Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Altitude
Related Articles: Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Altitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Altitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Altitude
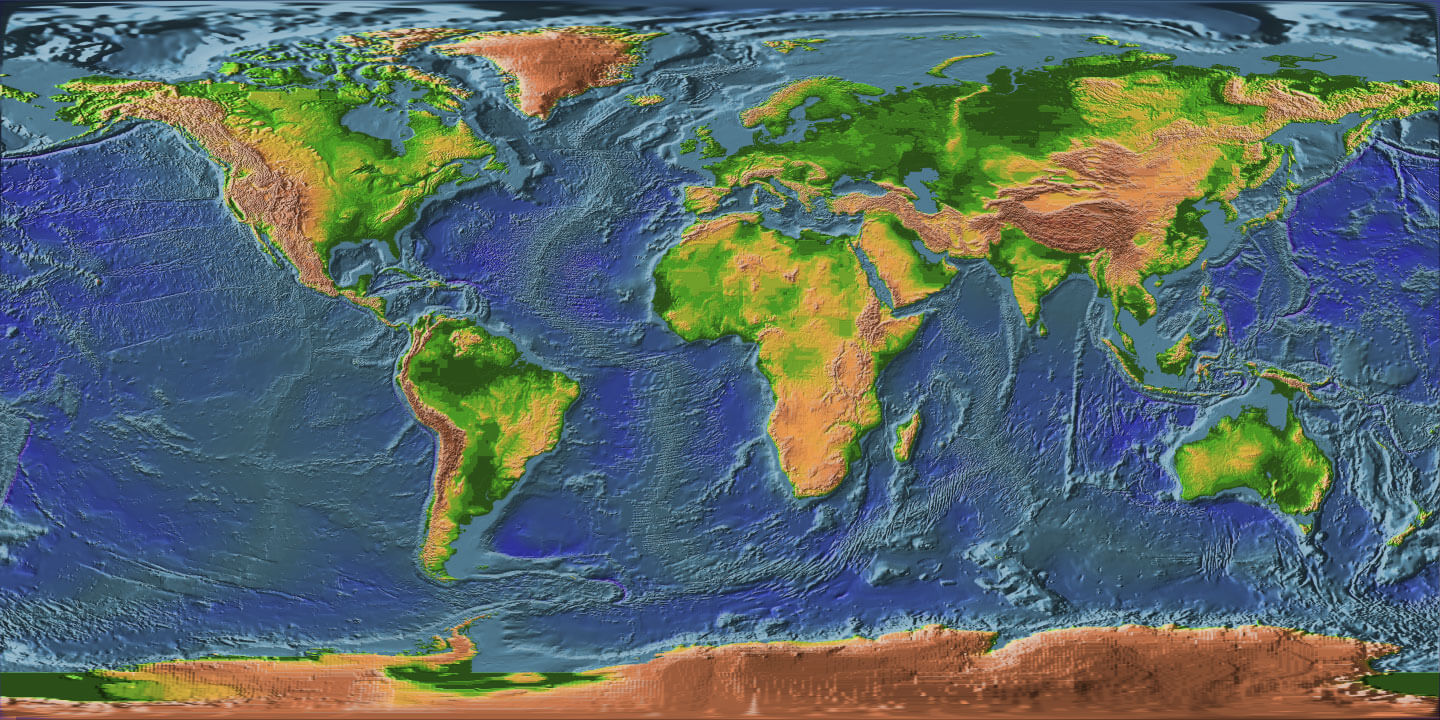
The Earth’s surface is far from uniform. It boasts a breathtaking tapestry of towering mountains, deep ocean trenches, sprawling plains, and vast deserts, each sculpted by geological forces over millennia. This intricate landscape is aptly captured in the concept of altitude, a fundamental geographical parameter that measures the vertical distance of a point on Earth’s surface above or below sea level.
Understanding world map altitude is not merely an academic pursuit. It holds significant implications for diverse fields, including:
- Climate and Weather: Altitude directly influences temperature, precipitation, and wind patterns. Higher altitudes experience colder temperatures due to thinner air and reduced atmospheric pressure. This, in turn, affects vegetation types, agricultural practices, and even the distribution of human populations.
