Understanding Radon Levels in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Radon Levels in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Radon Levels in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Radon Levels in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide
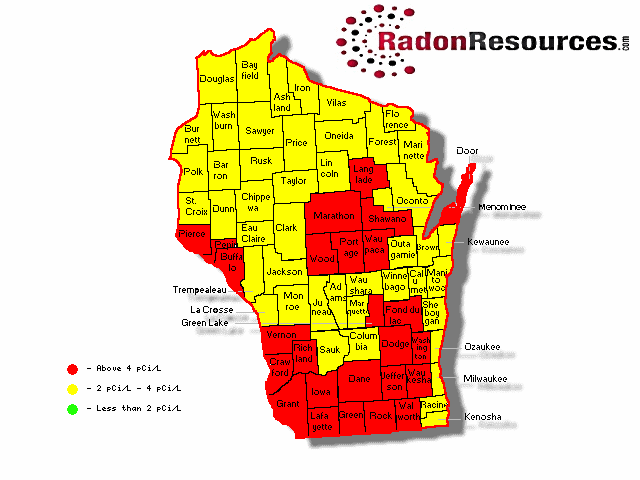
Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, is a significant public health concern across the United States, and Wisconsin is no exception. This colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas can seep into homes and buildings, posing a serious health risk to residents. Understanding the distribution of radon levels across the state is crucial for mitigating this risk.
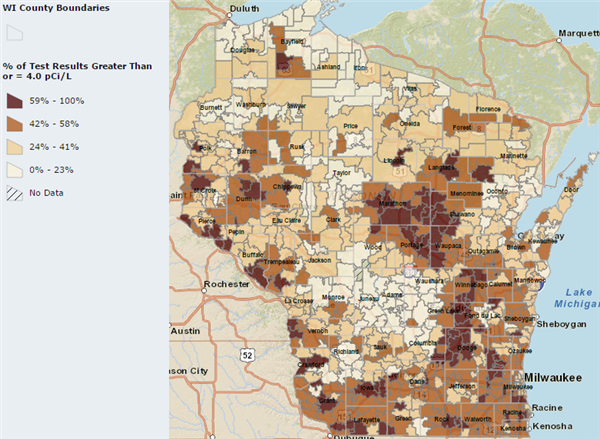
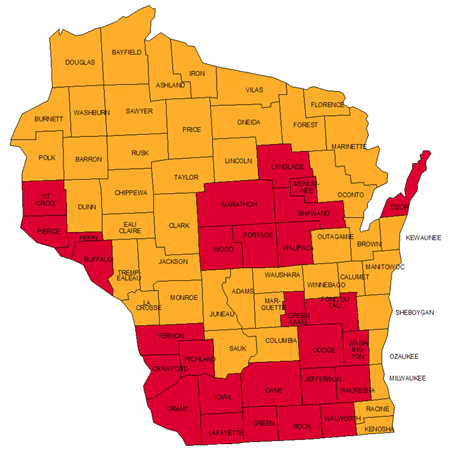
The Importance of the Radon Map
The Wisconsin Radon Map serves as a valuable tool for homeowners, real estate professionals, and public health officials alike. It provides a visual representation of estimated radon levels across the state, based on data collected from various sources. This information allows individuals to assess the potential risk of radon exposure in their area and take appropriate steps to protect their health.
How the Radon Map is Created and Updated
The Wisconsin Radon Map is generated using a combination of data sources, including:
- Historical Radon Testing Data: This data comes from various sources, including residential radon tests, public water system testing, and soil gas surveys.
- Geological and Hydrological Data: Information about the underlying geology and groundwater flow patterns provides insights into the potential for radon migration.
- Statistical Modeling: Sophisticated statistical models are used to analyze the collected data and create a comprehensive map that estimates radon levels across the state.
The map is regularly updated as new data becomes available, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Interpreting the Radon Map
The Wisconsin Radon Map typically uses color gradients to depict radon levels. Higher levels are usually represented by darker shades, while lower levels are indicated by lighter shades. The map may also include county-specific information and links to additional resources, such as testing recommendations and mitigation information.
Understanding Radon Levels and Risk
The map’s color scheme represents estimated average radon levels in different areas. However, it’s important to remember that individual homes can have significantly different radon levels, even within the same neighborhood.
