Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective
- 3.1 A Shared Landscape: The Geography of Palestine and Israel
- 3.2 The World Map Perspective: Defining Boundaries and Territories
- 3.3 Historical and Political Context: A Legacy of Conflict and Negotiation
- 3.4 The World Map Perspective: A Tool for Understanding and Dialogue
- 4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Palestine and Israel
- 5 Tips for Understanding the World Map Perspective of Palestine and Israel
- 6 Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Landscape
- 7 Closure
Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective
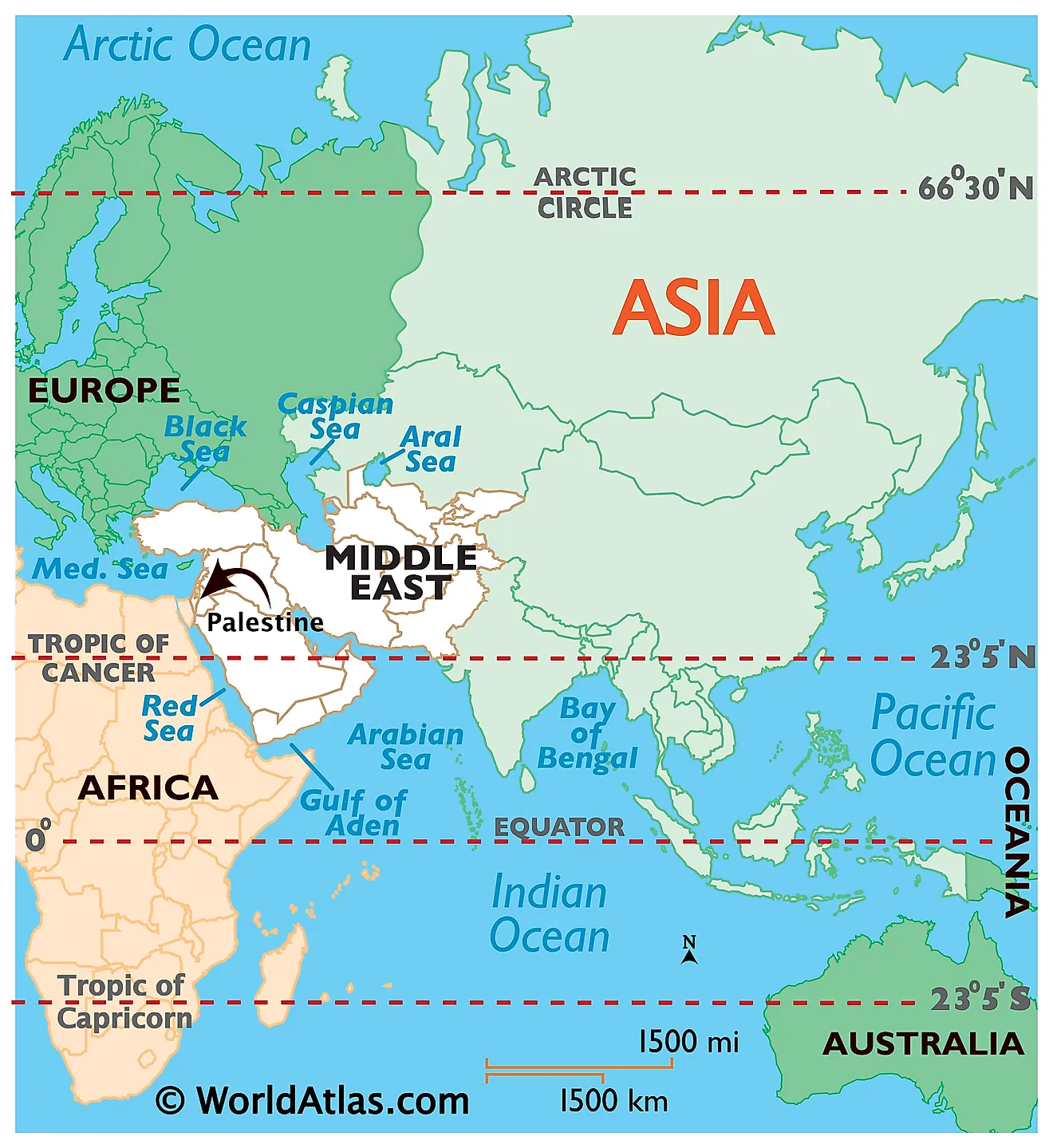
The intricate relationship between Palestine and Israel is deeply intertwined with the land they share. Understanding their geographical context is essential for comprehending the historical, political, and social complexities of the region. This article provides a comprehensive overview of Palestine and Israel, using a world map perspective to illustrate their geographical realities and the multifaceted challenges they face.
