Unveiling the Red Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to NASA’s Mars Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Red Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to NASA’s Mars Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Red Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to NASA’s Mars Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Red Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to NASA’s Mars Maps

The allure of Mars, the red planet, has captivated humanity for centuries. Its potential for harboring past or present life, its intriguing geological features, and its potential as a future destination for human exploration make it a constant source of fascination and scientific inquiry. To unravel the mysteries of Mars, scientists rely heavily on detailed maps created from data collected by NASA missions. These maps are invaluable tools for understanding the planet’s history, composition, and potential for supporting life.
A Journey Through Time: Mapping Mars’s Evolution
NASA’s Mars maps are not mere static representations of the planet’s surface. They are dynamic records of its evolution, reflecting billions of years of geological processes, climate changes, and potential past habitability.
1. The Foundation: Topographic Maps
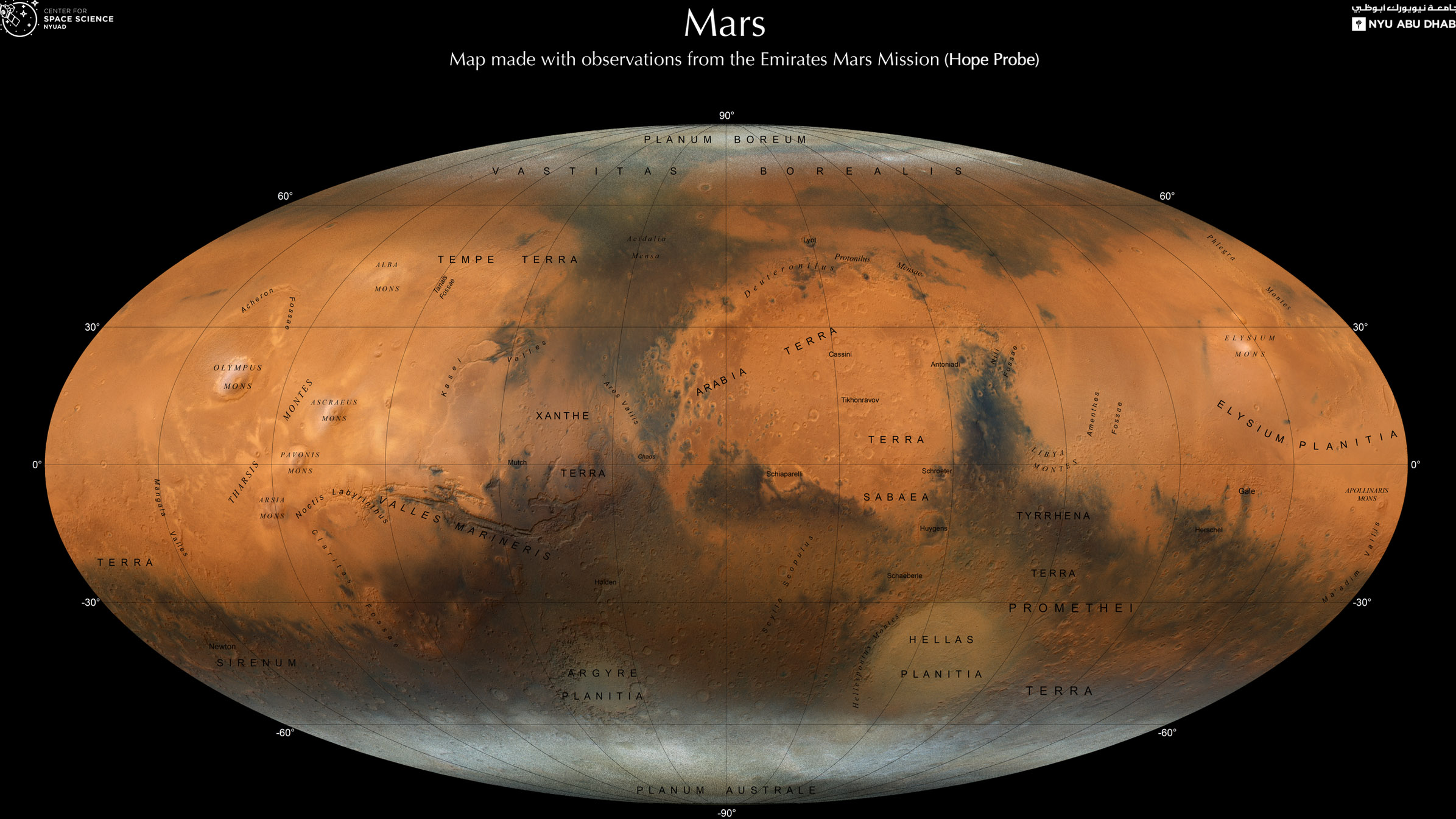
The foundation of our understanding of Mars lies in topographic maps. These maps depict the planet’s surface elevation, revealing towering volcanoes like Olympus Mons, vast canyons like Valles Marineris, and ancient impact craters. By analyzing the distribution of these features, scientists can infer the forces that have shaped Mars over time.
