Navigating the World’s Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Global Food Map
Related Articles: Navigating the World’s Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Global Food Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World’s Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Global Food Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World’s Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Global Food Map
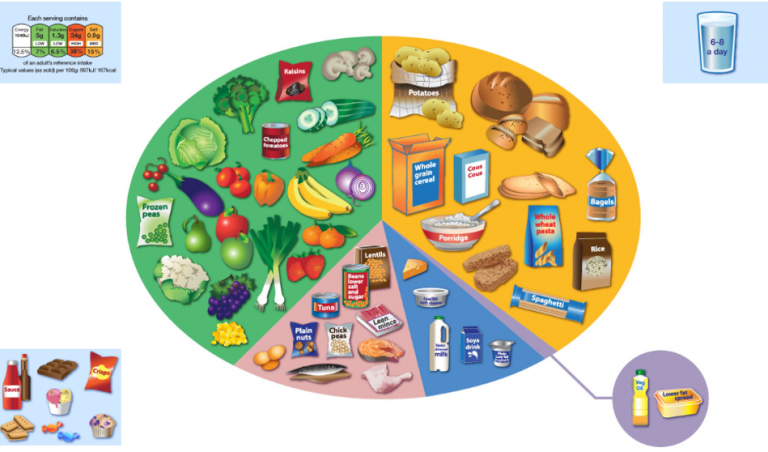

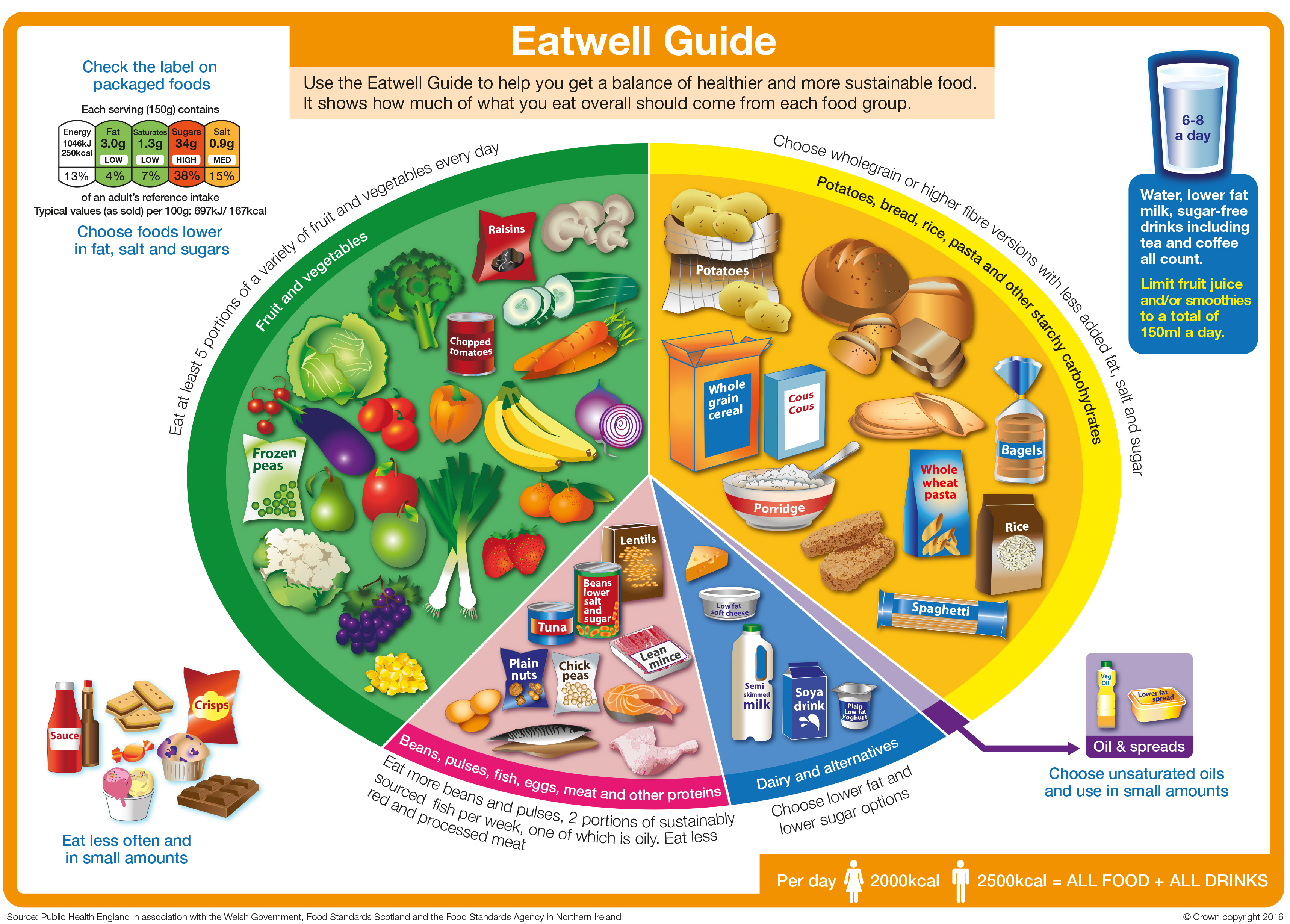
The world’s food system is a complex tapestry woven from diverse agricultural practices, culinary traditions, and economic realities. Understanding this intricate network is crucial for addressing global food security, promoting sustainable agriculture, and fostering cultural appreciation. A global food map provides a visual representation of this intricate system, offering insights into the production, consumption, and trade of food across the globe.
