Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity
- 3.1 What is Process Mapping?
- 3.2 The Importance of Process Mapping
- 3.3 Types of Process Maps
- 3.4 How to Create a Process Map
- 3.5 Process Mapping Tools and Software
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Process Mapping
- 3.7 FAQs on Process Mapping
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity
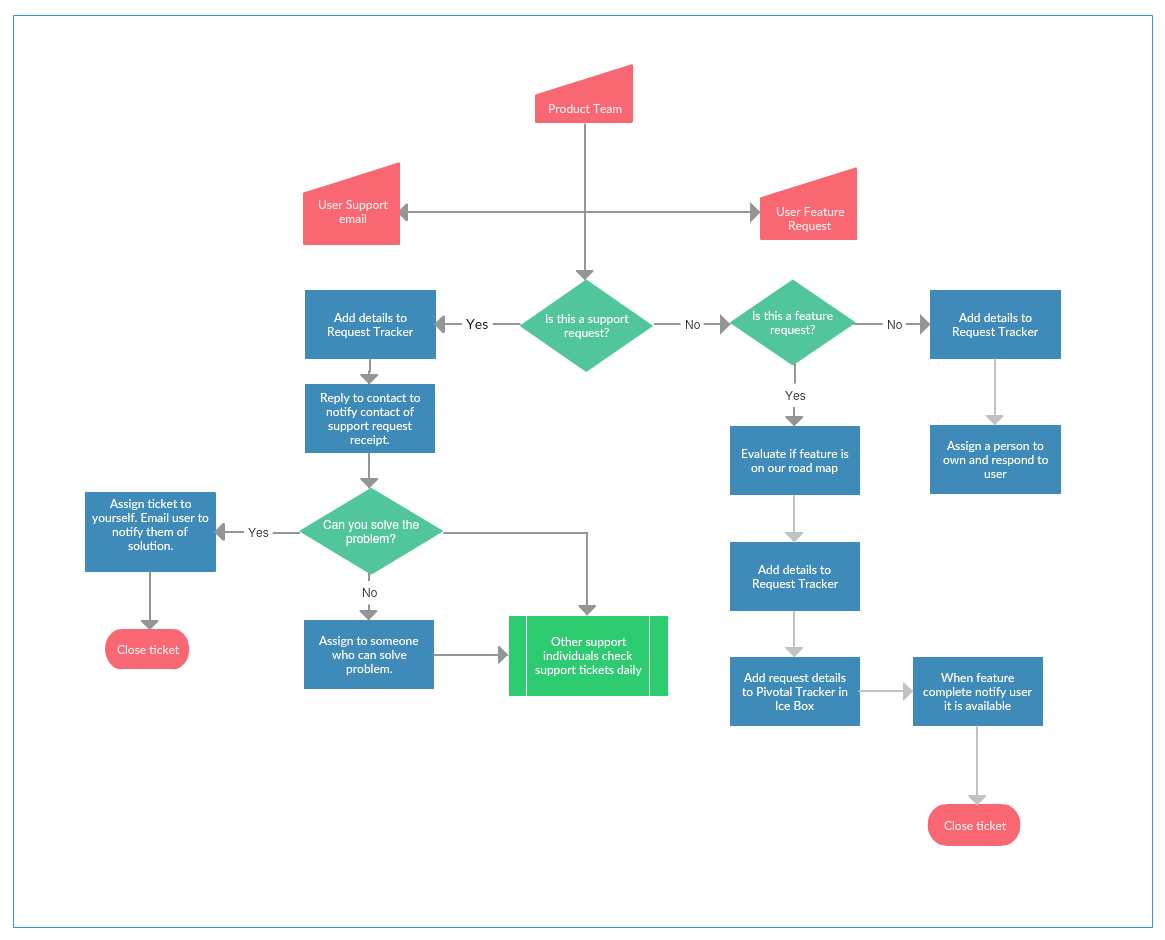
In the intricate tapestry of modern business operations, a clear understanding of processes is paramount. This is where process mapping emerges as a powerful tool, enabling organizations to visualize, analyze, and ultimately optimize their workflows.