2. Unveiling the Surface: Color and Mineral Maps
Color and mineral maps provide a deeper understanding of the planet’s composition. These maps are created by analyzing spectral data, which measures how different materials reflect light. They reveal the presence of various minerals, including iron oxides that give Mars its characteristic red hue, as well as hydrated minerals that suggest past water activity.
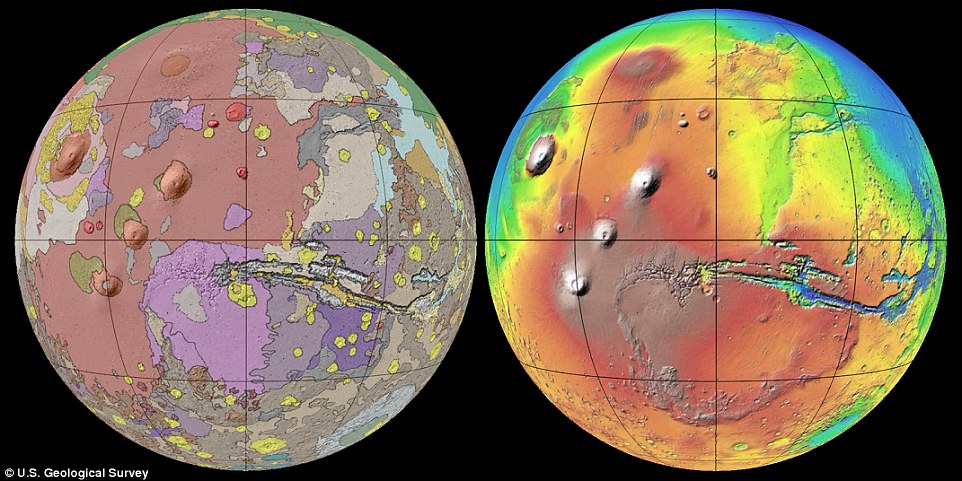
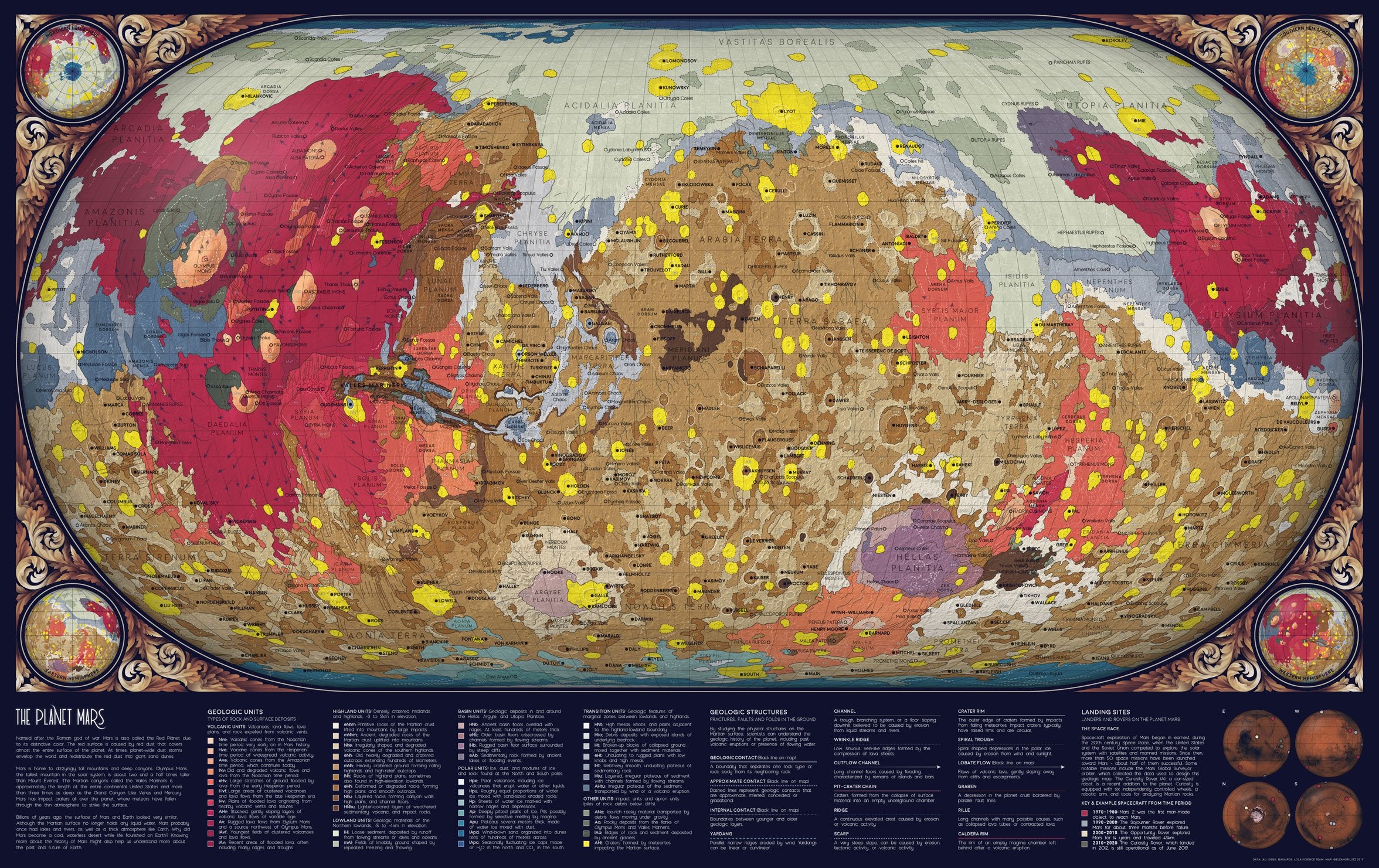
3. Mapping the Past: Geologic Maps
Geologic maps are the culmination of data from topographic, color, and mineral maps. These maps depict the distribution of different rock units, providing insights into the planet’s geological history. They help scientists understand the formation of mountains, canyons, and plains, and how these features relate to past volcanic activity, tectonic shifts, and water erosion.
4. Searching for Signs of Life: Geochemical Maps
Geochemical maps focus on the distribution of key elements and molecules that are indicative of past or present life. These maps are essential for identifying potential habitable environments, such as ancient lake beds or hydrothermal vents. They analyze data from instruments like spectrometers and mass spectrometers, which can detect organic molecules and other biosignatures.
5. Unlocking the Secrets of the Atmosphere: Atmospheric Maps
Atmospheric maps provide crucial information about the planet’s weather patterns, temperature variations, and atmospheric composition. They are created from data collected by orbiters and landers, which measure atmospheric pressure, temperature, wind speed, and the abundance of various gases.
