Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration
- 3.1 The Island of Timor: A Divided Landscape
- 3.2 Mapping the Island’s History
- 3.3 The Importance of Maps in Understanding Timor
- 3.4 FAQs about the Map of Timor
- 3.5 Tips for Using Maps of Timor
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration
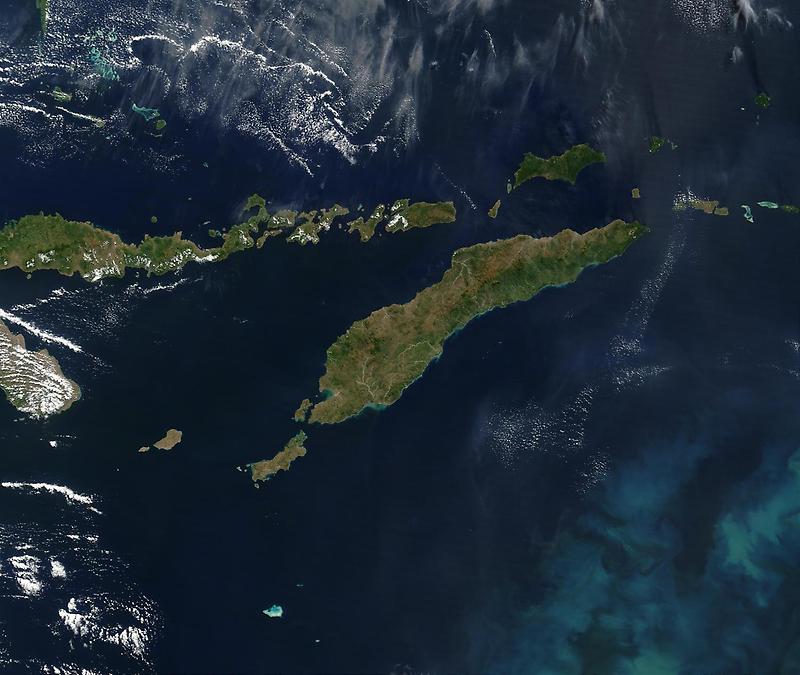
Timor, an island nation in Southeast Asia, is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture. Understanding its geography through maps is crucial for appreciating its unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces.
The Island of Timor: A Divided Landscape
Timor, the largest island in the Lesser Sunda Islands, is divided into two distinct nations: East Timor, an independent nation, and West Timor, which forms part of Indonesia. This division, a product of historical events, is reflected in the island’s geographical features.
East Timor:
- Mountainous Terrain: East Timor is characterized by rugged, mountainous terrain, with the highest peak, Mount Ramelau, reaching 2,963 meters. This mountainous landscape contributes to the island’s biodiversity and provides a unique backdrop for its diverse ecosystems.
- Coastal Plains: The north and south coasts feature narrow coastal plains, which provide fertile land for agriculture and are important for fishing communities. These plains offer a stark contrast to the mountainous interior, highlighting the island’s diverse topography.
- Island Dependencies: East Timor also includes the small islands of Atauro and Jaco, offering further geographical diversity and unique ecosystems.
West Timor:
- Volcanic Landscape: West Timor’s landscape is dominated by volcanic activity, with several active volcanoes, including Mount Mutis, adding to the region’s dynamic geography. These volcanoes contribute to the island’s fertile soils and create a unique geological setting.
- Coastal Plains: West Timor also features coastal plains, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting coastal communities. These plains are often bordered by mangrove forests, which serve as important habitats for marine life.
- Savanna Grasslands: The interior of West Timor is characterized by extensive savanna grasslands, providing a distinct landscape and habitat for a variety of wildlife.
Mapping the Island’s History
The map of Timor tells a story of historical struggles and transformations. The island’s strategic location, positioned between Asia and Australia, has made it a crossroads of cultures and empires.
- Colonial Influence: The island has been influenced by Portuguese and Dutch colonialism, leaving a mark on its cultural landscape and administrative divisions. The map reflects these historical influences through the distinct boundaries of East and West Timor.
- Independence Struggle: The map also reveals the long and arduous struggle for independence by East Timor, culminating in the nation’s recognition in 2002. The island’s political landscape is deeply intertwined with its geography, as the struggle for self-determination was fought on its rugged terrain.
- Border Disputes: The division of the island has also led to border disputes, as the exact demarcation of the border remains a contentious issue. The map highlights the complexities of the political landscape and the ongoing challenges of defining national boundaries.
The Importance of Maps in Understanding Timor
Maps are essential tools for understanding the complexities of Timor’s geography and history. They provide a visual representation of the island’s diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and political divisions.
- Resource Management: Maps are crucial for managing the island’s natural resources, including forests, fisheries, and mineral deposits. They help identify areas of ecological importance and guide sustainable development practices.
- Infrastructure Development: Maps are essential for planning infrastructure development, such as roads, bridges, and power grids. They help identify optimal routes and minimize environmental impact.
- Disaster Management: Maps are vital for disaster preparedness and response, as they provide information on potential hazards, evacuation routes, and vulnerable areas.
FAQs about the Map of Timor
1. What are the major geographical features of East Timor?
East Timor is characterized by its mountainous terrain, with the highest peak, Mount Ramelau, reaching 2,963 meters. The island also features narrow coastal plains along the north and south coasts, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting fishing communities.
2. What are the major geographical features of West Timor?
West Timor is dominated by volcanic activity, with several active volcanoes, including Mount Mutis. The island also features coastal plains and extensive savanna grasslands in the interior.