Factors Influencing Radon Levels
Several factors contribute to varying radon levels across Wisconsin:
- Geology: Certain geological formations, such as granite and shale, are known to have higher radon concentrations.
- Soil Type: Soils with high clay content tend to trap radon, increasing its concentration in the surrounding air.
- Building Construction: The construction materials and techniques used in a building can influence radon entry points.
- Weather Conditions: Wind and air pressure can impact radon levels, with higher levels often observed during colder months.
The Health Risks of Radon Exposure
Radon is a known carcinogen, and prolonged exposure can significantly increase the risk of developing lung cancer, even in non-smokers. The risk of lung cancer increases with the level of radon exposure and the duration of exposure.
Taking Action to Protect Your Health
The Wisconsin Radon Map provides valuable information about potential radon levels in different areas. However, it’s crucial to take proactive steps to assess and mitigate radon exposure in your home.
Here’s how you can address radon concerns:
- Test Your Home: The most effective way to determine your radon levels is to conduct a radon test. Several testing kits are available for purchase online or at local hardware stores.
- Mitigation: If your radon levels are above the recommended limit of 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L), you should consider professional radon mitigation. This involves installing a system to vent radon gas from your home.
- Stay Informed: Continuously monitor your radon levels and follow recommended guidelines for radon testing and mitigation.
FAQs about Radon in Wisconsin
1. How often should I test my home for radon?
It is recommended to test your home for radon at least once, and ideally every two years. If you have recently renovated or remodeled your home, or if you have any concerns about radon levels, you should test more frequently.
2. What are the signs of radon exposure?
Radon exposure doesn’t typically cause immediate symptoms. However, prolonged exposure can lead to lung cancer, which may manifest with symptoms like coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
3. What is the recommended radon level in a home?
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends a radon level of 4 pCi/L or lower.
4. Can I mitigate radon myself?
While DIY radon mitigation kits are available, it’s highly recommended to hire a qualified professional for radon mitigation. This ensures that the system is installed correctly and effectively reduces radon levels.
5. How much does radon mitigation cost?
The cost of radon mitigation varies depending on the size of your home, the complexity of the installation, and the type of system used. However, it’s a wise investment in your health and the value of your home.
6. Is radon a problem in all areas of Wisconsin?
Radon levels can vary significantly across Wisconsin. The Radon Map can provide a general indication of risk levels, but testing your home is crucial to determine your specific radon exposure.
7. What resources are available for homeowners in Wisconsin?
The Wisconsin Department of Health Services (DHS) offers a wealth of information and resources related to radon, including testing kits, mitigation information, and financial assistance programs.
8. How does radon enter a home?
Radon typically enters homes through cracks in the foundation, gaps around pipes and wires, and other openings.
9. Can I prevent radon from entering my home?
While it’s impossible to completely prevent radon entry, proper construction techniques, regular maintenance, and effective mitigation systems can significantly reduce radon levels.
10. What are the long-term effects of radon exposure?
The most significant long-term effect of radon exposure is an increased risk of lung cancer. The risk increases with the level and duration of exposure.
Tips for Reducing Radon Levels in Your Home
- Seal cracks and gaps: Inspect your foundation, basement, and crawl space for cracks, gaps, and openings that could allow radon to enter. Seal these openings with caulk, sealant, or other appropriate materials.
- Improve ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your basement or crawl space. This can help reduce radon levels by drawing it out of the home.
- Install a vent fan: Consider installing a vent fan in your basement or crawl space to exhaust radon gas to the outside.
- Maintain your sump pump: A properly functioning sump pump can help prevent radon from entering your home through the sump pit.
- Regularly test your home: Monitor your radon levels regularly and take appropriate action if levels exceed the recommended limit.
Conclusion
Radon exposure is a significant health concern in Wisconsin, and understanding the distribution of radon levels across the state is crucial for mitigating this risk. The Wisconsin Radon Map provides valuable information about potential radon levels in different areas, encouraging homeowners to take proactive steps to protect their health. By testing your home for radon, implementing appropriate mitigation measures, and staying informed about radon risks, you can significantly reduce your exposure to this invisible threat.