- Geography and Geology: Altitude plays a crucial role in defining landforms and understanding geological processes. Mountain ranges, for instance, arise from tectonic plate collisions, while valleys and canyons are often formed by erosion.
- Navigation and Travel: Altitude is a critical factor in navigation, particularly for aviation and marine transportation. Pilots rely on altitude data for safe flight paths, while sailors use it for charting courses and avoiding hazards.
- Ecology and Biodiversity: Altitude gradients create unique habitats and ecosystems. As elevation increases, species composition changes, leading to distinct flora and fauna at different altitudes. This biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecological balance.
- Resource Management: Altitude is a key consideration in resource management, including water resources, forestry, and agriculture. Understanding the altitude of different regions helps optimize land use and resource allocation.
Visualizing the World’s Altitude
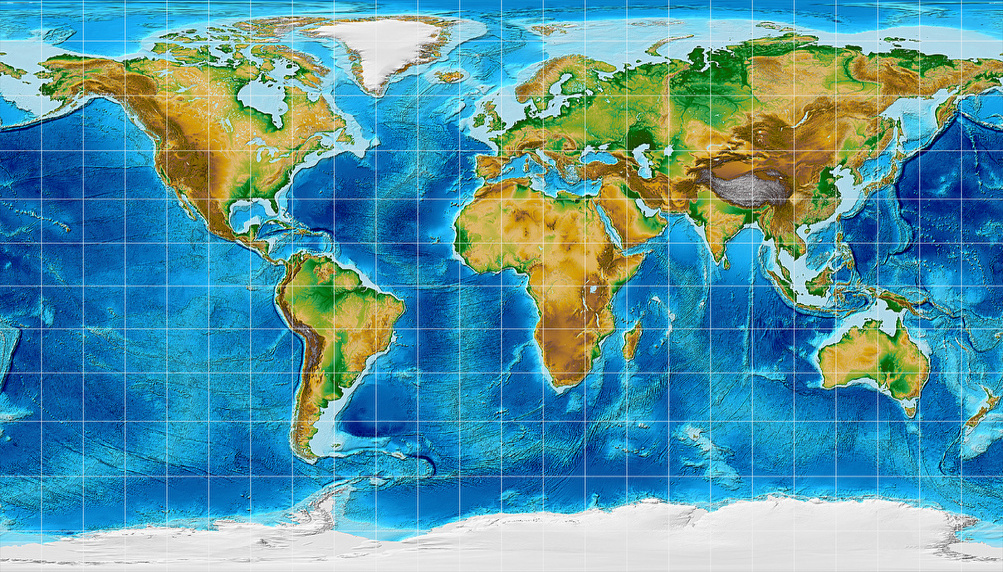
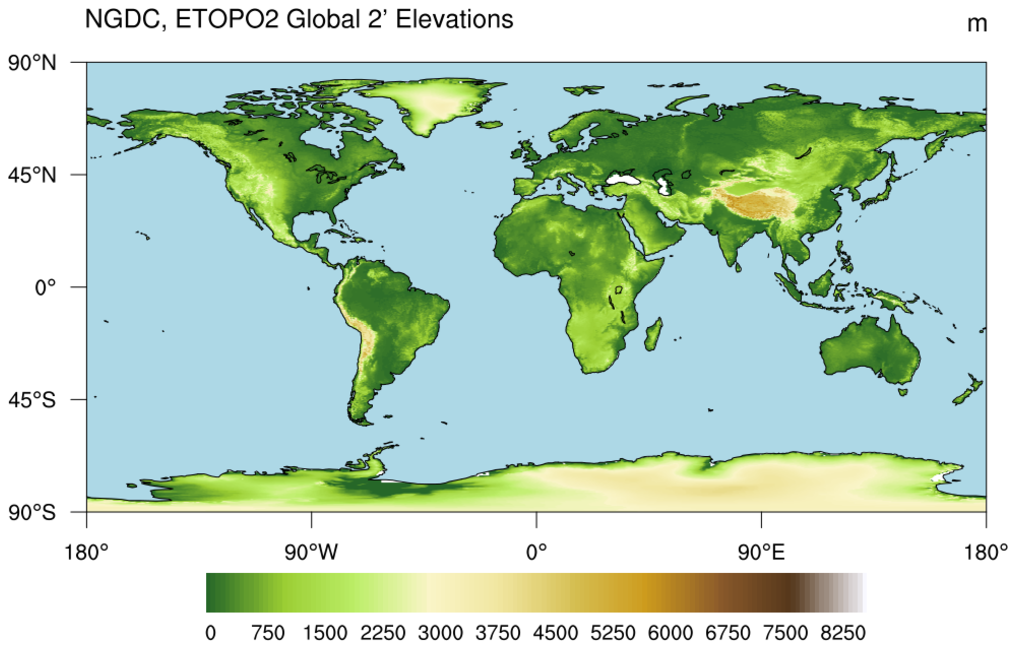
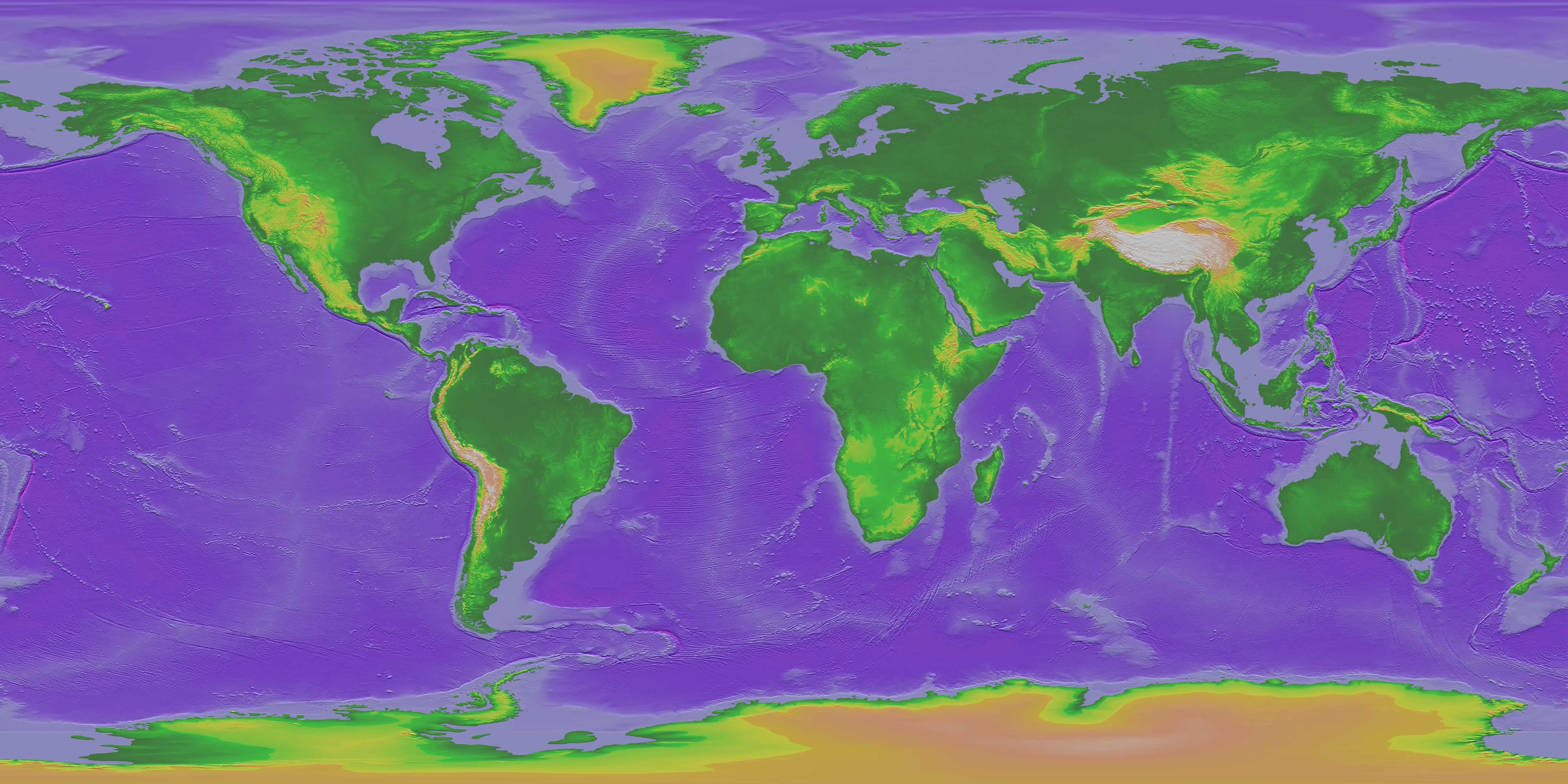
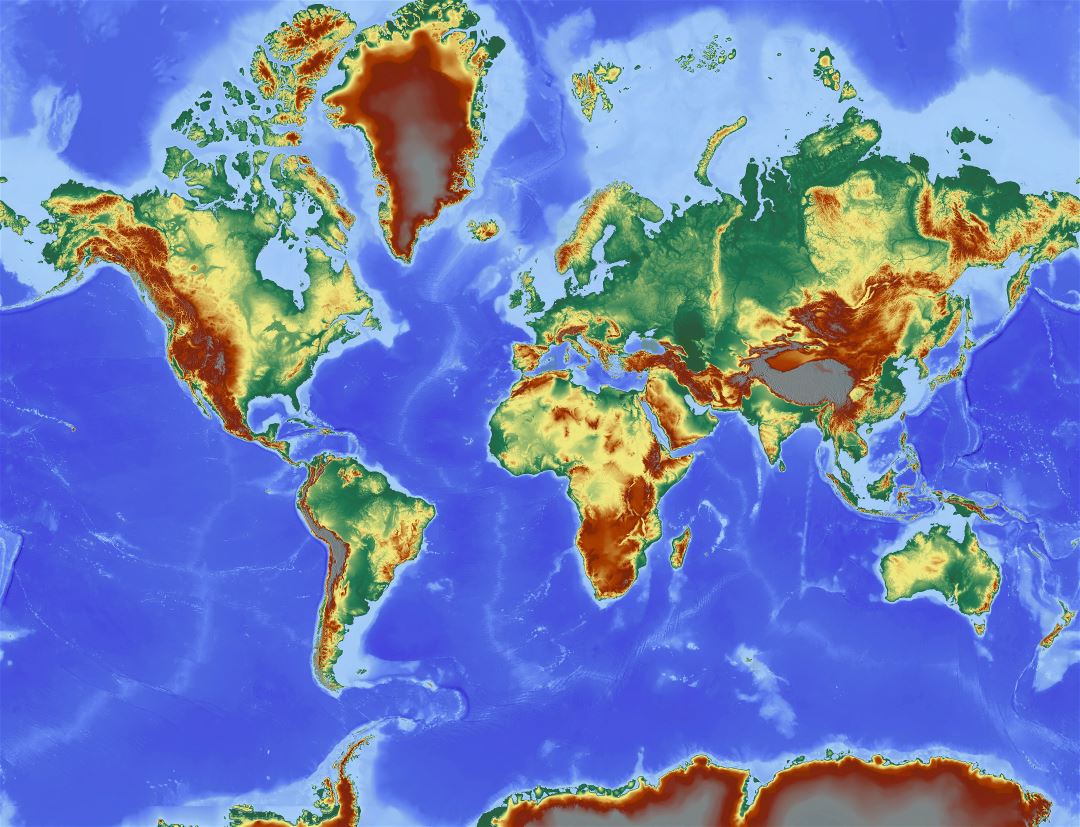
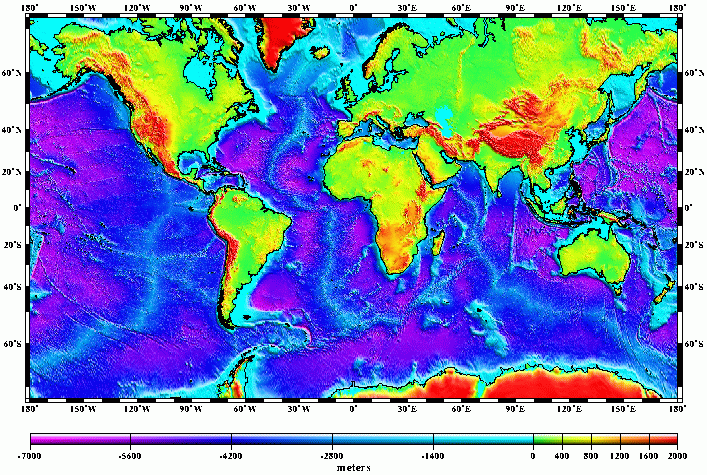
World maps that depict altitude offer a powerful visual representation of Earth’s topography. These maps typically employ a color gradient or contour lines to illustrate elevation differences.