This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of process mapping, offering a practical roadmap for its effective implementation.
What is Process Mapping?
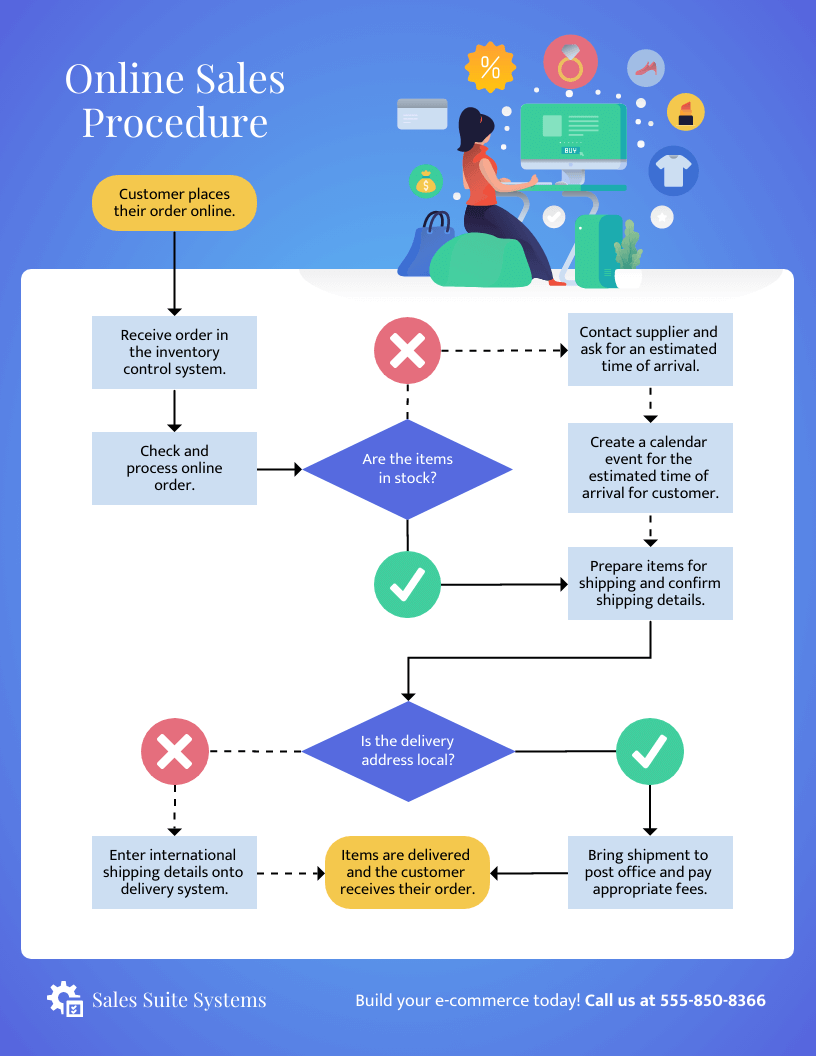
Process mapping is a visual representation of a process, outlining its various steps, decision points, and inputs/outputs. It serves as a blueprint, depicting the flow of activities from start to finish. This graphical representation provides a clear and concise understanding of how work gets done, revealing potential areas for improvement and streamlining.
The Importance of Process Mapping
Process mapping offers a plethora of benefits, making it an invaluable tool for organizations of all sizes and industries:
- Enhanced Clarity and Understanding: Process maps provide a shared understanding of how work is executed, eliminating ambiguity and fostering collaboration.
- Identification of Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: By visualizing the process flow, potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies become readily apparent, enabling targeted interventions for optimization.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Process maps serve as a common language, facilitating effective communication and collaboration across teams and departments.
- Streamlined Operations: Identifying and eliminating redundancies, minimizing rework, and optimizing workflows lead to significant improvements in efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Quality Control: Process maps enable the identification of potential error points, facilitating the implementation of quality control measures and minimizing defects.
- Improved Documentation and Training: Process maps provide a comprehensive record of how work is done, simplifying documentation and training efforts for new employees.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Process maps support data-driven decision-making by providing insights into process performance, enabling informed adjustments and improvements.
