj Mahal’s location, its relationship to the surrounding city, and its architectural layout, offering a deeper understanding of its historical context and significance.
Tips for Exploring the Taj Mahal Using Maps
- Study Maps Before Your Visit: Familiarize yourself with the Taj Mahal’s location within Agra and its layout within the complex.
- Use Interactive Maps: Utilize online maps to explore the Taj Mahal’s surroundings, identifying nearby attractions and transportation options.
- Trace Historical Routes: Explore maps that depict the Mughal Empire’s trade routes, gaining insight into the cultural exchange that shaped the Taj Mahal’s design.
- Create Your Own Map: Draw your own map of the Taj Mahal complex, noting key features and their significance.
Conclusion: The Taj Mahal: A Timeless Masterpiece
The Taj Mahal, with its timeless beauty and enduring legacy, continues to captivate the world. Understanding its location, history, and architectural significance through maps allows us to appreciate its profound impact on human history and its enduring power as a symbol of love, beauty, and architectural excellence. Through the lens of maps, we can embark on a journey of discovery, unraveling the layers of history and geography that have shaped this iconic monument.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Taj Mahal: A Journey Through Maps and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!