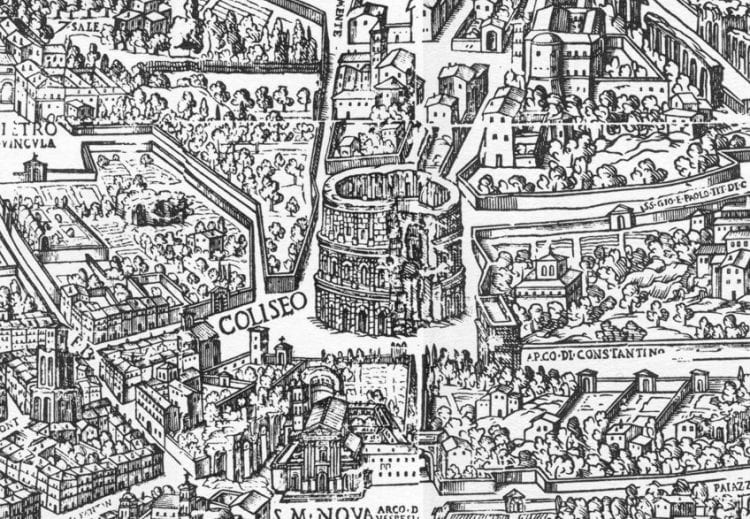
The Colosseum: A Map Through Time and History
Related Articles: The Colosseum: A Map Through Time and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Colosseum: A Map Through Time and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Colosseum: A Map Through Time and History

The Colosseum, or Flavian Amphitheatre, is a towering monument to Roman ingenuity and grandeur. This iconic structure, located in the heart of Rome, stands as a testament to the Roman Empire’s power and its fascination with spectacle. While the Colosseum itself is a marvel, understanding its layout and its role in Roman society requires delving into its intricate design and the stories it holds.
A Glimpse into the Colosseum’s Layout
The Colosseum is not merely a circular arena; it is a complex architectural masterpiece. Its design, a testament to Roman engineering, allowed for the seamless flow of crowds and the execution of elaborate performances. Understanding the Colosseum’s layout reveals its purpose and its significance within Roman society.
The Arena: The heart of the Colosseum, the arena, was a vast space measuring 83 meters by 54 meters. The arena floor was covered in sand, which absorbed blood and provided a buffer for gladiators during combat. The arena was accessed through underground tunnels, known as the "hypogeum," where animals and gladiators were kept before their performances.
The Seating: The Colosseum’s seating capacity was immense, capable of holding approximately 50,000 spectators. The seating was meticulously arranged in tiers, with different sections catering to different social classes. The lowest tier, known as the "podium," was reserved for dignitaries, senators, and the Emperor himself. Above the podium were the "maenianum," which accommodated the general public. The top tier, the "summa cavea," housed the poorest citizens.
The Walls and Façade: The Colosseum’s walls were built with a combination of travertine stone and brick, creating a durable and visually striking structure. The exterior of the Colosseum was adorned with arches, pilasters, and cornices, further enhancing its grandeur. The building’s façade was punctuated by eighty entrances, allowing for the efficient movement of crowds in and out of the amphitheatre.
The Underground Network: Beneath the arena floor lay a complex network of tunnels and chambers, known as the "hypogeum." This underground system was used for various purposes:
- Animal Holding: The hypogeum housed cages for wild animals used in gladiatorial combats and public spectacles.
- Gladiator Preparation: Gladiators prepared for their battles in the hypogeum, awaiting their cues to enter the arena.
- Stage Machinery: The hypogeum housed elaborate mechanisms for raising and lowering props, animals, and even entire sets for theatrical performances.
The Colosseum: More Than Just a Gladiator Arena
While the Colosseum is often associated with gladiatorial combat, its purpose extended far beyond bloodsport. The Colosseum served as a multifaceted entertainment venue, hosting a variety of events:
- Gladiatorial Combat: Gladiatorial combat was a central attraction at the Colosseum, drawing massive crowds to witness the spectacle of fighting. These battles were not merely entertainment; they served as a form of public spectacle, showcasing Roman power and military prowess.
- Wild Animal Hunts: The Colosseum hosted elaborate hunts featuring exotic animals brought from across the Roman Empire. These hunts were a testament to the Roman Empire’s vast reach and its ability to control and display its power through exotic animals.
- Naumachiae: The Colosseum occasionally hosted mock naval battles, known as naumachiae. These spectacles involved flooding the arena with water and staging battles between ships. These events were a testament to Roman ingenuity and their ability to recreate naval warfare on land.
- Theatrical Performances: The Colosseum hosted theatrical performances, including plays, dances, and musical acts. These performances were a testament to Roman culture and its appreciation for the arts.
The Colosseum’s Legacy
The Colosseum stands as a testament to the Roman Empire’s power and its fascination with spectacle. Its impressive architecture, intricate design, and the diverse events it hosted have captivated audiences for centuries. The Colosseum’s legacy extends beyond its physical presence; it has become a symbol of Roman power, culture, and entertainment.
FAQs about the Colosseum Map
1. What is the best way to explore the Colosseum?
The best way to explore the Colosseum is to take a guided tour. Guided tours provide valuable insights into the Colosseum’s history, architecture, and significance. They also offer access to areas of the Colosseum that are not typically open to the public.
2. What are the best times to visit the Colosseum?
The best time to visit the Colosseum is early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the crowds. Summer months can be particularly crowded, so it is advisable to plan your visit during the shoulder seasons or early mornings.
3. Are there any restrictions on photography inside the Colosseum?
Photography is permitted inside the Colosseum, but there are some restrictions. Tripods are generally not allowed, and flash photography is prohibited. It is always best to check with the official website or visitor information center for the most up-to-date regulations.
4. How long does it take to explore the Colosseum?
A typical visit to the Colosseum takes about 1-2 hours, depending on your level of interest and the time spent exploring different areas. Allowing more time will give you the opportunity to fully appreciate the Colosseum’s grandeur and history.
5. Is the Colosseum accessible to people with disabilities?
The Colosseum is accessible to people with disabilities, with ramps and elevators available for access to different levels. However, some areas may be difficult to navigate, so it is advisable to check with the visitor information center for specific details.
Tips for Visiting the Colosseum
- Book your tickets in advance: The Colosseum is a popular tourist destination, and tickets often sell out quickly. Booking your tickets online in advance will ensure your entry and save you time at the entrance.
- Wear comfortable shoes: The Colosseum is a large site, and you will be doing a lot of walking. Comfortable shoes are essential for a pleasant experience.
- Bring water and snacks: There are limited food and drink options available inside the Colosseum, so it is advisable to bring your own water and snacks.
- Be prepared for crowds: The Colosseum can get crowded, especially during peak season. Be patient and allow ample time for exploring the site.
- Take a guided tour: A guided tour will provide valuable insights into the Colosseum’s history, architecture, and significance. They also offer access to areas of the Colosseum that are not typically open to the public.
Conclusion
The Colosseum stands as a testament to Roman ingenuity and grandeur, offering a glimpse into the past and the lives of those who once inhabited this magnificent structure. Its intricate design, diverse events, and enduring legacy continue to captivate audiences centuries later. A visit to the Colosseum is a journey through time, a reminder of the power and magnificence of the Roman Empire.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Colosseum: A Map Through Time and History. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!