The Power of Data: Creating Mars Maps
NASA’s Mars maps are not created by a single instrument or mission. They are the result of a collaborative effort involving multiple spacecraft and ground-based telescopes. Each mission contributes a unique piece of the puzzle, and the data is combined to create a comprehensive and ever-evolving picture of the red planet.
1. Orbiters: A Global Perspective
Orbiters like Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), Mars Odyssey, and Mars Express have provided a wealth of data about the planet’s surface, atmosphere, and geology. They carry a variety of instruments, including cameras, spectrometers, and radar systems, that gather data from different wavelengths of light.
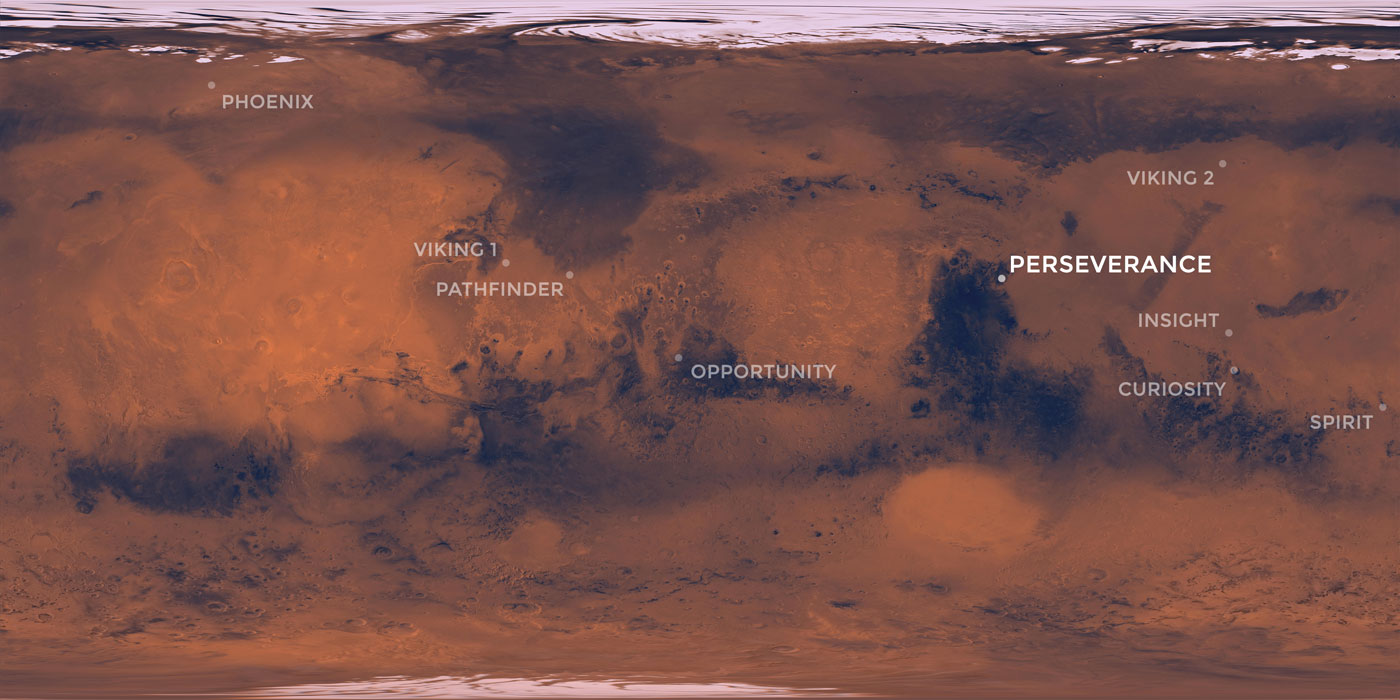
2. Landers: A Close-up View
Landers like the Mars Exploration Rovers (Spirit and Opportunity) and the Curiosity rover have provided detailed information about specific locations on Mars. They carry instruments that can analyze the composition of rocks and soil, measure atmospheric conditions, and search for signs of past water activity.