- Increased Accountability: By clearly defining roles and responsibilities within the process, accountability is enhanced, fostering ownership and responsibility.
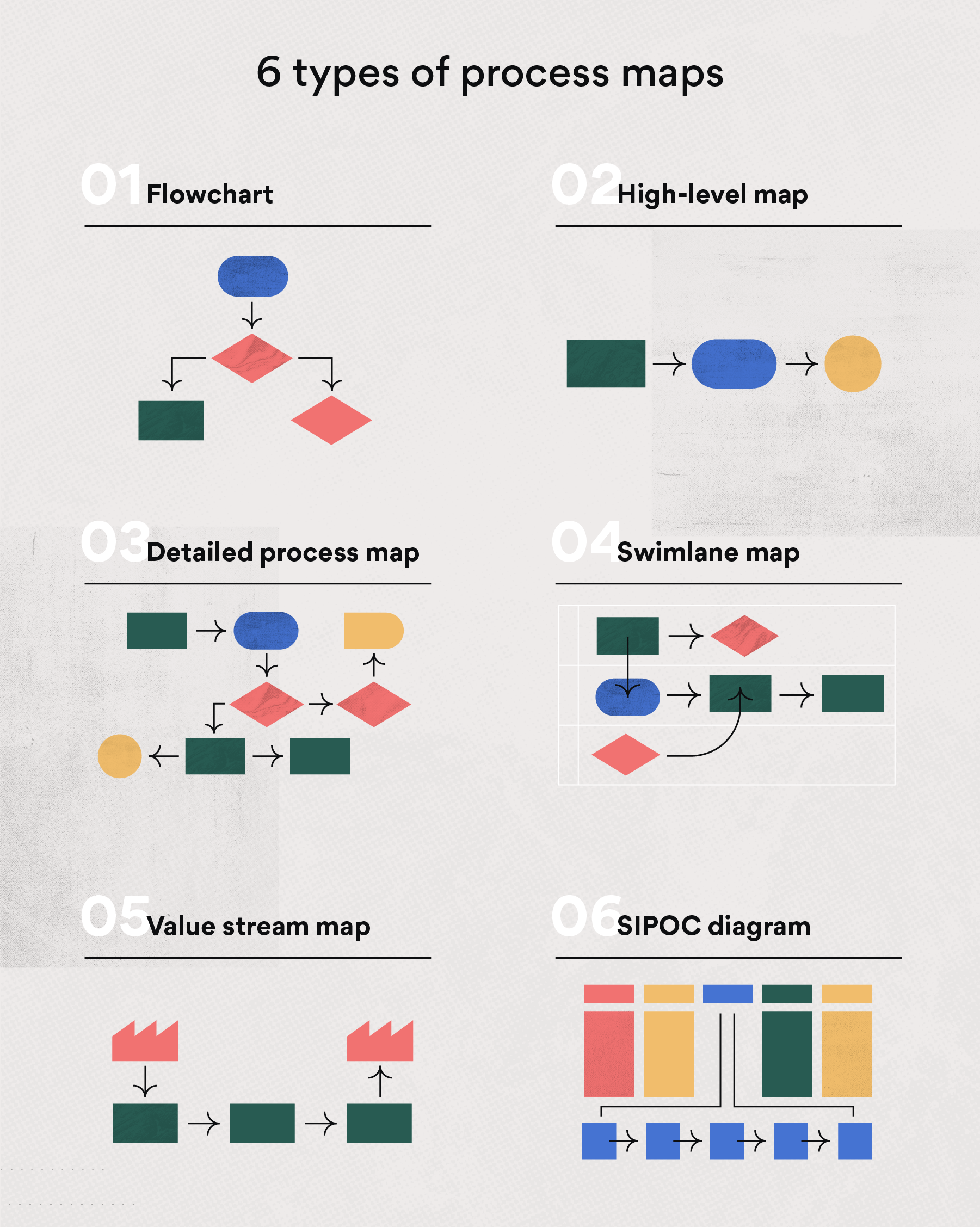
Types of Process Maps
Process mapping encompasses various methodologies, each offering unique strengths and applications:
- Swimlane Diagrams: These maps visually represent different roles and responsibilities within a process, using horizontal lanes to delineate distinct areas of ownership.
