Unlocking the Potential of Rail Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Rail Freight Maps
Related Articles: Unlocking the Potential of Rail Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Rail Freight Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Potential of Rail Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Rail Freight Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Potential of Rail Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Rail Freight Maps
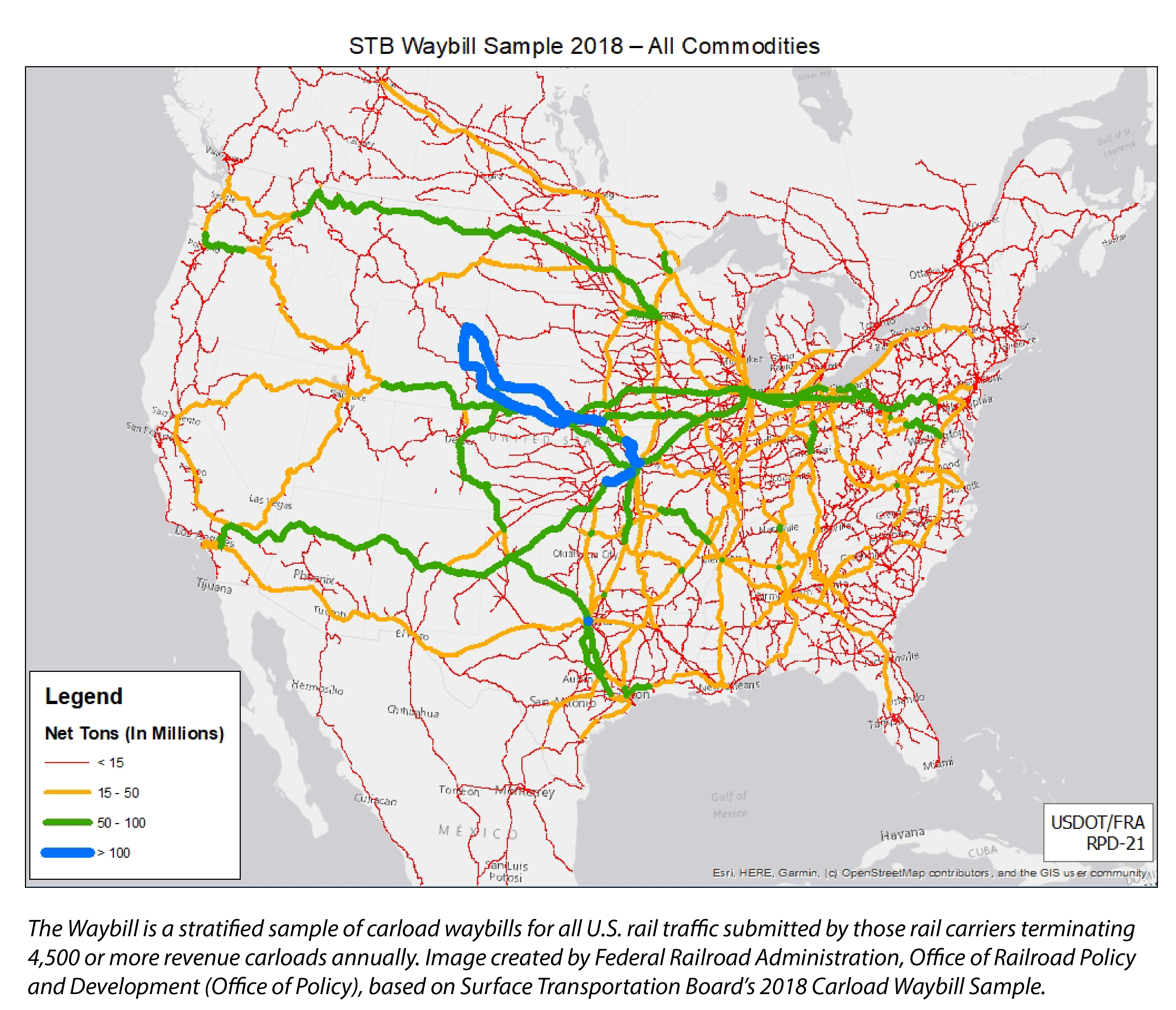
In the intricate web of global trade and logistics, rail freight plays a vital role in moving goods efficiently and sustainably. Rail freight maps, often overlooked, serve as essential tools for navigating this complex system. They provide a visual representation of the intricate network of rail lines, terminals, and intermodal connections that underpin the movement of goods across continents. Understanding these maps unlocks a wealth of information, empowering businesses to optimize their supply chains and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Significance of Rail Freight Maps
Rail freight maps are more than just visual representations; they are powerful analytical tools that offer a comprehensive overview of the rail freight landscape. Their importance stems from several key aspects:
- Strategic Planning: By visualizing the entire rail network, businesses can identify the most efficient routes for transporting goods, minimizing transit time and costs. This enables them to optimize their supply chains, ensuring timely deliveries and reducing operational expenses.