3. What are the historical influences reflected on the map of Timor?
The map of Timor reflects the influences of Portuguese and Dutch colonialism, as well as the long struggle for independence by East Timor.
4. What are the challenges associated with the division of Timor?
The division of the island has led to border disputes, as the exact demarcation of the border remains a contentious issue.
5. How are maps used in the development of Timor?
Maps are used for resource management, infrastructure development, and disaster preparedness and response.
Tips for Using Maps of Timor
- Consider the scale and purpose of the map: Different maps serve different purposes. Choose a map that is appropriate for your needs.
- Look for key features: Pay attention to the major geographical features, including mountains, rivers, and coastlines.
- Identify political boundaries: Understand the division of the island into East Timor and West Timor.
- Explore historical maps: Historical maps can provide insights into the island’s past and how its geography has shaped its development.
- Use online mapping tools: Online mapping tools provide interactive maps with detailed information about Timor’s geography, history, and culture.
Conclusion
The map of Timor is a powerful tool for understanding the island’s diverse landscapes, rich history, and cultural heritage. By exploring the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the island’s unique character and the challenges and opportunities it faces. As Timor continues to develop, maps will remain essential for guiding its progress and ensuring a sustainable future.

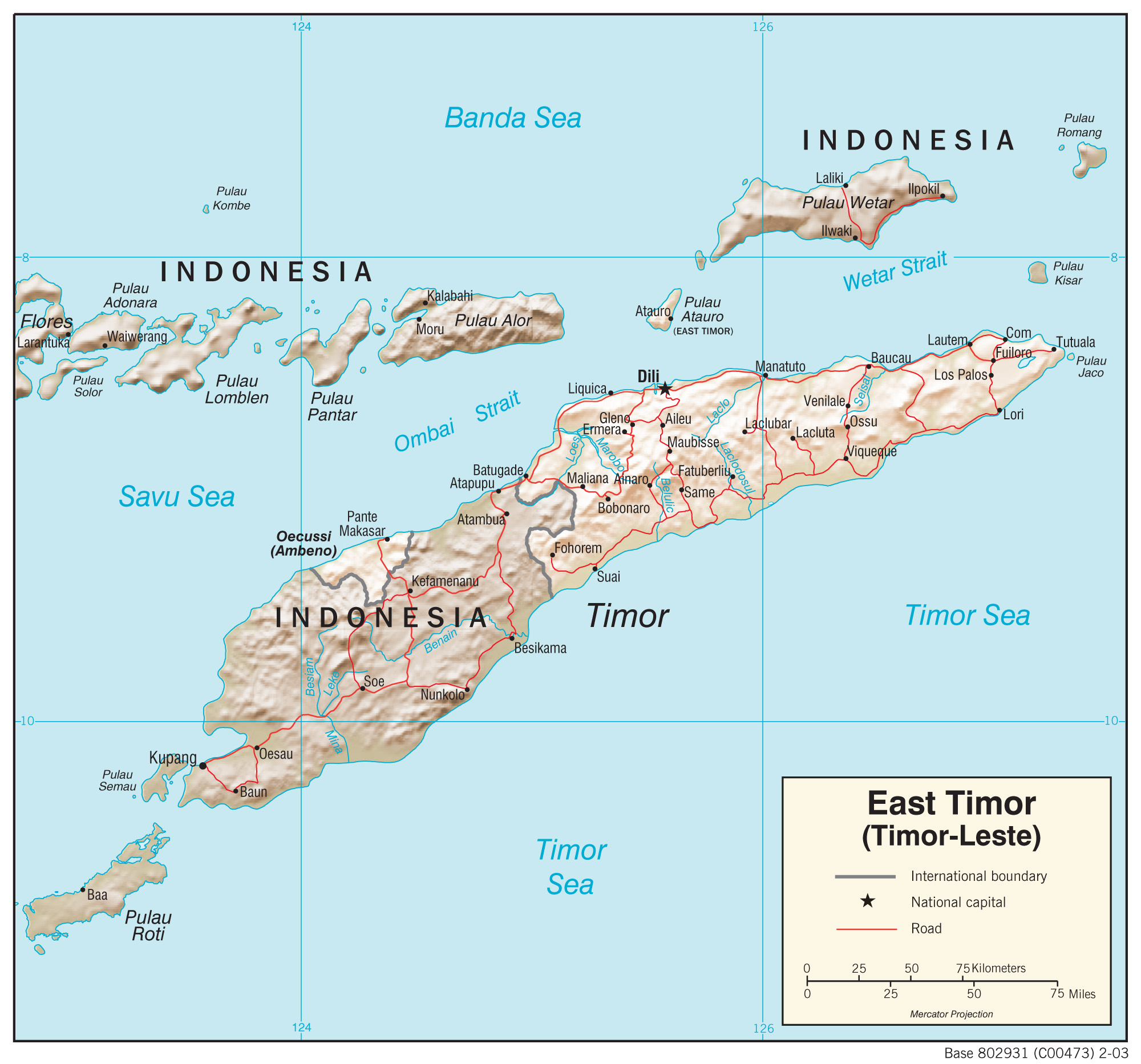





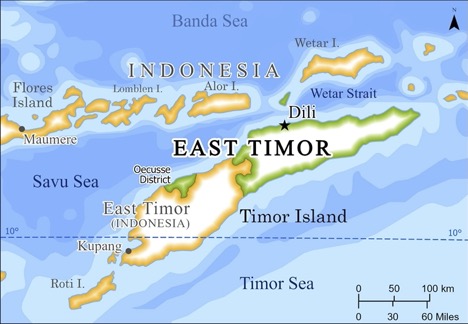
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Timor: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!