- Flowcharts: This classic process mapping technique utilizes standard symbols to illustrate the sequence of steps and decision points within a process.
- Value Stream Maps: Focusing on the value-adding activities within a process, these maps highlight areas for potential improvement by identifying non-value-adding steps.
- SIPOC Diagrams: This type of map outlines the Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers involved in a specific process, providing a high-level overview.
How to Create a Process Map
The process of creating a process map is a structured approach involving several key steps:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the process to be mapped, establishing its boundaries and objectives.
- Gather Information: Collect data through interviews, observations, and document reviews to understand the current process flow.
- Identify Key Steps: Break down the process into distinct, manageable steps, ensuring a clear understanding of each activity.
- Determine Inputs and Outputs: Identify the inputs required for each step and the outputs produced, providing a comprehensive picture of the process flow.
- Map the Process: Utilizing a chosen process mapping technique, visually represent the steps, decision points, and flow of information.
- Review and Validate: Share the draft process map with stakeholders for feedback, ensuring accuracy and comprehensiveness.
- Refine and Finalize: Incorporate feedback, refine the map, and finalize it as a clear and concise representation of the process.
Process Mapping Tools and Software
Various tools and software solutions are available to facilitate process mapping, offering advanced functionalities for collaboration, analysis, and visualization:
- Microsoft Visio: A widely used tool for creating professional-looking diagrams, including process maps.
- Lucidchart: A cloud-based platform offering collaborative process mapping, integration with various software, and extensive customization options.
- Draw.io: A free and open-source tool for creating diagrams, offering a user-friendly interface and a wide range of templates.
- Canva: A versatile design platform that includes process mapping templates and features, enabling visually appealing and interactive maps.
Tips for Effective Process Mapping
- Focus on the Value Stream: Prioritize mapping processes that directly contribute to customer value, focusing on core activities.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Employ simple, unambiguous language to ensure understanding and avoid confusion.
- Include Relevant Details: Include essential information, such as decision points, roles, and responsibilities, to create a comprehensive map.
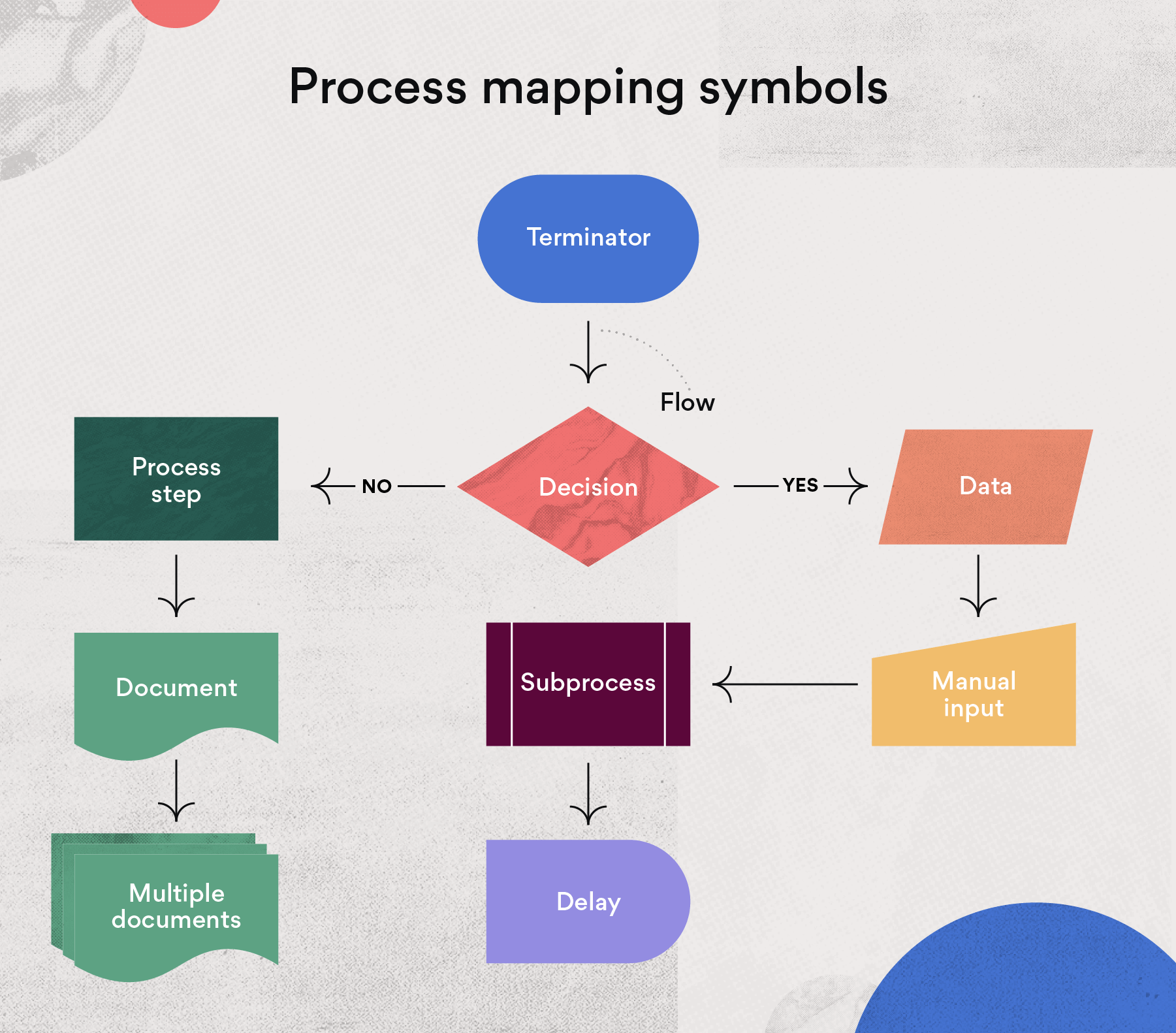
- Maintain Consistency: Ensure consistency in the use of symbols, terminology, and layout throughout the map.