- Color Gradient Maps: These maps utilize a spectrum of colors, typically ranging from green for low altitudes to brown or white for high altitudes. This color scheme provides a clear visual indication of the relative height of different landmasses.
- Contour Line Maps: Contour lines connect points of equal altitude, creating a network of lines that trace the contours of the terrain. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope.
Key Features of World Map Altitude
- Highest Points: The highest point on Earth is Mount Everest, located in the Himalayas, with a summit elevation of 8,848.86 meters (29,031.7 feet) above sea level.
- Lowest Points: The lowest point on Earth is the Challenger Deep, located in the Mariana Trench, with a depth of approximately 10,929 meters (35,856 feet) below sea level.
- Mountain Ranges: Major mountain ranges, such as the Himalayas, Andes, and Rockies, are characterized by high altitudes and dramatic elevation changes.
- Plateaus: Plateaus are elevated flatlands that stand above the surrounding terrain. They often feature unique ecosystems and geological formations.
- Plains: Plains are extensive, relatively flat areas with low altitudes. They are often fertile and suitable for agriculture.
Understanding Altitude Data
Altitude data is collected through various methods, including:
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites equipped with radar and lidar sensors can measure altitude with high accuracy.
- Global Positioning System (GPS): GPS receivers can determine altitude by measuring the time it takes for signals from multiple satellites to reach the receiver.
- Barometric Pressure: Altimeters use barometric pressure to calculate altitude, as air pressure decreases with increasing altitude.
- Topographic Surveys: Ground-based surveys use instruments like theodolites and levels to measure elevation differences.
Benefits of World Map Altitude
- Enhanced Spatial Awareness: Altitude data helps us visualize and understand the three-dimensional nature of the Earth’s surface.
- Improved Decision-Making: Altitude information is crucial for making informed decisions in various fields, including urban planning, infrastructure development, and disaster management.
- Scientific Research: Altitude data is essential for conducting research on climate change, biodiversity, and geological processes.
- Education and Outreach: World map altitude provides valuable insights into the Earth’s topography and its impact on our planet.
FAQs about World Map Altitude
1. What is the difference between altitude and elevation?
Altitude refers to the vertical distance of a point above sea level, while elevation refers to the height of a point above a reference datum, which may be a local or regional reference point.
2. How is altitude measured?
Altitude is typically measured in meters or feet above sea level. Modern methods include satellite imagery, GPS, barometric pressure, and topographic surveys.
3. What are the factors that influence altitude?
Altitude is influenced by geological processes such as tectonic plate movement, volcanic activity, and erosion. Climate also plays a role, as erosion rates are influenced by precipitation and temperature.
4. How does altitude affect climate?
Higher altitudes experience colder temperatures due to thinner air and reduced atmospheric pressure. This also affects precipitation patterns, wind speeds, and vegetation types.
5. What are the implications of altitude for human populations?
Altitude affects human health, agriculture, and transportation. High altitudes can lead to altitude sickness, while low altitudes may be more susceptible to flooding.
Tips for Using World Map Altitude
- Use multiple sources of altitude data: Compare data from different sources to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Consider the scale of the map: The level of detail provided by a map will influence the accuracy of altitude information.
- Understand the limitations of altitude data: Altitude data may be inaccurate in areas with dense vegetation or complex terrain.
- Use altitude data in conjunction with other geographical information: Combine altitude data with information on land cover, soil type, and climate to gain a comprehensive understanding of a region.
Conclusion
World map altitude is a fundamental geographical parameter that provides invaluable insights into the Earth’s topography and its impact on our planet. Understanding altitude is crucial for a wide range of applications, from climate modeling and resource management to navigation and scientific research. By visualizing and analyzing altitude data, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of our world and the interconnectedness of its various systems. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more precise and detailed altitude data, further enhancing our understanding of the Earth’s intricate landscape.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Earth’s Topography: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Altitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!