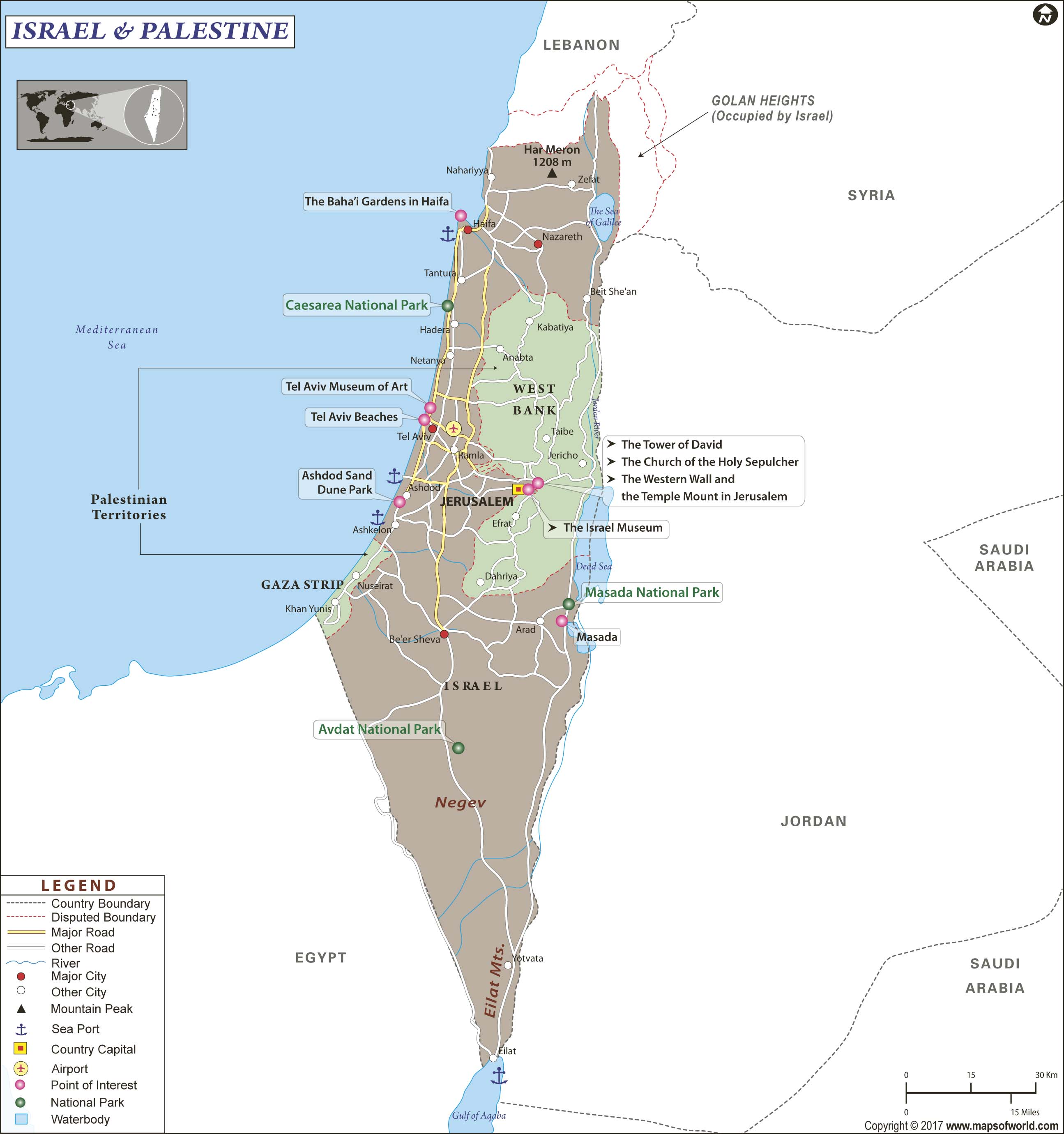
A Shared Landscape: The Geography of Palestine and Israel
Palestine and Israel occupy a relatively small area in the eastern Mediterranean region, encompassing a diverse landscape that includes:
- Coastal Plain: A narrow strip along the Mediterranean Sea, characterized by fertile land and urban centers like Tel Aviv and Gaza City.
