Unlocking Earth’s Heat: A Guide to Geothermal Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Unlocking Earth’s Heat: A Guide to Geothermal Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking Earth’s Heat: A Guide to Geothermal Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking Earth’s Heat: A Guide to Geothermal Maps and Their Significance

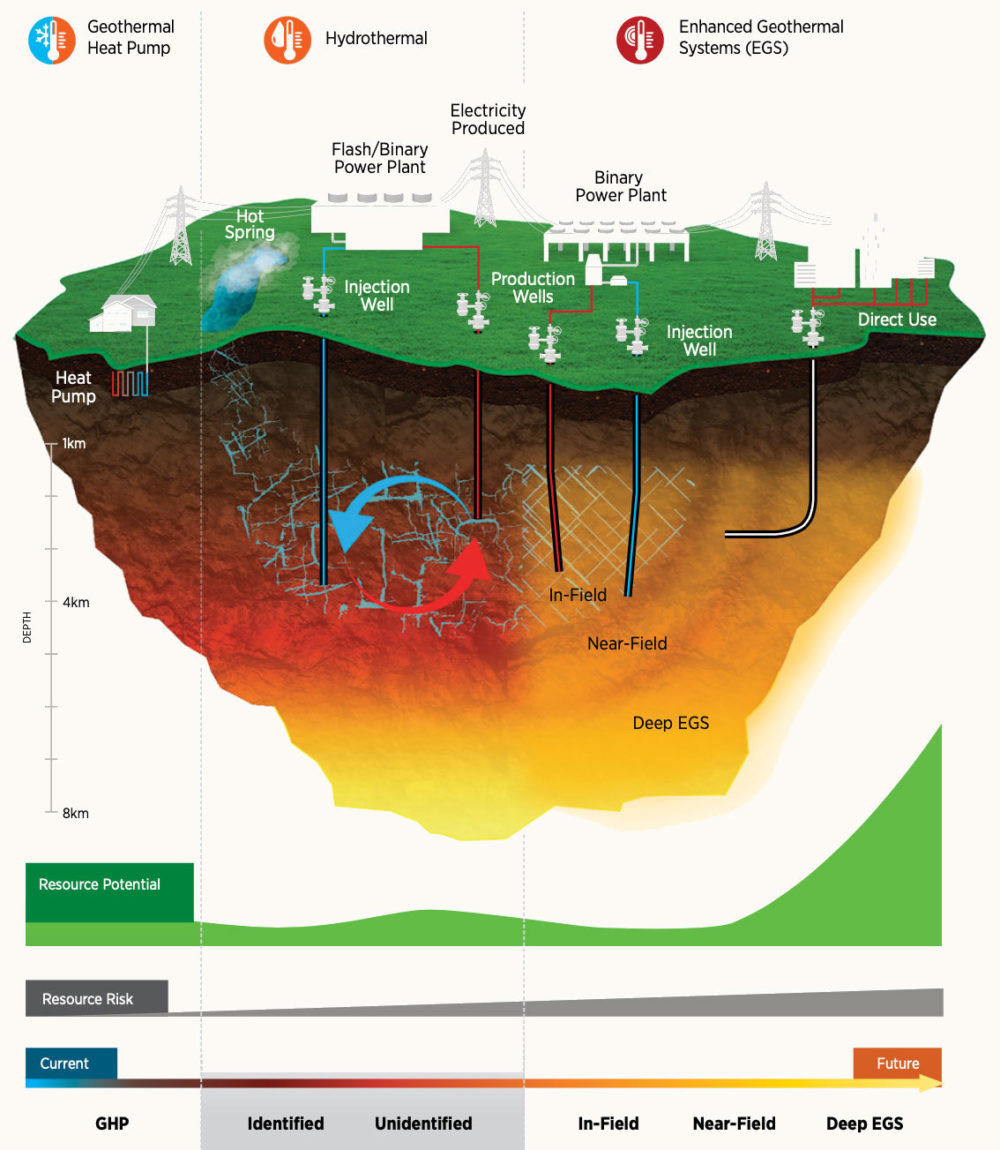
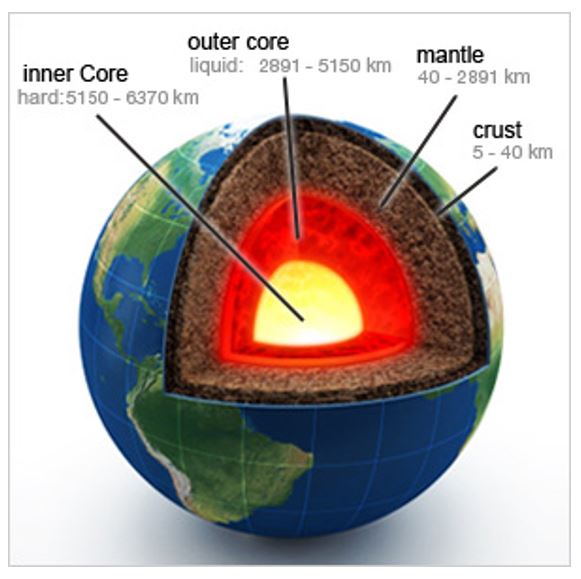
Geothermal energy, a clean and sustainable source of power, harnesses the heat residing deep within the Earth. Understanding the distribution and potential of this resource is crucial for developing geothermal energy projects. Geothermal maps, visual representations of geothermal activity and resource potential, play a vital role in this endeavor.
Defining the Scope: What is a Geothermal Map?
