Understanding the United States Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Guide for Gardeners
Related Articles: Understanding the United States Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Guide for Gardeners
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the United States Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Guide for Gardeners. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the United States Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Guide for Gardeners
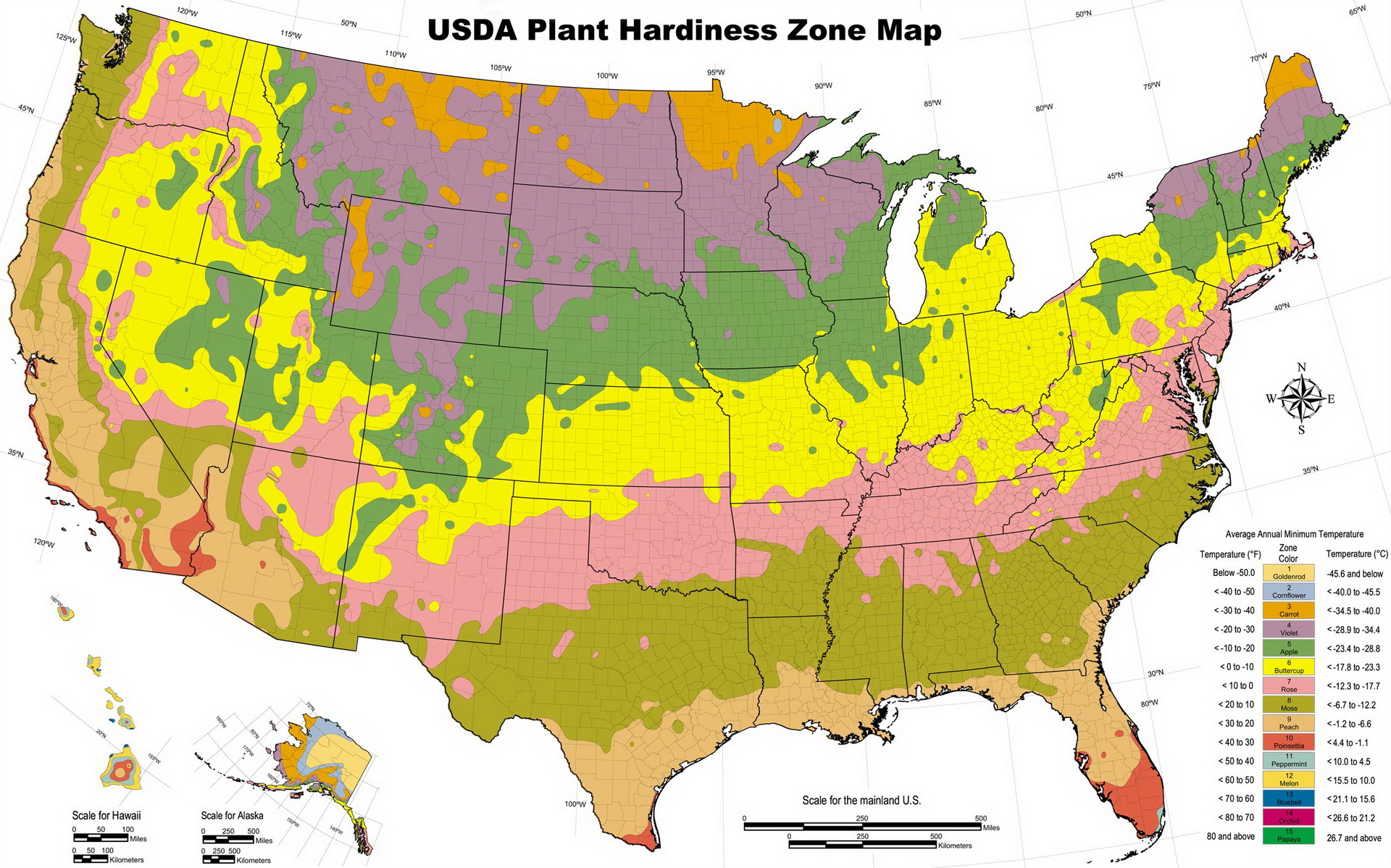
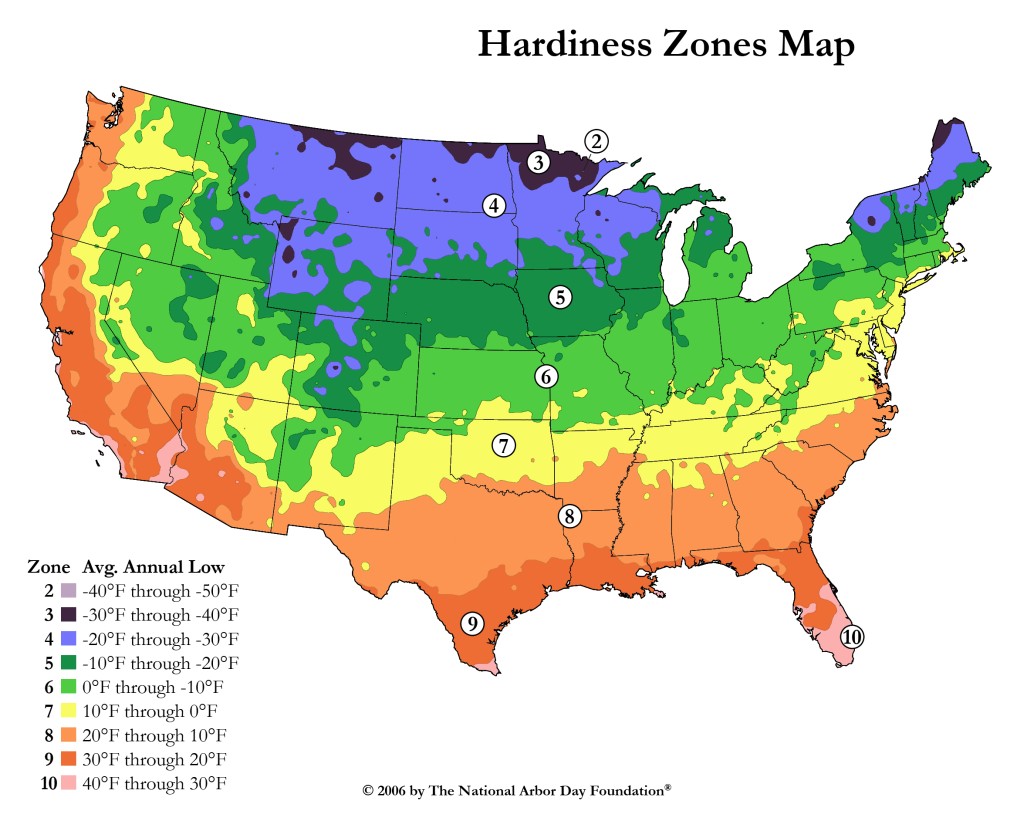
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a crucial tool for gardeners across the country. This map, updated in 2021, provides valuable information about the average lowest winter temperatures in different regions, helping gardeners determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific climate.
The Importance of Plant Hardiness Zones
Understanding plant hardiness zones is vital for successful gardening. Choosing plants that are suited to the local climate ensures they can withstand the coldest temperatures, maximizing their chances of survival and flourishing.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Comprehensive Overview
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is divided into 11 zones, ranging from Zone 1, the coldest, to Zone 11, the warmest. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit range of average minimum winter temperatures. For example, Zone 5 encompasses areas with average minimum winter temperatures between -20 and -10 degrees Fahrenheit.
Key Features of the 2021 Update:
The 2021 update of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map reflects the changing climate and its impact on average winter temperatures. This update offers several notable features:
- Refined Zone Boundaries: Based on updated climate data, the boundaries between zones have been adjusted to reflect more accurate temperature ranges.
- New Zones in Certain Regions: In some areas, particularly along the coasts and in warmer regions, new zones have been introduced to better represent the subtle variations in winter temperatures.
- Increased Awareness of Microclimates: The 2021 map highlights the significance of microclimates within a zone, acknowledging that variations in elevation, proximity to water bodies, and other factors can influence local temperatures.