- Central Highlands: Rolling hills and valleys, home to Jerusalem, Bethlehem, and other significant historical and religious sites.
- Jordan Valley: A rift valley running along the eastern border, known for its agricultural potential and the Dead Sea.
- Negev Desert: A vast arid region in the south, encompassing a diverse ecosystem and holding significant mineral resources.
- Golan Heights: A strategically important plateau overlooking the Galilee region, currently controlled by Israel but claimed by Syria.
This shared landscape has been a source of both unity and conflict throughout history. The fertile land and strategic location have drawn people to the region for millennia, resulting in a rich cultural tapestry and a complex history of competing claims and aspirations.
The World Map Perspective: Defining Boundaries and Territories
The geographical realities of Palestine and Israel are often misunderstood due to the complexities of their territorial claims. A world map perspective helps clarify these intricacies:
- The West Bank: Located on the western side of the Jordan River, the West Bank is considered occupied territory by the international community. It is claimed by both Palestine and Israel, leading to ongoing disputes and territorial conflicts.
- Gaza Strip: A densely populated coastal enclave, the Gaza Strip is governed by Hamas, a Palestinian political and militant group. Israel maintains a blockade on the territory, citing security concerns.
- East Jerusalem: The eastern part of Jerusalem, including the Old City, is claimed by both Palestine and Israel. It holds immense religious significance for both communities, further complicating the issue of territorial control.
The world map perspective underscores the contested nature of the region, highlighting the need for a negotiated solution that addresses the legitimate aspirations of both Palestinians and Israelis.
Historical and Political Context: A Legacy of Conflict and Negotiation
The history of Palestine and Israel is marked by conflict and negotiation, deeply intertwined with the geographical realities of the region. Key events include:
- The British Mandate: After World War I, the British Mandate for Palestine was established, setting the stage for the future conflict. The mandate aimed to create a Jewish national home while safeguarding the rights of the existing Arab population.
- The 1948 Arab-Israeli War: Following the declaration of the State of Israel, the 1948 war led to the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, known as the Nakba.
- The Six-Day War: In 1967, Israel captured the West Bank, East Jerusalem, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights, expanding its territory significantly.
- The Oslo Accords: In the 1990s, the Oslo Accords aimed to establish a Palestinian state alongside Israel. However, the peace process stalled due to continued violence and disagreements over key issues, including Jerusalem and settlements.
This historical context highlights the deep-rooted nature of the conflict and the challenges faced by both sides in achieving a lasting peace.
The World Map Perspective: A Tool for Understanding and Dialogue
The world map perspective offers a valuable tool for understanding the complex geographical realities of Palestine and Israel. It provides a visual representation of:
- The shared landscape: Emphasizing the interconnectedness of the region and the need for cooperation.
- Contested territories: Illustrating the complexities of territorial claims and the need for a negotiated solution.
- The human cost of conflict: Showing the impact of conflict on the lives of Palestinians and Israelis.
By understanding the geography of the region, we can engage in more informed and constructive dialogue, fostering a path towards peace and reconciliation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Palestine and Israel
Q: What are the main differences between Palestine and Israel?
A: The main difference lies in their political status and territorial control. Israel is a recognized state with a defined territory and internationally recognized borders. Palestine, while recognized by many countries, is not a fully sovereign state and its territory is subject to ongoing disputes and occupation.
Q: Why is the region so contested?
A: The region has been contested for centuries due to its religious, cultural, and strategic significance. The land is sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims, and its location at the crossroads of continents has made it a target for empires throughout history.
Q: What are the main challenges facing both Palestinians and Israelis?
A: Palestinians face challenges related to occupation, displacement, and limited self-governance. Israelis face threats from terrorism, the need to maintain security, and the ongoing conflict with Palestinians.
Q: What are the prospects for peace in the region?
A: The prospects for peace remain uncertain due to the deep-rooted nature of the conflict and the challenges in reaching a mutually acceptable solution. However, there is hope for progress through dialogue, reconciliation, and a commitment to a two-state solution.
Q: How can individuals contribute to peace in the region?