3. Telescopes: Observing from Earth
Ground-based telescopes, like the Very Large Telescope (VLT) in Chile, can also contribute to our understanding of Mars. They can observe the planet’s atmosphere and surface features, providing additional data to complement the information gathered by spacecraft.
Beyond Mapping: The Benefits of Mars Maps
NASA’s Mars maps are not only essential for scientific research, but they also have significant practical implications.
1. Guiding Future Missions:
These maps are crucial for planning future missions to Mars, both robotic and human. They help scientists identify potential landing sites, choose safe and scientifically interesting areas for exploration, and understand the challenges associated with navigating the Martian surface.
2. Understanding Climate Change:
By studying the geological features and atmospheric composition of Mars, scientists can gain insights into the planet’s climate history. This knowledge can help us understand the processes that have led to the current state of Mars and potentially inform our understanding of climate change on Earth.
3. Searching for Life:
Mars maps are essential for identifying potential signs of past or present life. They help scientists pinpoint areas where water may have once existed, locate potential biosignatures, and prioritize future exploration efforts.
4. Inspiring Future Generations:
The stunning visuals and detailed information provided by NASA’s Mars maps have captivated the public imagination and sparked a renewed interest in space exploration. They inspire future generations of scientists and engineers to push the boundaries of human knowledge and explore the cosmos.
FAQs About NASA’s Mars Maps
1. What is the most detailed Mars map available?
The most detailed Mars maps are created from data collected by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), which has been orbiting the planet since 2006. Its high-resolution camera, known as HiRISE, has captured stunning images of the Martian surface, revealing features as small as a few feet across.
2. How often are Mars maps updated?
Mars maps are constantly being updated as new data is collected by NASA missions. The frequency of updates depends on the mission and the type of data being gathered. Some maps are updated daily, while others are updated less frequently.
3. Are Mars maps publicly available?
Yes, NASA makes its Mars maps publicly available through its website and data archives. These maps are used by scientists, educators, and the public alike to learn about the red planet.
4. What are the limitations of current Mars maps?
Current Mars maps are limited by the resolution of the instruments used to collect data. While some maps provide incredibly detailed information, others are less precise. Additionally, the maps are based on data collected from a limited number of locations, meaning that there are still large areas of the planet that remain unexplored.
5. What are the future goals for Mars mapping?
Future Mars mapping efforts will focus on increasing the resolution and coverage of maps, as well as incorporating new data from future missions. Scientists are also developing new techniques for mapping the planet’s subsurface and its magnetic field.
Tips for Using NASA’s Mars Maps
1. Explore Different Data Sources:
NASA provides a variety of Mars maps, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Explore different data sources to get a comprehensive understanding of the planet.
2. Use Interactive Tools:
NASA’s website offers interactive tools that allow you to explore Mars maps in three dimensions. These tools can help you visualize the planet’s surface and understand the relationship between different features.
3. Combine Maps with Other Data:
Mars maps can be combined with other data sources, such as images from landers and rovers, to provide a more complete picture of the planet.
4. Share Your Discoveries:
NASA encourages the public to explore its Mars maps and share their discoveries. You can contribute to scientific research by identifying interesting features or reporting potential errors in the maps.
Conclusion
NASA’s Mars maps are invaluable tools for understanding the red planet’s history, composition, and potential for supporting life. They are the product of decades of scientific research and technological innovation, and they continue to evolve as new data is collected. These maps not only guide future missions to Mars, but they also inspire a sense of wonder and curiosity about the universe we inhabit. As our exploration of Mars continues, these maps will play an increasingly important role in unraveling the mysteries of this fascinating world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Red Planet: A Comprehensive Guide to NASA’s Mars Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