A geothermal map is a specialized geographical representation that depicts the distribution and characteristics of geothermal resources within a specific area. These maps are not simply static visuals; they are powerful tools used by geologists, energy developers, and policymakers to:
- Identify Geothermal Zones: Geothermal maps highlight areas with elevated heat flow, often associated with volcanic activity, tectonic plate boundaries, or deep-seated geological formations.
- Assess Resource Potential: They provide insights into the temperature, depth, and volume of geothermal reservoirs, crucial for determining the feasibility and economic viability of geothermal energy projects.
- Guide Exploration and Development: Geothermal maps serve as roadmaps for exploration efforts, directing drilling activities towards promising locations and minimizing risks.
- Promote Sustainable Energy Development: By identifying suitable geothermal sites, these maps contribute to the transition towards renewable energy sources and mitigate environmental impacts associated with fossil fuels.
Types of Geothermal Maps: A Spectrum of Information
Geothermal maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and levels of detail. Common types include:
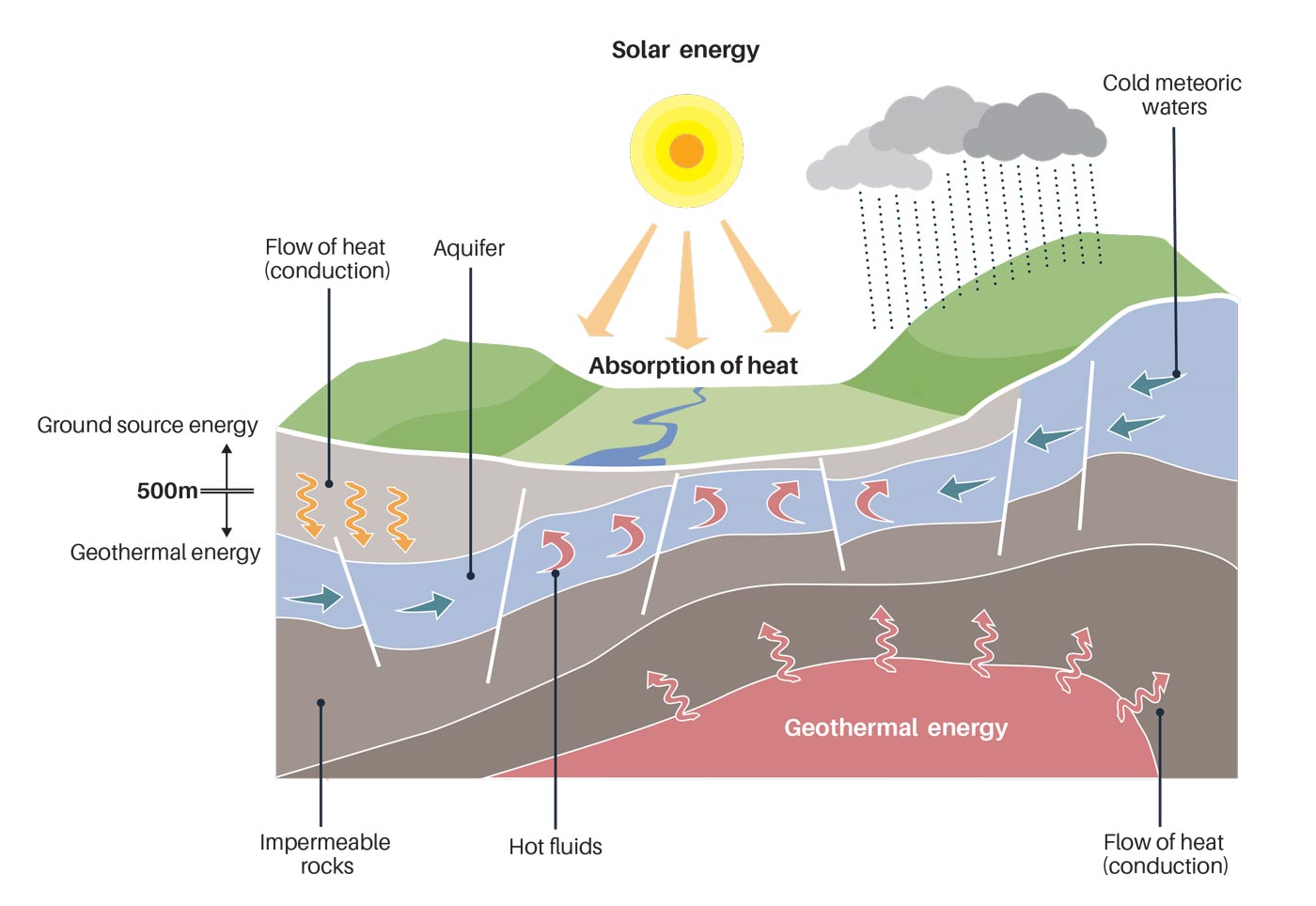
- Surface Heat Flow Maps: These maps depict the heat flow from the Earth’s surface, highlighting areas with elevated temperatures. They are useful for initial reconnaissance and identifying potential geothermal zones.
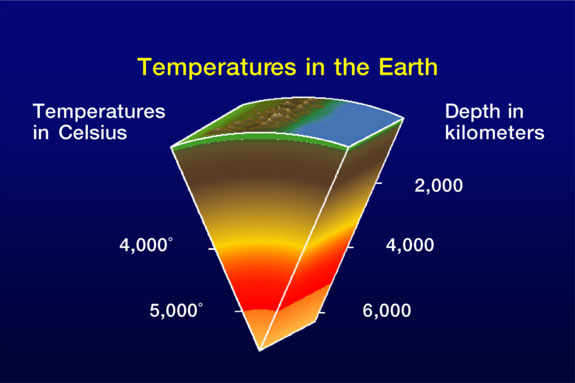
- Geothermal Gradient Maps: These maps illustrate the rate of temperature increase with depth, providing information on the temperature profiles of underground formations. They are essential for assessing the viability of geothermal reservoirs.
- Geothermal Resource Potential Maps: These maps integrate geological, geophysical, and geochemical data to assess the potential of geothermal resources in a given area. They often incorporate factors like subsurface temperature, permeability, and fluid chemistry.