A: Individuals can contribute by:
- Educating themselves about the conflict: Understanding the historical context, the perspectives of both sides, and the complexities of the situation.
- Supporting organizations working for peace and reconciliation: Donating to NGOs or participating in initiatives promoting dialogue and understanding.
- Advocating for a peaceful solution: Engaging in constructive conversations, supporting diplomatic efforts, and advocating for policies that promote peace.
Tips for Understanding the World Map Perspective of Palestine and Israel
- Use reliable resources: Consult maps and information from reputable sources, such as the United Nations, the International Committee of the Red Cross, and academic institutions.
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze information from multiple perspectives, considering the biases and motivations of different sources.
- Emphasize human stories: Focus on the individual experiences of Palestinians and Israelis, understanding the impact of the conflict on their lives.
- Promote dialogue and understanding: Engage in respectful conversations with people from different backgrounds, seeking to bridge divides and build common ground.
Conclusion: Navigating a Complex Landscape
The world map perspective provides a valuable tool for understanding the complex geographical realities of Palestine and Israel. It highlights the shared landscape, contested territories, and historical context that have shaped the conflict. While the challenges are significant, a commitment to dialogue, reconciliation, and a two-state solution offers hope for a peaceful future. Through informed understanding, constructive engagement, and a shared commitment to peace, we can contribute to building a more just and equitable future for both Palestinians and Israelis.
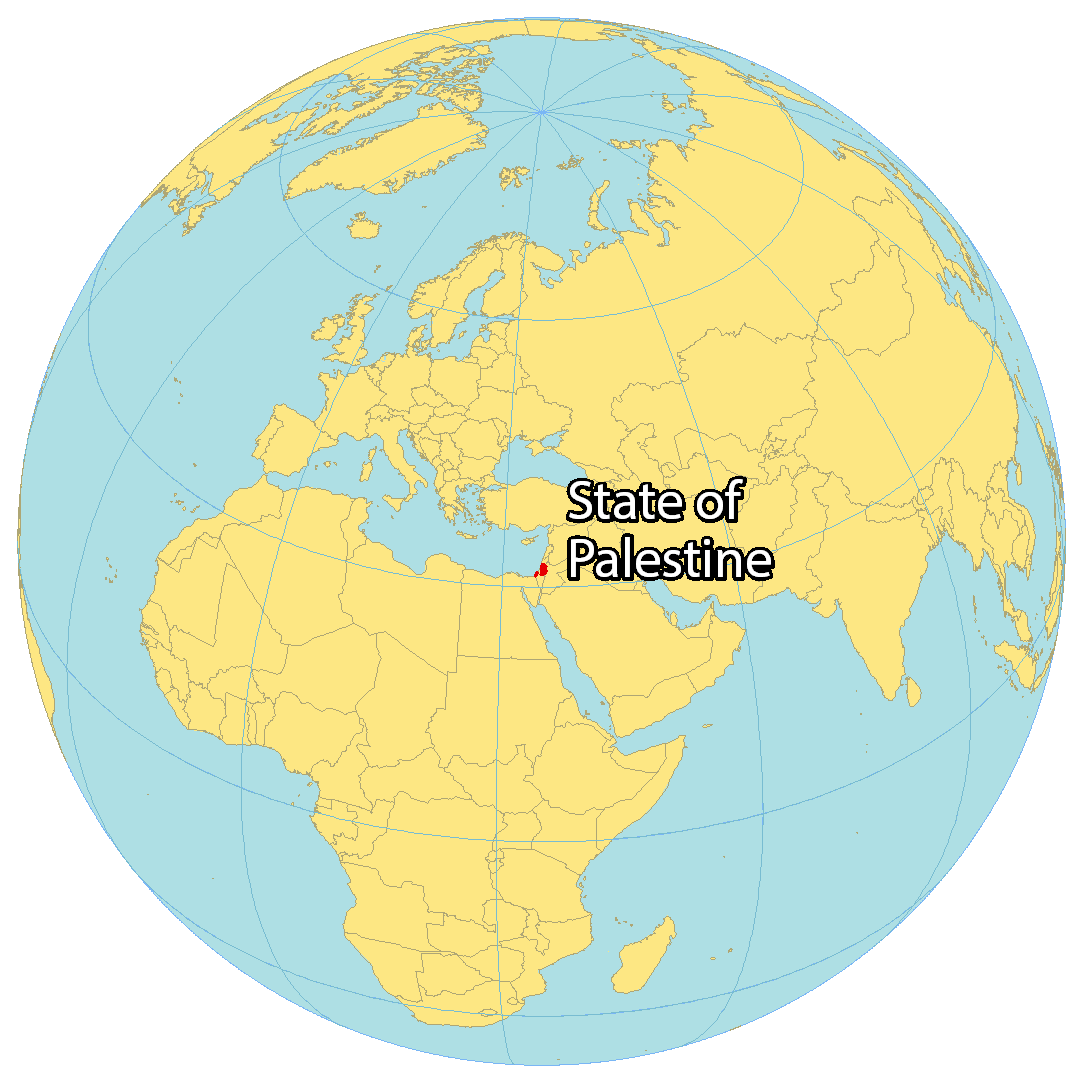
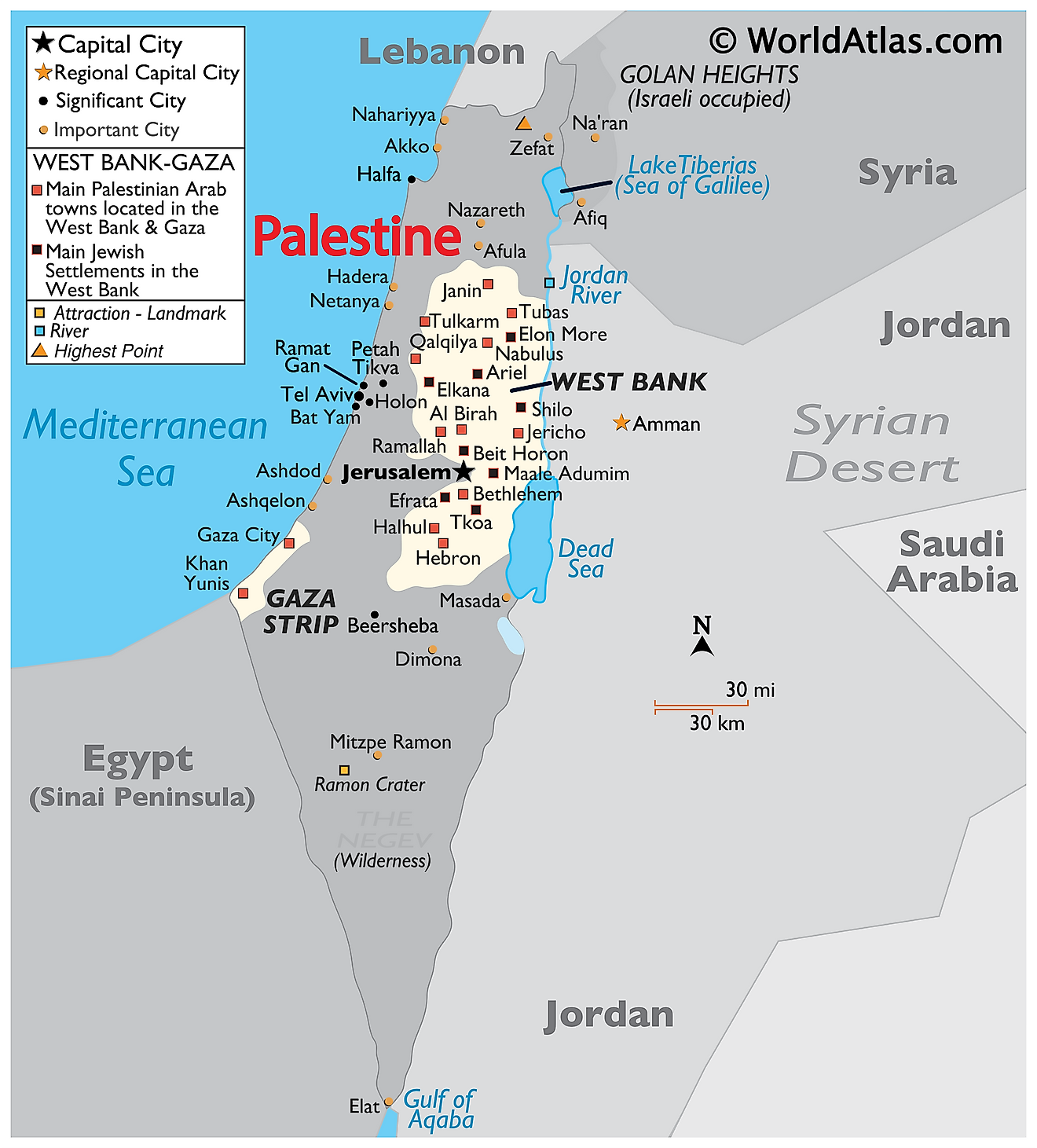
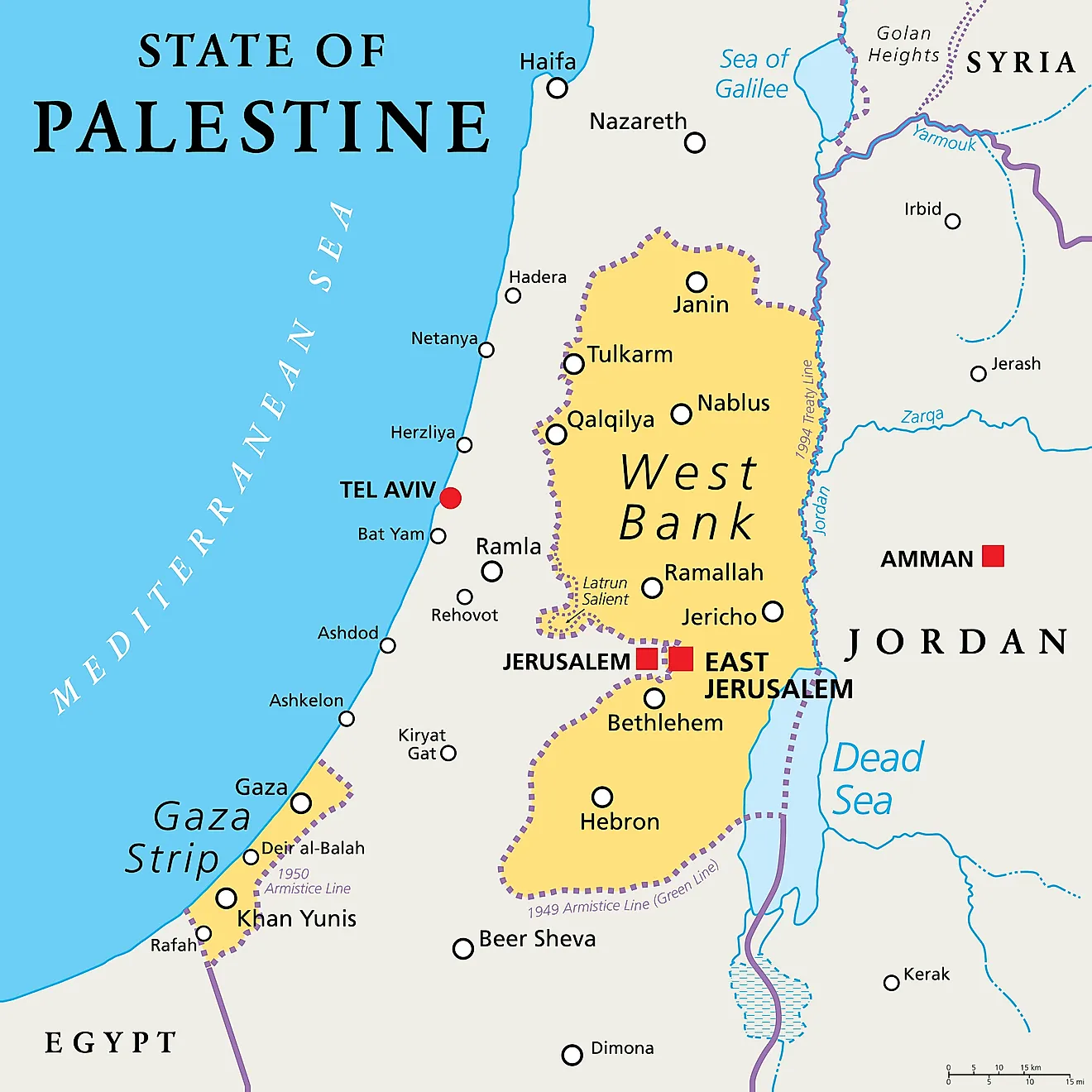



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complex Geography of Palestine and Israel: A World Map Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!