Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa
Related Articles: Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa
- 3.1 A Journey Through the Waterways: Key Rivers of Africa
- 3.2 Reflecting the Landscape: Key Lakes of Africa
- 3.3 The Intertwined Relationship: Rivers and Lakes in Africa
- 3.4 Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of Africa’s Waterways
- 3.5 FAQs: Understanding Africa’s Rivers and Lakes
- 3.6 Tips for Navigating Africa’s Waterways
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Call for Action
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa
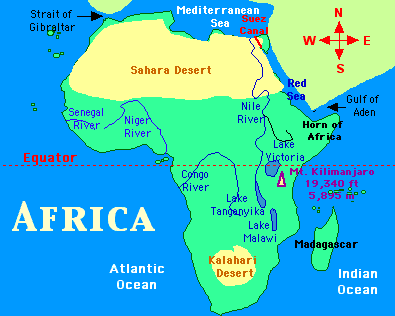
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a rich tapestry of geographical features, including an extensive network of rivers and lakes. These bodies of water play a vital role in the continent’s ecosystem, supporting diverse flora and fauna, sustaining human populations, and shaping the cultural landscape. Understanding the intricate web of rivers and lakes in Africa is crucial for appreciating its ecological significance, navigating its challenges, and fostering sustainable development.
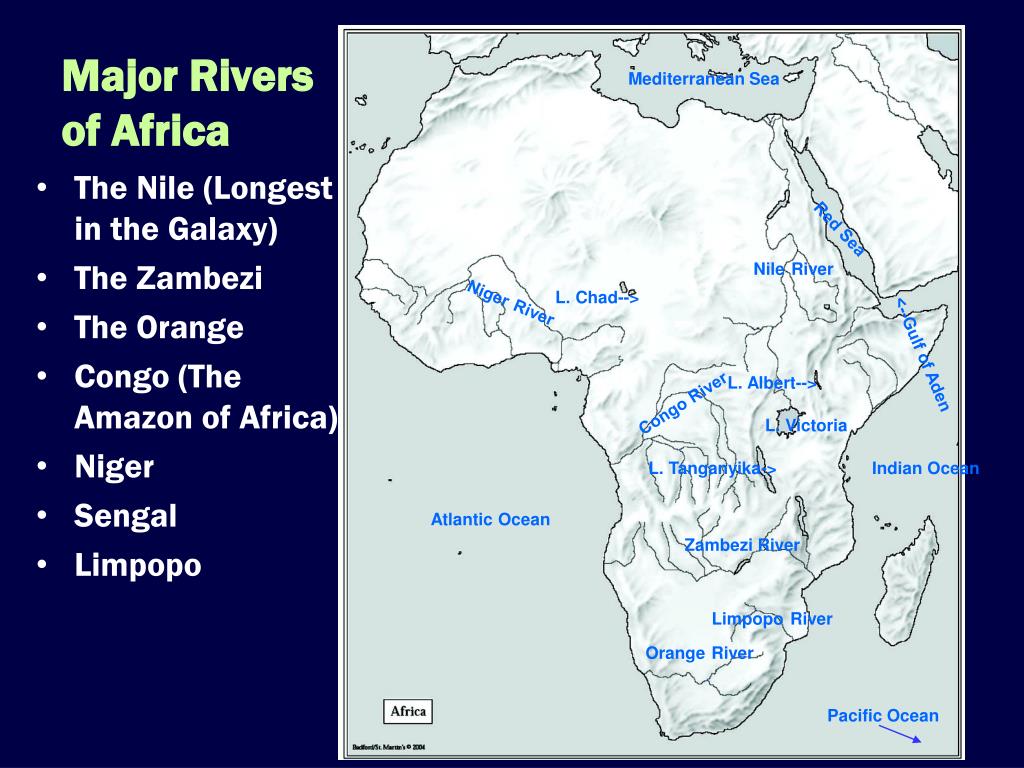
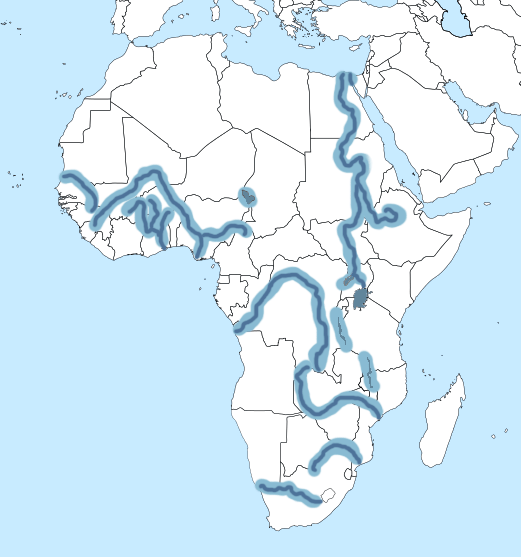
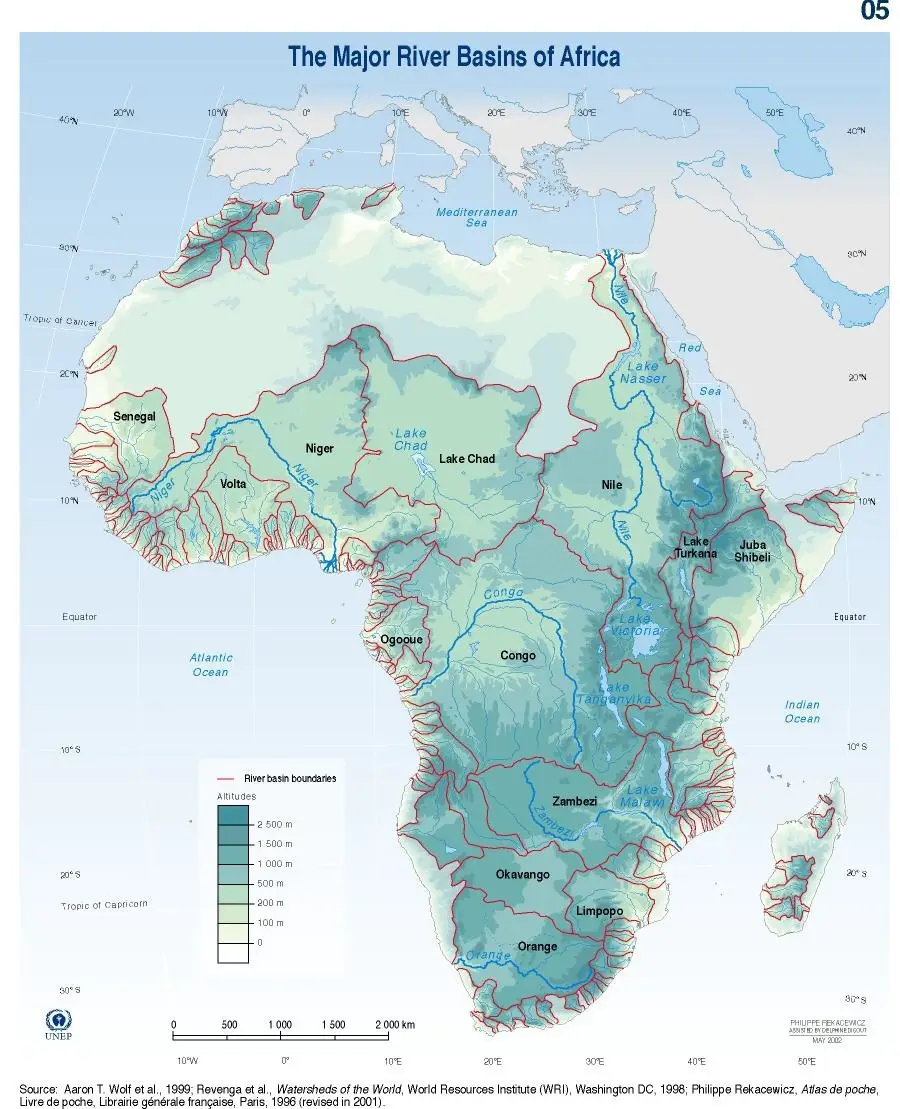
A Journey Through the Waterways: Key Rivers of Africa
The continent’s rivers are diverse, ranging from mighty, meandering giants to smaller, ephemeral streams. Each river holds unique characteristics, influenced by the surrounding terrain, climate, and human activity.
1. The Nile: A River of Legends
The Nile, the longest river in the world, is a defining feature of Africa. It flows northwards from its headwaters in the East African highlands, traversing eleven countries before emptying into the Mediterranean Sea. Its fertile basin cradles ancient civilizations, from the pharaohs of Egypt to the Nubian kingdoms. The Nile’s significance extends beyond its historical importance; it provides water for irrigation, drinking, and transportation, sustaining a vast population.