- Network Visibility: Rail freight maps provide a clear picture of the available infrastructure, including rail lines, terminals, and intermodal connections. This allows businesses to assess the capacity and accessibility of the network, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding transportation options.
- Capacity Analysis: By analyzing the rail freight map, businesses can gauge the available capacity on different routes and identify potential bottlenecks. This information helps them anticipate potential delays, adjust shipping schedules, and ensure smooth transportation operations.
- Sustainability Insights: Rail freight is a more sustainable mode of transportation compared to road freight, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and environmental impact. Rail freight maps can highlight routes that prioritize sustainable practices, enabling businesses to make environmentally conscious choices.
- Market Analysis: By studying rail freight maps, businesses can gain insights into the regional distribution of goods, identify key market hubs, and understand the flow of commodities. This information helps them identify new opportunities and expand their reach.
Decoding the Elements of a Rail Freight Map
Rail freight maps are designed to be intuitive and informative, incorporating various elements to provide a comprehensive view of the network. Understanding these elements is crucial for effectively utilizing the map:
- Rail Lines: These lines represent the physical infrastructure of the rail network, connecting major cities, industrial centers, and ports. Different colors or line thicknesses can indicate the capacity or type of rail line (e.g., high-speed lines, freight-only lines).
- Terminals: These are strategically located points where goods are loaded and unloaded from trains. Terminals can be categorized based on their function, such as intermodal terminals (connecting rail and road transport), container terminals, and industrial terminals.
- Intermodal Connections: These points mark the intersection of rail lines with other modes of transport, such as road and sea freight. Intermodal connections facilitate seamless movement of goods between different transportation systems.
- Freight Flows: Arrows or color gradients can indicate the direction and volume of freight movement along different routes. This information reveals the busiest corridors and highlights potential areas for network expansion.
- Key Infrastructure: Maps often include information about key infrastructure elements, such as bridges, tunnels, and rail yards, which play a critical role in the efficient operation of the rail network.
Types of Rail Freight Maps
Rail freight maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and levels of detail. Understanding the different types helps in choosing the most appropriate map for a given purpose:
- National Rail Freight Maps: These maps provide an overview of the entire rail freight network within a country, highlighting major lines, terminals, and intermodal connections. They are useful for understanding the overall capacity and infrastructure of the network.
- Regional Rail Freight Maps: These maps focus on specific regions within a country, providing a more detailed view of the local rail network. They are helpful for businesses operating within a particular geographic area.
- Intermodal Rail Freight Maps: These maps highlight the connections between rail freight and other modes of transport, such as road and sea freight. They are essential for businesses involved in intermodal transportation, enabling them to optimize their logistics and minimize transit times.
- Commodity-Specific Rail Freight Maps: These maps focus on the movement of specific types of goods, such as agricultural products, industrial materials, or finished goods. They are useful for businesses dealing with specialized cargo and understanding the flow of specific commodities.
Navigating the World of Rail Freight Maps: A Practical Guide
To make the most of rail freight maps, consider the following steps:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine the specific purpose for which you require a rail freight map. Are you looking for an overview of the national network, a detailed regional map, or a specific commodity-focused map?
- Choose the Right Map: Select a map that aligns with your needs and provides the necessary level of detail. Consider the type of map, its source, and its date of publication.
- Analyze the Data: Study the map carefully, paying attention to the elements discussed earlier. Identify key routes, terminals, and intermodal connections relevant to your business.
- Compare and Contrast: If you are considering multiple transportation options, compare different rail freight maps to evaluate the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of each route.
- Stay Informed: The rail freight landscape is constantly evolving, with new lines being built, terminals being expanded, and regulations being updated. Stay informed about these changes by regularly accessing updated rail freight maps and industry publications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Rail Freight Maps
Q: Where can I find reliable rail freight maps?
A: Reliable rail freight maps can be obtained from various sources, including:
- Government agencies: Many national transportation agencies publish comprehensive rail freight maps.
- Industry associations: Associations representing rail freight operators and logistics companies often provide maps specific to their industry.
- Private companies: Specialized mapping companies offer detailed rail freight maps tailored to specific needs.