Using the Plant Hardiness Zone Map Effectively
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource, but it’s essential to use it effectively:
- Locate Your Zone: The first step is to find your specific zone on the map. Online tools and interactive maps make this process easy.
- Understand the Zone Range: Remember that the zone represents an average minimum winter temperature. Local variations within a zone can occur, so it’s essential to consider your specific microclimate.
- Consult Plant Labels: Plant labels often include the USDA hardiness zone range, providing guidance on their suitability for your area.
- Seek Local Expertise: Consulting local nurseries or garden centers can offer valuable insights into plants that perform well in your region, considering specific microclimates and soil conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Q: What if I live in a transition zone between two zones?
A: When located between two zones, it’s generally advisable to choose plants that are suitable for the colder of the two zones. This ensures greater resilience against unexpected cold snaps.
Q: Does the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map account for other climatic factors like rainfall and humidity?
A: While the map focuses on winter temperatures, other factors like rainfall and humidity are also important for plant growth. It’s essential to consider these factors in addition to the hardiness zone.
Q: How does climate change impact the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map?
A: Climate change is causing shifts in average temperatures, leading to changes in plant hardiness zones. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is regularly updated to reflect these changes.
Q: Can I grow plants outside their designated hardiness zone?
A: While it’s possible to grow plants outside their designated zone with careful selection and proper care, it’s generally recommended to choose plants within your zone for optimal success.
Tips for Using the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
- Consider Your Microclimate: Factors like elevation, proximity to water bodies, and wind exposure can influence local temperatures within a zone.
- Pay Attention to Plant Labels: Plant labels often include the USDA hardiness zone range, providing valuable information on suitability.
- Consult Local Experts: Nurseries and garden centers can offer guidance on plants that thrive in your region.