2. The Congo: A River of Depth
The Congo River, the second-largest river in Africa by volume, is a powerful force in Central Africa. It flows through dense rainforests, creating a unique ecosystem and contributing to the continent’s biodiversity. The Congo River’s vast basin is home to diverse indigenous communities, relying on its resources for sustenance and livelihood.
3. The Niger: A River of Life
The Niger River, the third-longest in Africa, flows through the Sahel region, providing a lifeline for millions. Its fertile valley supports agriculture, while its tributaries sustain diverse ecosystems. The Niger River is crucial for transportation, connecting communities and facilitating trade across West Africa.
4. The Zambezi: A River of Power
The Zambezi River, known for its dramatic waterfalls at Victoria Falls, flows through Southern Africa. Its basin encompasses a diverse range of ecosystems, from savannas to forests. The Zambezi River is crucial for hydroelectric power generation, supporting economic development in the region.
5. The Orange: A River of Boundaries
The Orange River, flowing along the border between South Africa and Namibia, is a significant water source for the region. Its course is marked by dramatic canyons and desert landscapes. The Orange River plays a vital role in irrigation, water supply, and tourism.
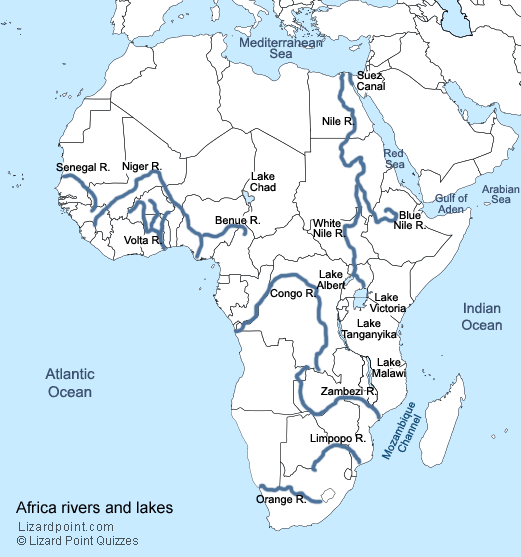
Reflecting the Landscape: Key Lakes of Africa
Africa’s lakes are equally diverse, ranging from vast, freshwater reservoirs to smaller, saline lakes. These bodies of water provide essential resources, contribute to regional climates, and support unique biodiversity.
1. Lake Victoria: A Lake of Abundance
Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa and the second-largest freshwater lake in the world, is a vital resource for East Africa. It provides water for irrigation, drinking, and fishing, sustaining millions of people. Lake Victoria is also a crucial habitat for diverse fish species and supports a thriving fishing industry.
2. Lake Tanganyika: A Lake of Depth
Lake Tanganyika, the second-largest lake in Africa by volume, is a haven of biodiversity. It is home to over 2,000 fish species, many endemic to the lake. Lake Tanganyika plays a crucial role in regulating the regional climate and supports a diverse range of wildlife.
3. Lake Malawi: A Lake of Color
Lake Malawi, known for its vibrant cichlid fish population, is a unique ecosystem in Southern Africa. Its clear waters and diverse fish species attract tourists and scientists alike. Lake Malawi is an important source of protein for local communities and supports a growing tourism industry.
4. Lake Chad: A Lake of Change
Lake Chad, located in the Sahel region, has been shrinking in recent decades due to climate change and overexploitation. Its shrinking size poses a significant threat to the livelihoods of millions who depend on its resources. Lake Chad’s fate highlights the challenges facing Africa’s water resources.
5. Lake Turkana: A Lake of Salt
Lake Turkana, the largest desert lake in the world, is a unique ecosystem in East Africa. Its saline waters support a diverse range of wildlife, including crocodiles, hippos, and numerous bird species. Lake Turkana is an important source of salt and attracts tourists seeking to witness its unique landscape.
The Intertwined Relationship: Rivers and Lakes in Africa
The rivers and lakes of Africa are interconnected, forming a complex web of life. Rivers flow into lakes, contributing to their water levels and influencing their ecosystems. Lakes, in turn, can regulate river flows and contribute to regional rainfall patterns.
1. Nutrient Cycling and Biodiversity: Rivers transport nutrients from upstream sources to lakes, enriching their ecosystems and supporting diverse aquatic life. These nutrients also nourish surrounding lands, promoting plant growth and supporting terrestrial biodiversity.
