Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications
Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of GPS Tracking
- 3.2 The Evolution of GPS Tracking
- 3.3 Diverse Applications of GPS Tracking
- 3.4 Advantages of GPS Tracking
- 3.5 Challenges and Considerations in GPS Tracking
- 3.6 FAQs About GPS Tracking
- 3.7 Tips for Using GPS Tracking Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications

The modern world is interconnected by a vast network of information, and at the heart of this network lies the Global Positioning System (GPS). This technology, often taken for granted, plays a crucial role in our daily lives, guiding us through unfamiliar streets, helping us find our way back home, and even enabling us to track the movement of objects across continents. This article delves into the world of GPS tracking, exploring its underlying principles, diverse applications, and the impact it has on various industries and aspects of our lives.
Understanding the Fundamentals of GPS Tracking
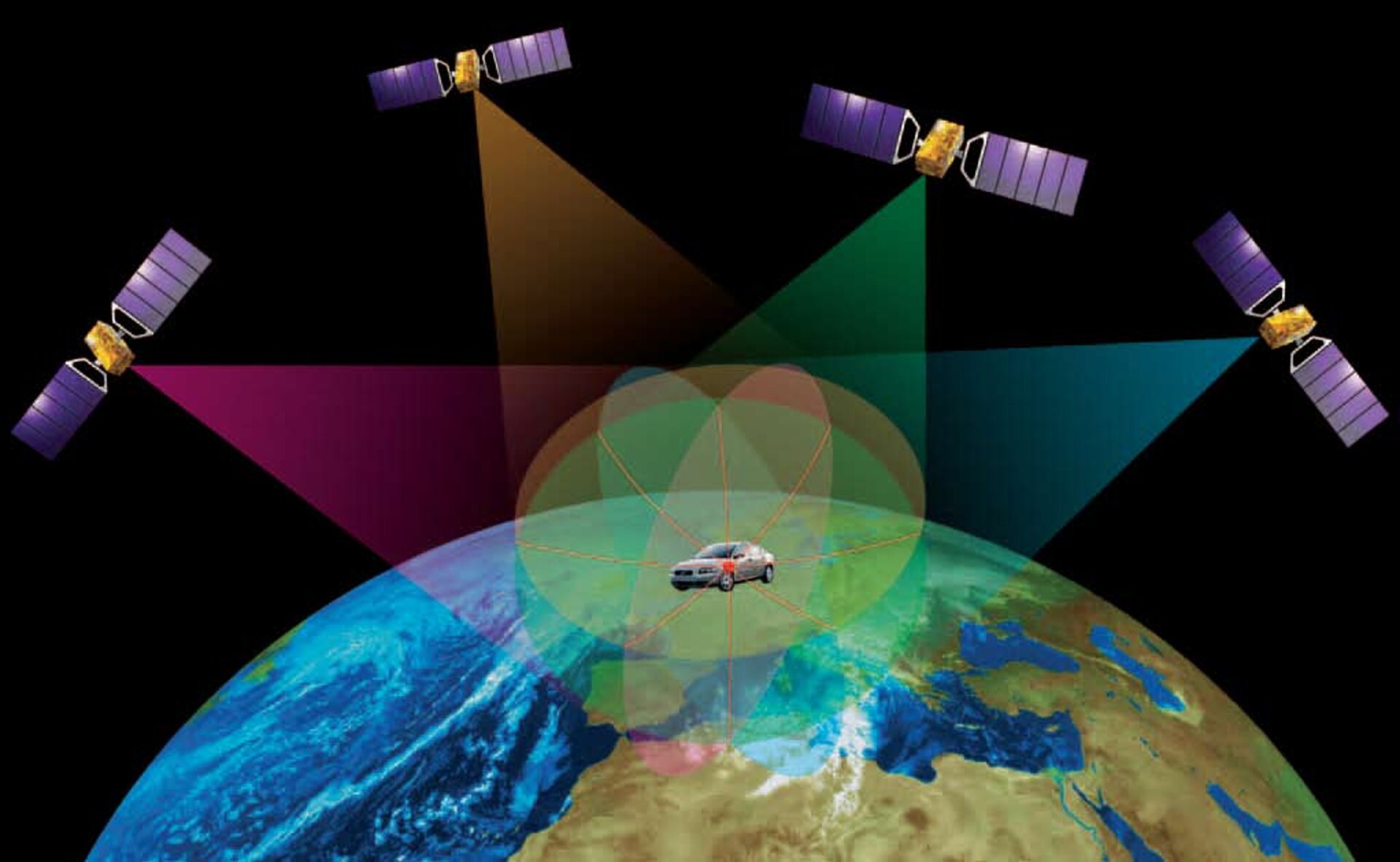
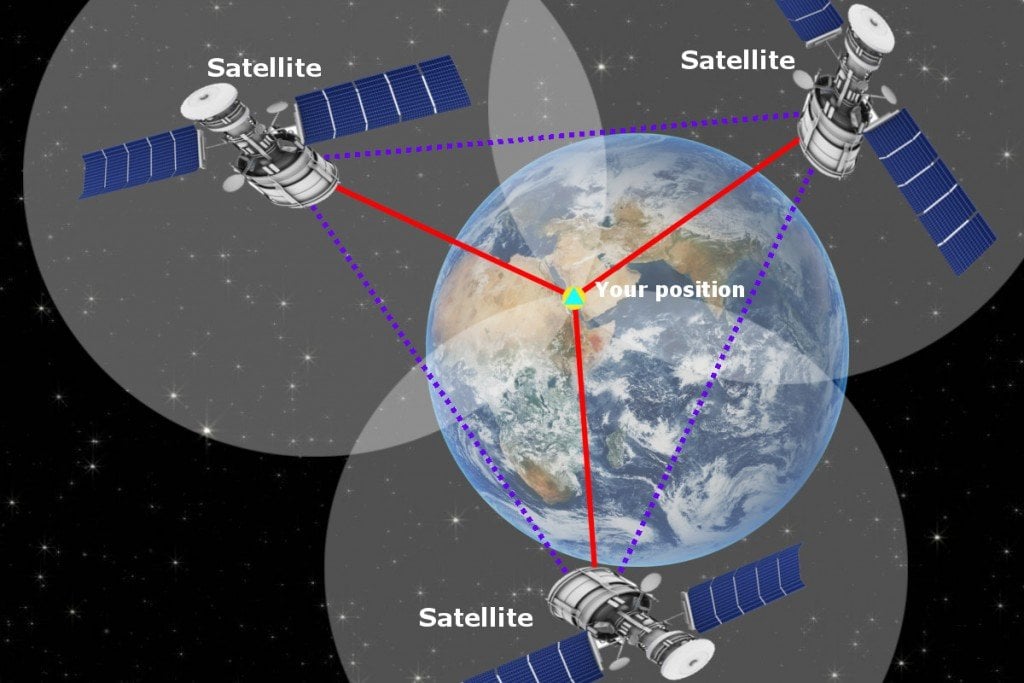
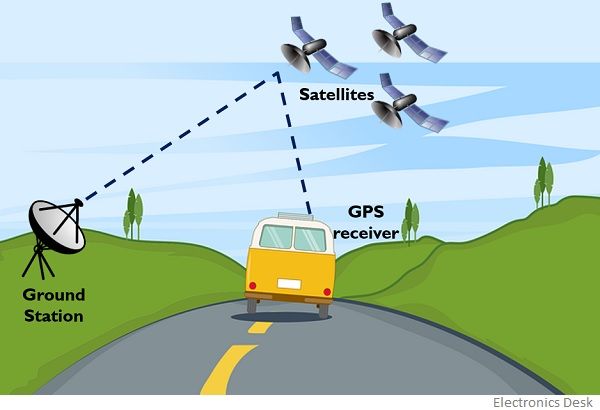
GPS tracking relies on a network of satellites orbiting Earth, continuously transmitting radio signals. These signals contain precise time information, allowing receivers on Earth to calculate their position. The principle is based on trilateration, where the receiver measures the time it takes for signals from at least four satellites to reach it. Using this information, the receiver calculates its distance from each satellite and, consequently, its precise location on Earth.
GPS tracking systems consist of three main components:
- Satellites: The constellation of satellites orbiting Earth, constantly transmitting radio signals.
- Receivers: Devices that receive signals from satellites and calculate the user’s location.
- Control Segment: A network of ground stations that monitor and maintain the satellite constellation.
The Evolution of GPS Tracking
GPS technology has undergone significant advancements since its inception. Early GPS receivers were bulky and expensive, primarily used for military purposes. However, with technological progress, these devices have become smaller, more affordable, and accessible to the general public. The introduction of smartphones equipped with built-in GPS receivers has revolutionized the way we navigate, making real-time location tracking a ubiquitous feature in our daily lives.
Diverse Applications of GPS Tracking
GPS tracking has transcended its initial role in navigation, finding applications in a wide range of fields, including:
1. Transportation and Logistics:
- Fleet Management: GPS tracking systems allow businesses to monitor their vehicles in real-time, optimizing routes, reducing fuel consumption, and improving overall efficiency.
- Asset Tracking: Businesses can track valuable assets like containers, equipment, and even livestock, ensuring their safety and security.