Understanding the World Food Map: A Visual Representation of Global Food Flows
A global food map is not merely a static image but a dynamic representation of interconnected food systems. It showcases:
- Production Zones: Identifying regions specializing in specific crops or livestock, highlighting geographical advantages in climate, soil, and water resources.
- Trade Routes: Illustrating the movement of food products across borders, revealing patterns of global trade and dependence.
- Consumption Patterns: Revealing the dietary habits of different populations, showcasing regional variations in food consumption and cultural preferences.
- Food Security Challenges: Highlighting areas experiencing food shortages, malnutrition, or vulnerability to food price fluctuations.
- Environmental Impacts: Demonstrating the environmental consequences of food production, such as deforestation, water depletion, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Beyond the Map: Delving Deeper into the Global Food System
The global food map serves as a starting point for exploring the multifaceted nature of food production and consumption. It prompts further investigation into:
- Agricultural Practices: Examining the techniques employed in different regions, from traditional subsistence farming to large-scale industrial agriculture.
- Food Processing and Distribution: Understanding the complex chain of processes involved in transforming raw ingredients into consumable products and delivering them to consumers.
- Food Policy and Regulation: Investigating the role of governments and international organizations in shaping food production, trade, and access.
- Food Waste and Sustainability: Examining the environmental and social impacts of food waste and exploring solutions for reducing waste throughout the food supply chain.
- Cultural and Social Dimensions: Recognizing the cultural significance of food, its role in social gatherings, and its impact on health and well-being.
The Importance of the Global Food Map: A Tool for Informed Decision-Making
The global food map serves as a valuable tool for various stakeholders:
- Governments: Providing insights into national food security, trade policies, and agricultural development strategies.
- International Organizations: Informing initiatives aimed at addressing food insecurity, promoting sustainable agriculture, and improving global food systems.
- Businesses: Guiding investment decisions, supply chain optimization, and market analysis.
- Consumers: Raising awareness about the origins of their food, promoting responsible consumption, and fostering appreciation for diverse culinary traditions.
- Researchers and Academics: Providing data for studies on food security, nutrition, and environmental sustainability.
FAQs about the World Food Map
1. What are the main challenges facing the global food system?
The global food system faces numerous challenges, including:
- Food Insecurity: Millions worldwide lack access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food.
- Climate Change: Climate variability and extreme weather events disrupt food production and increase food prices.
- Population Growth: Rising population demands increased food production, placing pressure on resources.
- Water Scarcity: Competition for water resources between agriculture, industry, and urban centers.
- Land Degradation: Soil erosion, salinization, and deforestation threaten agricultural productivity.
- Food Waste: Significant amounts of food are wasted throughout the supply chain, contributing to environmental damage and economic losses.
2. How can the global food map contribute to solving these challenges?
The global food map can contribute to addressing these challenges by:
- Identifying Areas of Vulnerability: Highlighting regions at risk of food insecurity, facilitating targeted interventions.
- Promoting Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Encouraging the adoption of environmentally friendly farming methods to protect natural resources.
- Optimizing Food Distribution: Improving food distribution systems to ensure equitable access to food.
- Reducing Food Waste: Raising awareness about food waste and promoting strategies for reducing waste at all levels.
3. What are some key trends shaping the future of the global food system?
Several trends are shaping the future of the global food system, including:
- Urbanization: Growing urban populations require efficient and sustainable food supply chains.
- Technological Advancements: Precision agriculture, biotechnology, and digital technologies are transforming food production and distribution.
- Consumer Demand for Healthy and Sustainable Food: Consumers are increasingly demanding food that is healthy, ethically produced, and environmentally sustainable.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The need for resilient food systems that can adapt to climate change impacts.
Tips for Using the Global Food Map
- Explore Different Data Sources: Compare data from various sources to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Consider Geographic and Temporal Scales: Analyze the map at different scales, from local to global, and across different time periods.
- Analyze Trends and Patterns: Identify trends in food production, consumption, and trade to understand the dynamics of the global food system.
- Engage in Critical Thinking: Question the assumptions and biases embedded in the data presented.
- Collaborate with Others: Share insights and engage in discussions with other stakeholders to develop solutions to global food challenges.
Conclusion: A Call for Collaboration and Innovation
The global food map is a valuable tool for understanding the complexities of the world’s food system. It highlights both the opportunities and challenges in ensuring food security, promoting sustainable agriculture, and fostering cultural appreciation. By utilizing the insights gained from this visual representation, stakeholders can collaborate and innovate to create a more equitable, sustainable, and resilient global food system.



![[PDF] Activity—World Map of Plate Boundaries](https://pdfprof.com/EN_PDFV2/Docs/PDF_9/256652_97_world_map_of_plate_boundaries.pdf.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World’s Plate: A Comprehensive Guide to the Global Food Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!