Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping
Related Articles: Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping
- 3.1 What are Perennial Zones?
- 3.2 Understanding the Perennial Zone Map
- 3.3 The Importance of Perennial Zones
- 3.4 Benefits of Utilizing Perennial Zones
- 3.5 Factors Influencing Perennial Zones
- 3.6 Using the Perennial Zone Map: A Practical Guide
- 3.7 FAQs about Perennial Zones
- 3.8 Tips for Utilizing Perennial Zones
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping
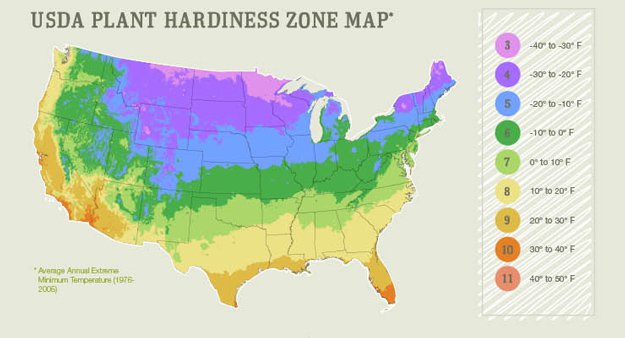
The concept of perennial zones, often depicted in the form of a map, plays a crucial role in guiding gardeners and landscapers toward sustainable and successful plant choices. These maps, based on climate data, provide valuable information on the hardiness of various plant species, enabling informed decisions regarding the selection and cultivation of perennial plants. This article delves into the intricacies of perennial zones, exploring their significance and providing a comprehensive understanding of their application in gardening and landscaping.
What are Perennial Zones?
Perennial zones are geographical areas categorized based on their average annual minimum temperature. This temperature, specifically the lowest recorded temperature during the coldest month of the year, serves as a key indicator of the hardiness of plants that can thrive in a particular region. Perennial zones, often referred to as hardiness zones, are represented on maps that visually depict the geographical distribution of these zones.
Understanding the Perennial Zone Map
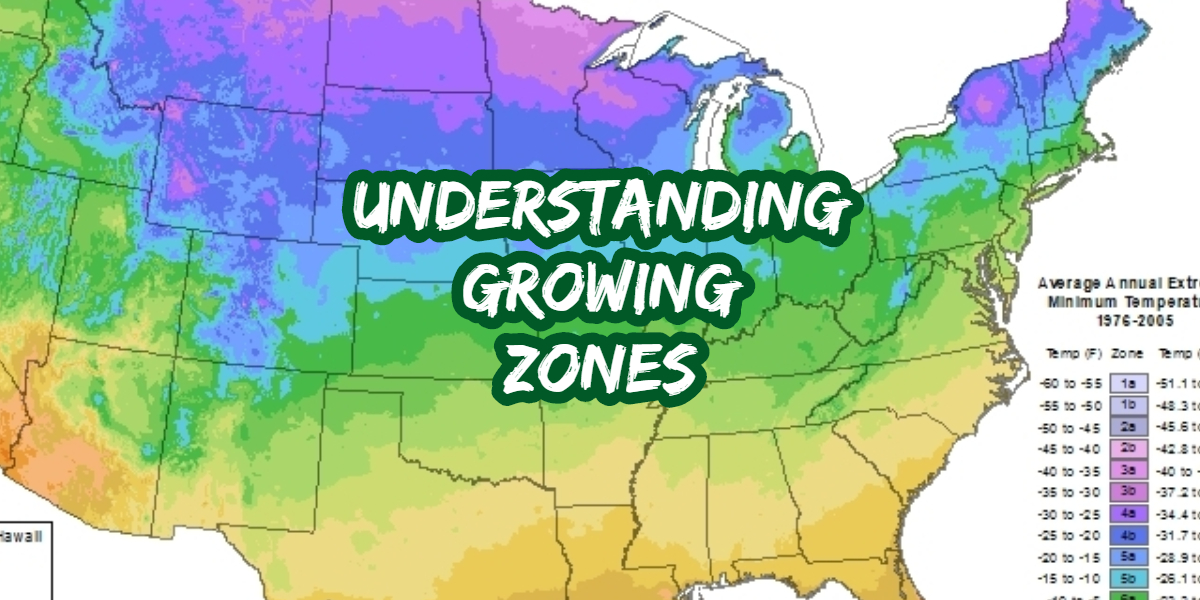
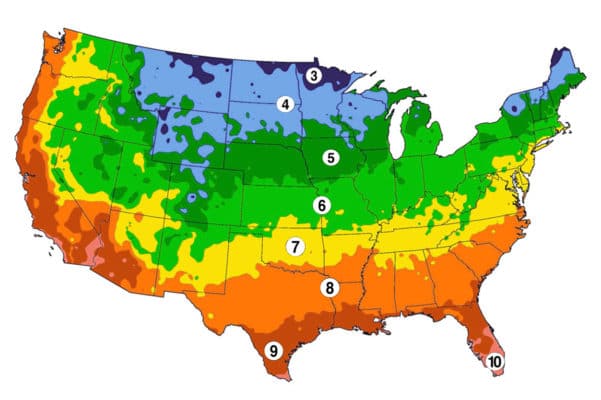
The most commonly used perennial zone map is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This map divides the United States into 11 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit temperature range. Zone 1, the coldest zone, experiences average minimum temperatures below -60 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 11, the warmest zone, experiences average minimum temperatures above 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Each zone on the map is further subdivided into "a" and "b" subzones, representing a 5-degree Fahrenheit temperature difference. For instance, Zone 5a encompasses areas with average minimum temperatures ranging from -20 to -15 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 5b encompasses areas with average minimum temperatures ranging from -15 to -10 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Importance of Perennial Zones
The significance of perennial zones lies in their ability to guide plant selection for optimal growth and survival. By understanding the hardiness zone of a particular region, gardeners and landscapers can choose plants that are best suited to the local climate. This knowledge enables them to avoid planting species that are likely to succumb to harsh winters or extreme temperatures, ultimately leading to a more successful and sustainable garden or landscape.