- Online databases: Several online platforms provide access to interactive rail freight maps, allowing users to customize their view and explore the network in detail.
Q: How can I use a rail freight map to optimize my supply chain?
A: Rail freight maps can be used to optimize supply chains in several ways:
- Route optimization: Identify the most efficient routes for transporting goods, minimizing transit time and costs.
- Capacity planning: Assess the available capacity on different routes and anticipate potential bottlenecks.
- Intermodal integration: Explore intermodal connections to optimize the movement of goods between different transportation modes.
- Cost analysis: Compare different routes and transportation options to identify the most cost-effective solution.
Q: What are the benefits of using rail freight for transportation?
A: Rail freight offers several advantages over other modes of transportation:
- Cost-effective: For long distances, rail freight is often more cost-effective than road freight.
- Sustainable: Rail freight generates significantly lower carbon emissions than road freight, contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
- Reliable: Rail freight is generally more reliable than road freight, less susceptible to traffic delays and weather disruptions.
- High capacity: Rail freight can transport large volumes of goods, making it ideal for bulk shipments.
Tips for Utilizing Rail Freight Maps Effectively
- Use the right tools: Utilize interactive rail freight maps that allow you to zoom in, pan around, and customize your view.
- Focus on your specific needs: Identify the specific routes, terminals, and intermodal connections relevant to your business.
- Consider the time frame: Factor in the time it takes to transport goods by rail, as this can vary depending on the route and the type of cargo.
- Stay up-to-date: Regularly update your knowledge of the rail freight network, as infrastructure and regulations are constantly evolving.
Conclusion
Rail freight maps are essential tools for navigating the complex world of rail freight transportation. They provide a visual representation of the network, offering valuable insights for strategic planning, capacity analysis, and sustainability assessments. By understanding the elements of a rail freight map and utilizing it effectively, businesses can optimize their supply chains, reduce transportation costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future.



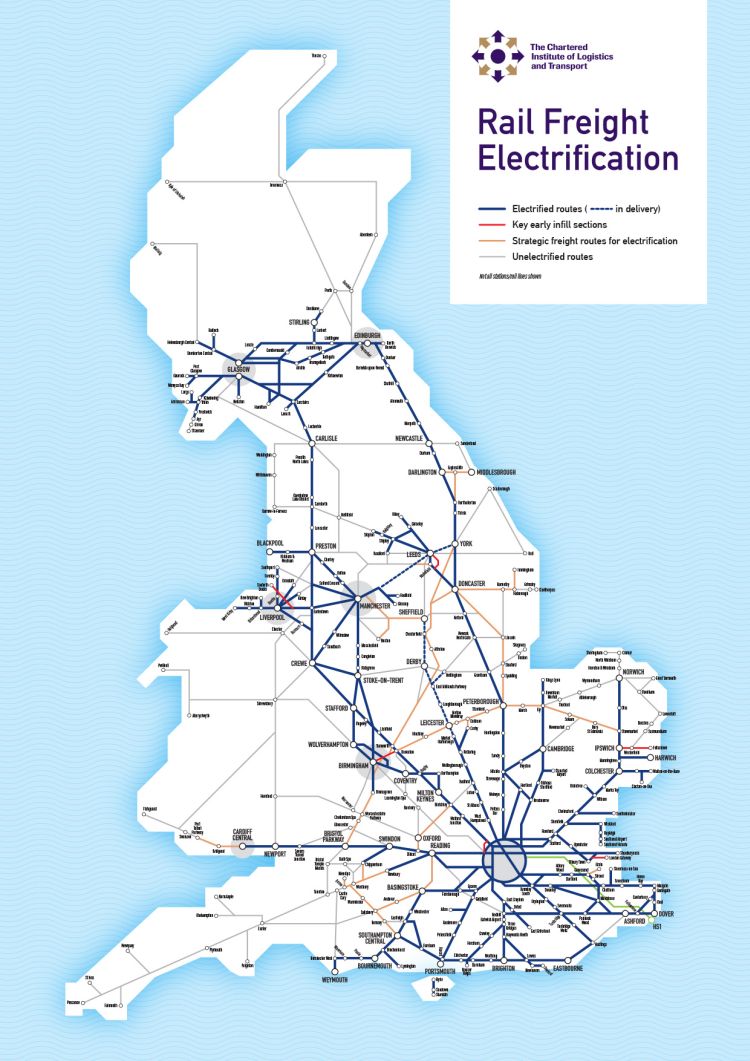

.jpg?itok=lpFI1cV0)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Potential of Rail Freight: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing Rail Freight Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!