- Start with Smaller Plants: Begin with smaller plants or seedlings, as they are generally more adaptable to new environments.
- Provide Adequate Protection: During cold spells, consider providing protection for sensitive plants, such as covering them with frost blankets or moving them indoors.
Conclusion
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an invaluable tool for gardeners, providing essential information about the average minimum winter temperatures in different regions. By understanding your plant hardiness zone and considering other climatic factors, you can make informed decisions about which plants are best suited for your garden, ensuring their successful growth and enhancing the beauty of your outdoor space. The 2021 update reflects the changing climate, highlighting the importance of adapting gardening practices to ensure the long-term health and resilience of our landscapes.
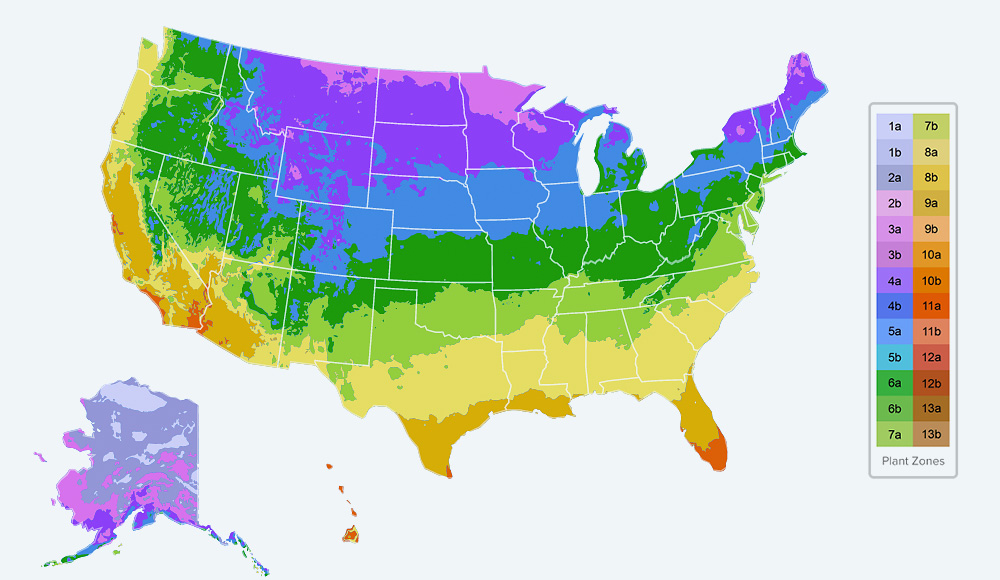
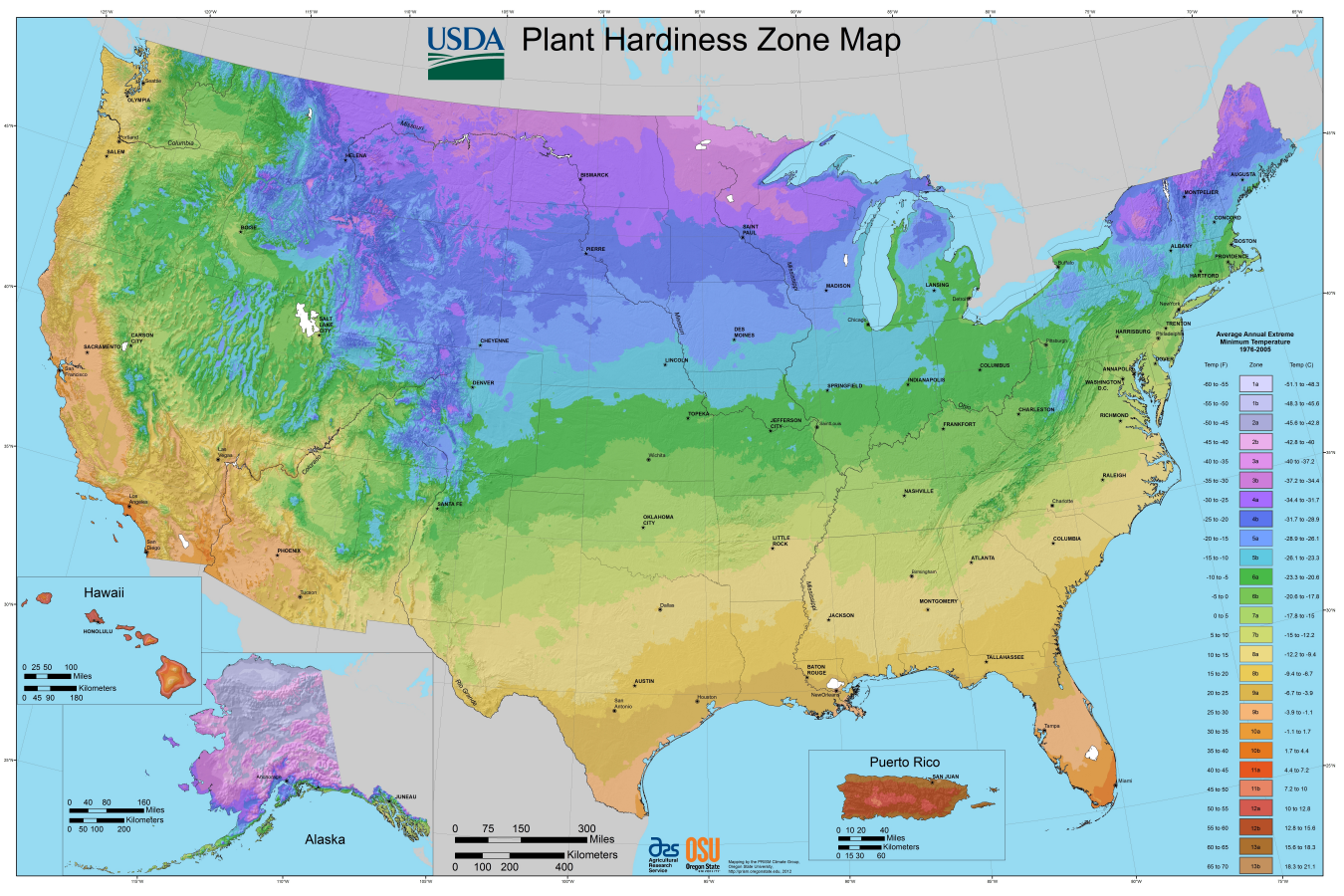
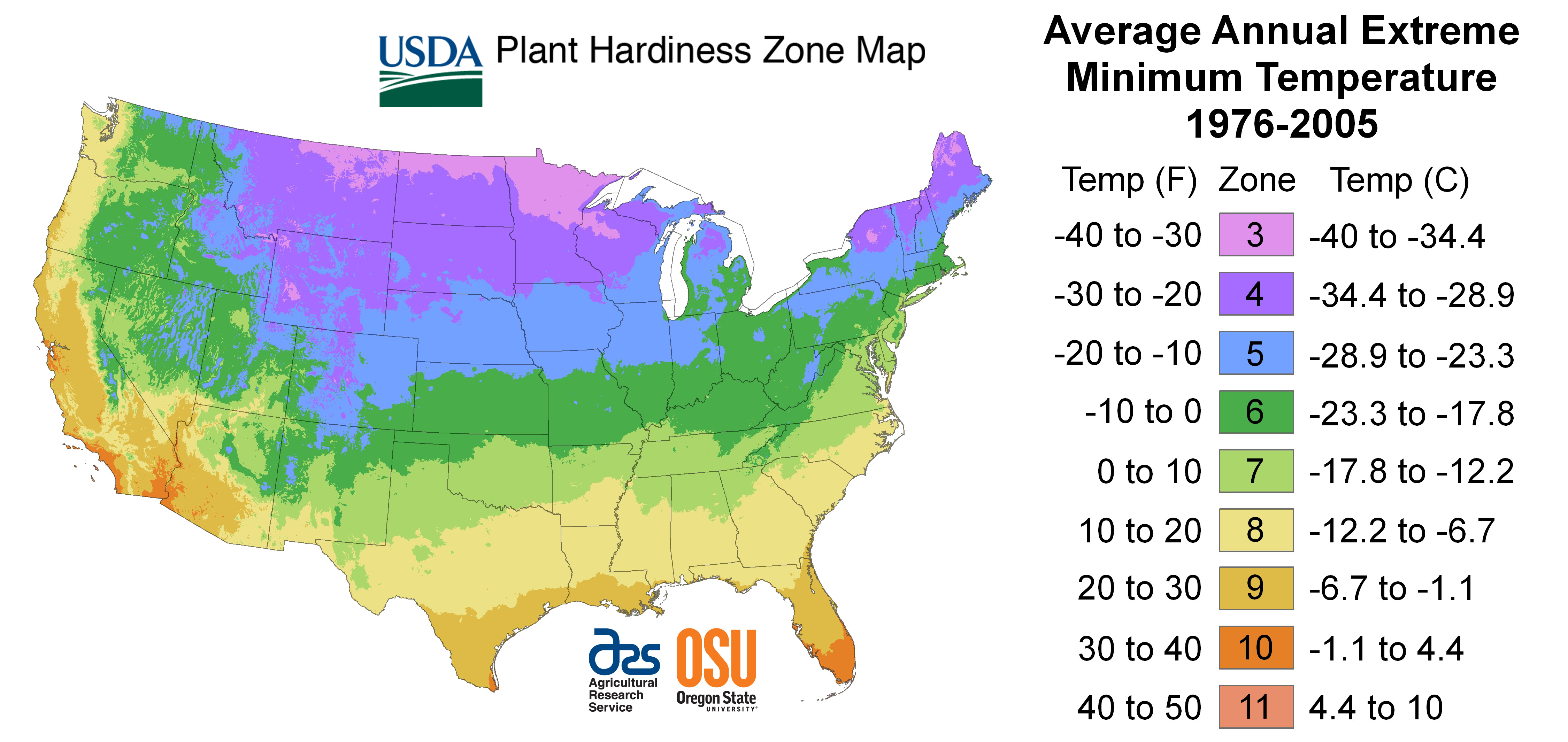




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the United States Plant Hardiness Zone Map: A Guide for Gardeners. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!