Benefits of Utilizing Perennial Zones
- Increased Plant Survival: By choosing plants that are suited to the local climate, gardeners and landscapers significantly increase the chances of plant survival. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, minimizing waste and promoting long-term sustainability.
- Reduced Maintenance: Perennial plants, by nature, are less demanding than annuals, requiring minimal maintenance. Understanding the hardiness zones ensures that the chosen plants are well-adapted to the local climate, further reducing the need for excessive watering, fertilizing, or pest control.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Selecting plants that thrive in a particular region ensures a vibrant and healthy garden or landscape. Plants that are well-suited to the local climate exhibit optimal growth, leading to a more aesthetically pleasing and visually appealing environment.
- Environmental Sustainability: By choosing plants that are naturally adapted to the local climate, gardeners and landscapers contribute to environmental sustainability. This reduces the need for artificial interventions, such as supplemental watering or the use of chemical fertilizers, minimizing environmental impact.
Factors Influencing Perennial Zones
While the average minimum temperature plays a crucial role in determining plant hardiness, other factors can also influence the suitability of a particular plant for a given location. These factors include:
- Microclimates: Variations in topography, such as hills, valleys, and bodies of water, can create localized microclimates that differ from the broader regional climate. These microclimates can influence plant hardiness, creating pockets of suitable growing conditions within a specific zone.
- Soil Type: Soil composition and drainage can influence the hardiness of plants. Well-drained soils generally provide better insulation, protecting plants from extreme temperatures. Conversely, poorly drained soils can lead to waterlogging, which can damage roots and make plants more susceptible to frost damage.
- Exposure: The amount of sunlight a plant receives can also affect its hardiness. Plants that are exposed to full sun may require a warmer zone than those that thrive in partial shade.
- Wind: Wind can exacerbate cold temperatures, making plants more susceptible to frost damage. Sheltered locations, protected from strong winds, may be able to support plants that are not hardy in the broader zone.
Using the Perennial Zone Map: A Practical Guide
- Identify Your Location: Determine the specific location for which you are planning to select plants. This could be your home garden, a park, or any other outdoor space.
- Find Your Zone: Consult the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map to identify the zone that corresponds to your location. Pay attention to the subzones to ensure the most accurate representation of your local climate.
- Consider Microclimates: Analyze your location for any microclimates that might influence plant hardiness. Factors like hills, valleys, and bodies of water can create localized variations in temperature and humidity.
- Research Plant Hardiness: Once you have identified your zone, research the hardiness of the plants you are considering. Look for information on the plant’s cold tolerance and any specific requirements for optimal growth.
- Choose Plants Within Your Zone: Select plants that are rated as hardy for your zone or a zone slightly warmer. This ensures that the plants have a higher chance of surviving the coldest temperatures in your region.
- Consider Other Factors: Factor in other factors like soil type, exposure, and wind exposure when making your final plant selection. Choose plants that are adapted to the specific conditions of your location.
FAQs about Perennial Zones
1. What is the difference between a perennial and an annual plant?
Perennial plants live for more than two years, typically returning year after year, while annual plants complete their life cycle within a single growing season.
2. How accurate are perennial zone maps?
Perennial zone maps provide a general guideline for plant hardiness. However, microclimates, soil conditions, and other factors can influence the actual hardiness of plants in a particular location.
3. Can I plant plants that are rated for a warmer zone than mine?
It is generally not recommended to plant plants that are rated for a warmer zone than yours. These plants may not survive the coldest temperatures in your region.
4. How can I protect plants during cold weather?
There are various methods to protect plants during cold weather, including mulching, providing windbreaks, and using frost blankets.
5. Can I change my zone?
Perennial zones are based on average minimum temperatures, which are relatively stable over time. However, climate change may lead to gradual shifts in zone boundaries.
Tips for Utilizing Perennial Zones
- Consult Local Garden Centers: Seek advice from local garden centers or nurseries. They can provide valuable insights into the hardiness of plants in your specific region.
- Observe Existing Plant Growth: Pay attention to the plants that are already thriving in your neighborhood. These plants can serve as indicators of the hardiness of various species in your local climate.
- Experiment with Different Species: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different plant species within your zone. This allows you to discover the best performers for your specific location.
- Consider Plant Hardiness Ratings: Pay close attention to plant hardiness ratings, which are often provided on plant tags or in online databases.
- Monitor Plant Health: Regularly monitor the health of your plants, especially during extreme weather conditions. Early intervention can help prevent plant damage and ensure their long-term survival.
Conclusion
Perennial zones, represented by maps that depict the geographical distribution of plant hardiness, provide valuable information for gardeners and landscapers. By understanding the hardiness of plants and selecting species that are suited to the local climate, individuals can create sustainable and thriving gardens and landscapes. The utilization of perennial zones promotes plant survival, reduces maintenance, enhances aesthetics, and contributes to environmental sustainability. By embracing this knowledge and following the guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can make informed plant choices that lead to long-lasting and vibrant outdoor spaces.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Perennial Zones: A Guide to Sustainable Gardening and Landscaping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!