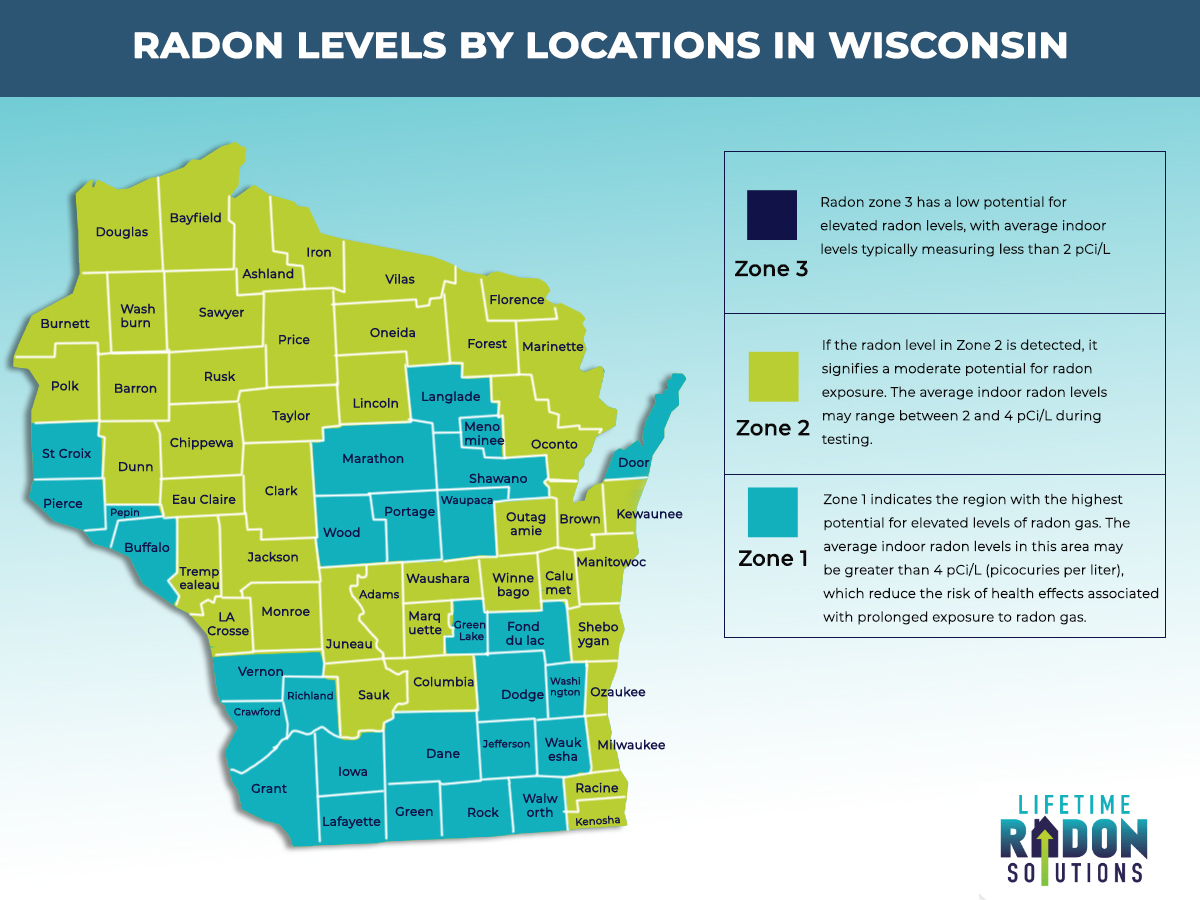

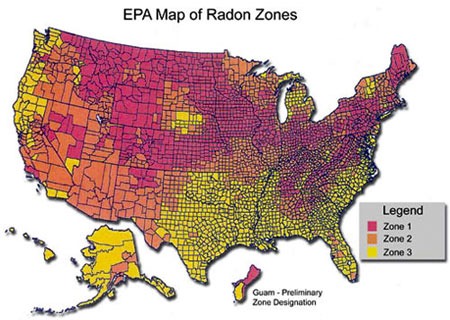
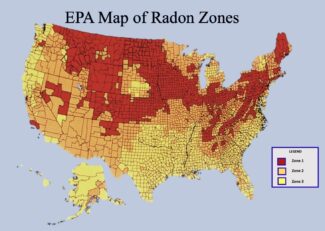


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Radon Levels in Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!