2. Climate Regulation and Precipitation: Lakes act as heat sinks, moderating regional temperatures and influencing rainfall patterns. Their evaporation contributes to humidity, creating a microclimate that supports surrounding ecosystems.
3. Transportation and Trade: Rivers and lakes have historically served as vital transportation routes, connecting communities and facilitating trade. They continue to play a role in transportation, particularly in remote areas, facilitating the movement of goods and people.
4. Water Supply and Irrigation: Rivers and lakes are crucial sources of water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use. Their water resources support agriculture, sustain human populations, and contribute to economic development.
Challenges and Opportunities: The Future of Africa’s Waterways
Africa’s rivers and lakes face numerous challenges, including pollution, overexploitation, climate change, and conflicts over water resources. These challenges threaten the livelihoods of millions, disrupt ecosystems, and hinder sustainable development.
1. Pollution and Degradation: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage disposal contribute to water pollution, degrading water quality and harming aquatic life. Pollution also poses health risks to human populations relying on these water resources.
2. Overexploitation and Water Scarcity: Increasing populations and economic development place growing pressure on water resources. Overexploitation of rivers and lakes can lead to water scarcity, affecting agriculture, drinking water supply, and ecosystems.
3. Climate Change and Variability: Climate change is altering rainfall patterns, leading to increased droughts and floods. These changes impact water availability, affecting agriculture, livelihoods, and ecosystems.
4. Conflicts Over Water Resources: Competition for water resources can lead to conflicts between communities, nations, and sectors. These conflicts can disrupt peace and stability, hindering development and undermining cooperation.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for sustainable management of Africa’s water resources.
1. Integrated Water Resource Management: Implementing integrated water resource management plans can ensure equitable distribution, efficient use, and sustainable management of water resources.
2. Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Promoting sustainable agricultural practices, such as rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation, can reduce water consumption and minimize pollution.
3. Water Conservation and Efficiency: Implementing water conservation measures in homes, industries, and agriculture can reduce water consumption and alleviate pressure on water resources.
4. Regional Cooperation and Collaboration: Fostering regional cooperation and collaboration on water resource management can promote equitable sharing, minimize conflicts, and facilitate sustainable development.
FAQs: Understanding Africa’s Rivers and Lakes
1. What is the longest river in Africa?
The Nile River is the longest river in Africa, stretching over 6,650 kilometers (4,132 miles).
2. Which lake is the largest in Africa?
Lake Victoria is the largest lake in Africa, covering an area of 68,800 square kilometers (26,564 square miles).
3. What is the significance of the Congo River?
The Congo River is the second-largest river in Africa by volume and plays a vital role in Central Africa’s ecosystem, supporting biodiversity and providing transportation routes.
4. What are the main challenges facing Africa’s rivers and lakes?
Challenges include pollution, overexploitation, climate change, and conflicts over water resources.
5. How can Africa’s water resources be managed sustainably?
Sustainable management strategies include integrated water resource management, sustainable agriculture practices, water conservation, and regional cooperation.
Tips for Navigating Africa’s Waterways
1. Respect the Environment: Be mindful of your impact on the environment when visiting rivers and lakes. Avoid littering, polluting the water, and disturbing wildlife.
2. Support Sustainable Practices: Choose accommodations and tour operators that prioritize sustainable practices, such as water conservation and responsible tourism.
3. Learn about Local Communities: Engage with local communities and learn about their relationship with the waterways. Respect their traditions, customs, and dependence on these vital resources.
4. Advocate for Conservation: Support organizations working to conserve Africa’s rivers and lakes. Encourage responsible water management practices and advocate for policies that protect these vital resources.
5. Share Your Knowledge: Educate others about the importance of Africa’s waterways and the challenges they face. Encourage responsible behavior and support efforts to conserve these precious resources.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Africa’s rivers and lakes are not just geographical features; they are lifelines for millions of people, vital ecosystems, and a testament to the continent’s rich biodiversity. Understanding the intricate web of these waterways is essential for appreciating their significance, navigating their challenges, and fostering sustainable development. By embracing responsible practices, promoting collaboration, and advocating for conservation, we can ensure that Africa’s rivers and lakes continue to flow for generations to come, supporting life and shaping the future of the continent.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Lifeline: A Comprehensive Look at Rivers and Lakes in Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!