- Geothermal Power Plant Suitability Maps: These maps focus on identifying areas suitable for geothermal power plant development, considering factors like resource availability, infrastructure, and environmental constraints.
Beyond Visualization: Data Integration and Interpretation
Geothermal maps are not merely visualizations; they are the product of extensive data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Data sources include:
- Geological Surveys: Detailed geological mapping, rock analysis, and structural studies provide insights into subsurface formations and their potential for geothermal energy.
- Geophysical Surveys: Techniques like seismic reflection, magnetotelluric surveys, and gravity measurements reveal subsurface structures, heat flow patterns, and the presence of geothermal reservoirs.
- Geochemical Analyses: Analyzing water and gas samples from hot springs, wells, and fumaroles helps determine the chemical composition and temperature of geothermal fluids.
- Remote Sensing Data: Satellite imagery and airborne surveys provide information on surface heat flow, vegetation patterns, and geological features, contributing to geothermal resource assessment.
The Importance of Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy and reliability of geothermal maps are paramount for successful geothermal energy development. Errors in data collection, analysis, or interpretation can lead to:
- Misallocation of Resources: Incorrect assessments of resource potential can result in wasted investments and exploration efforts.
- Environmental Risks: Unreliable maps might lead to drilling in unsuitable locations, potentially impacting sensitive ecosystems or triggering seismic events.
- Economic Losses: Misjudging the feasibility of geothermal projects can result in financial losses and discourage investment in renewable energy.
Utilizing Geothermal Maps for Sustainable Energy Development
Geothermal maps serve as essential tools for promoting sustainable energy development by:
- Optimizing Geothermal Project Planning: They guide the selection of suitable locations, minimizing environmental impacts and maximizing resource utilization.
- Facilitating Resource Management: By providing detailed information on resource characteristics, geothermal maps enable efficient resource management and long-term sustainability.
- Enhancing Environmental Stewardship: They help identify sensitive areas and mitigate potential risks associated with geothermal development, promoting responsible energy practices.
- Supporting Policy Decisions: Geothermal maps provide data-driven insights to policymakers, informing decisions on energy policy, resource allocation, and environmental regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How are geothermal maps created?
Geothermal maps are created through a multi-step process that involves data collection, analysis, and interpretation. This includes geological surveys, geophysical measurements, geochemical analyses, and remote sensing data.
2. What are the limitations of geothermal maps?
Geothermal maps are based on available data and interpretations, which can be subject to uncertainties. They may not always accurately reflect the complexities of subsurface conditions and resource characteristics.
3. How can I access geothermal maps?
Geothermal maps are often available from government agencies, research institutions, and energy companies. They can be found online through databases, publications, and mapping platforms.
4. Are geothermal maps updated regularly?
Yes, geothermal maps are typically updated as new data becomes available and technological advancements enhance mapping capabilities.
5. How are geothermal maps used for geothermal power plant development?
Geothermal power plant suitability maps are used to identify areas with high geothermal potential, favorable geological conditions, and suitable infrastructure for power plant development.
Tips for Utilizing Geothermal Maps
- Consult multiple sources: Cross-reference data from different sources to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Consider scale and resolution: Select maps with appropriate scales and resolutions for your specific needs.
- Interpret data cautiously: Be aware of potential limitations and uncertainties associated with data collection and interpretation.
- Engage experts: Consult with geologists, geophysicists, and geothermal specialists for professional advice and guidance.
- Stay informed: Keep abreast of advancements in geothermal mapping technologies and data availability.
Conclusion
Geothermal maps are indispensable tools for understanding and harnessing Earth’s heat for sustainable energy production. They provide crucial insights into the distribution, characteristics, and potential of geothermal resources, guiding exploration, development, and policy decisions. As we strive for a cleaner energy future, these maps play a vital role in unlocking the potential of geothermal energy and promoting a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking Earth’s Heat: A Guide to Geothermal Maps and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!