- Delivery Optimization: GPS tracking helps optimize delivery routes, improve delivery times, and enhance customer satisfaction.
2. Personal Safety and Security:
- Personal Tracking Devices: GPS trackers can be used to monitor the location of children, elderly individuals, and pets, providing peace of mind and ensuring their safety.
- Emergency Response: GPS tracking enables quick and accurate location identification in emergency situations, facilitating faster response times and saving lives.
3. Sports and Recreation:
- Fitness Tracking: GPS devices are used to track distance, speed, and elevation gain during activities like running, cycling, and hiking, providing valuable insights for fitness improvement.
- Navigation and Exploration: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on GPS devices to navigate challenging terrain, ensuring they stay on track and find their way back safely.
4. Agriculture and Farming:
- Precision Farming: GPS tracking helps farmers optimize fertilizer and pesticide application, reducing waste and improving crop yield.
- Livestock Management: GPS tracking allows farmers to monitor the location and health of livestock, ensuring their safety and maximizing productivity.
5. Environmental Monitoring and Research:
- Wildlife Tracking: GPS collars are used to track the movement and behavior of wild animals, providing valuable data for conservation efforts.
- Environmental Studies: GPS tracking helps researchers study the impact of climate change, deforestation, and other environmental factors on ecosystems.
Advantages of GPS Tracking
The widespread adoption of GPS tracking is driven by its numerous advantages:
- Real-time Location Information: GPS tracking provides precise and up-to-date location information, enabling users to monitor movement and make informed decisions.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: GPS tracking optimizes routes, improves time management, and enhances overall efficiency in various sectors.
- Enhanced Safety and Security: GPS tracking provides peace of mind by enabling location monitoring and facilitating faster response times in emergencies.
- Cost Savings: GPS tracking can reduce fuel consumption, optimize resource allocation, and minimize operational costs.
- Data Collection and Analysis: GPS tracking generates valuable data that can be analyzed to improve decision-making, optimize processes, and gain insights into various aspects of operations.
Challenges and Considerations in GPS Tracking
While GPS tracking offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges and ethical considerations:
- Privacy Concerns: The constant tracking of individuals’ location raises concerns about privacy violations and the potential for misuse of this information.
- Accuracy and Reliability: GPS signals can be affected by factors like weather, terrain, and interference, leading to inaccuracies in location data.
- Security Risks: GPS tracking devices can be hacked or compromised, potentially leading to unauthorized access and misuse of location information.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks: The use of GPS tracking is subject to various legal and regulatory frameworks, which vary depending on the jurisdiction.
FAQs About GPS Tracking
1. What is the difference between GPS and GNSS?
GPS refers specifically to the US-developed satellite navigation system. GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) is a broader term encompassing all satellite navigation systems, including GPS, GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (Europe), and BeiDou (China).
2. How accurate is GPS tracking?
GPS accuracy can vary depending on factors like satellite visibility, atmospheric conditions, and the quality of the GPS receiver. In ideal conditions, GPS accuracy can be within a few meters, while in challenging environments, it may be less precise.
3. Can GPS tracking be used indoors?
GPS signals have limited penetration through walls and other obstructions. Indoor tracking often relies on other technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks to provide location information.
4. Is GPS tracking legal?
The legality of GPS tracking depends on the specific context and jurisdiction. It is generally legal to track vehicles and assets owned by a business, but tracking individuals without their consent may be illegal in many countries.
5. What are the ethical considerations of GPS tracking?
Ethical concerns surrounding GPS tracking include privacy violations, potential misuse of location data, and the need for informed consent before tracking individuals.
Tips for Using GPS Tracking Effectively
- Choose a reputable provider: Select a GPS tracking service with a proven track record, strong security measures, and reliable customer support.
- Understand the terms and conditions: Carefully review the terms of service and privacy policy of the GPS tracking provider before signing up.
- Ensure proper installation and configuration: Properly install and configure the GPS tracking device to ensure optimal performance and accuracy.
- Monitor and analyze data regularly: Regularly review the data generated by the GPS tracking system to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement.
- Respect privacy and confidentiality: Use GPS tracking responsibly and ethically, respecting the privacy rights of individuals.
Conclusion
GPS tracking has become an indispensable tool in various aspects of our lives, enabling us to navigate, track assets, monitor movement, and enhance safety and security. While the technology offers numerous benefits, it is essential to be aware of its potential challenges and ethical considerations. By using GPS tracking responsibly and ethically, we can harness its power to improve efficiency, enhance safety, and drive progress in various fields.



![]()
![]()
![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: A Comprehensive Guide to GPS Tracking and Its Applications. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!