- Seek Feedback and Iterate: Actively solicit feedback from stakeholders and iteratively refine the map to ensure accuracy and clarity.
FAQs on Process Mapping
1. What are the best practices for process mapping?
- Start with a clear purpose: Define the objective of the process map before embarking on the mapping process.
- Involve stakeholders: Engage relevant stakeholders in the mapping process to ensure buy-in and accurate representation.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overly complex maps, focusing on clarity and conciseness.
- Use standardized symbols: Employ established symbols for consistent representation of activities and decision points.
- Prioritize value-adding activities: Focus on mapping processes that directly contribute to customer value.
2. How often should processes be mapped?
The frequency of process mapping depends on the complexity and dynamism of the process. However, it is generally recommended to review and update process maps at least annually or whenever significant changes occur.
3. Can process mapping be used for non-business processes?
Yes, process mapping can be applied to various contexts, including personal processes, project management, and even academic research.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating process maps?
- Overcomplicating the map: Avoid excessive detail and focus on the core steps and decision points.
- Failing to involve stakeholders: Neglecting to include relevant stakeholders in the mapping process can lead to inaccurate representations.
- Ignoring feedback: Disregarding feedback from stakeholders can hinder the effectiveness of the process map.
- Using inconsistent symbols: Employing inconsistent symbols can create confusion and hinder understanding.
5. What are some benefits of using process mapping software?
Process mapping software offers numerous advantages, including:
- Collaboration and sharing: Facilitates collaborative mapping and easy sharing of maps with stakeholders.
- Visualization and analysis: Provides advanced tools for visualizing and analyzing process data.
- Automation and integration: Enables automation of certain mapping tasks and integration with other software systems.
- Version control and history: Tracks changes and provides access to historical versions of the map.
Conclusion
Process mapping serves as a powerful tool for enhancing organizational efficiency, clarity, and collaboration. By visually representing processes, organizations can identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and foster a shared understanding of how work gets done. Through the use of various mapping techniques, tools, and best practices, process mapping empowers organizations to achieve significant improvements in their operations and overall performance.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimizing Efficiency and Clarity. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!