Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of North Dakota’s Indian Reservations
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of North Dakota’s Indian Reservations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of North Dakota’s Indian Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of North Dakota’s Indian Reservations
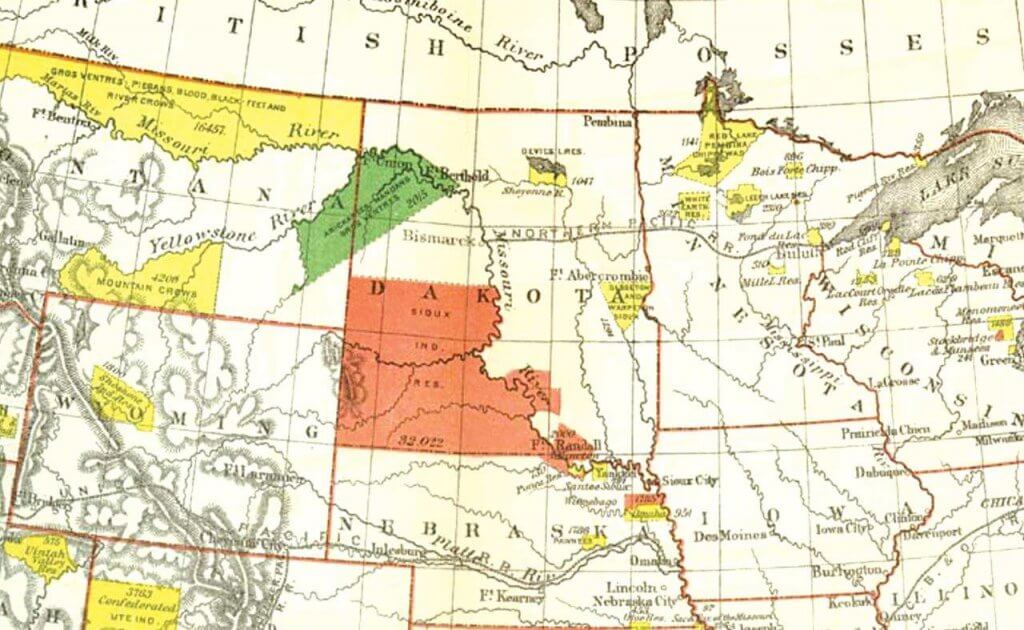
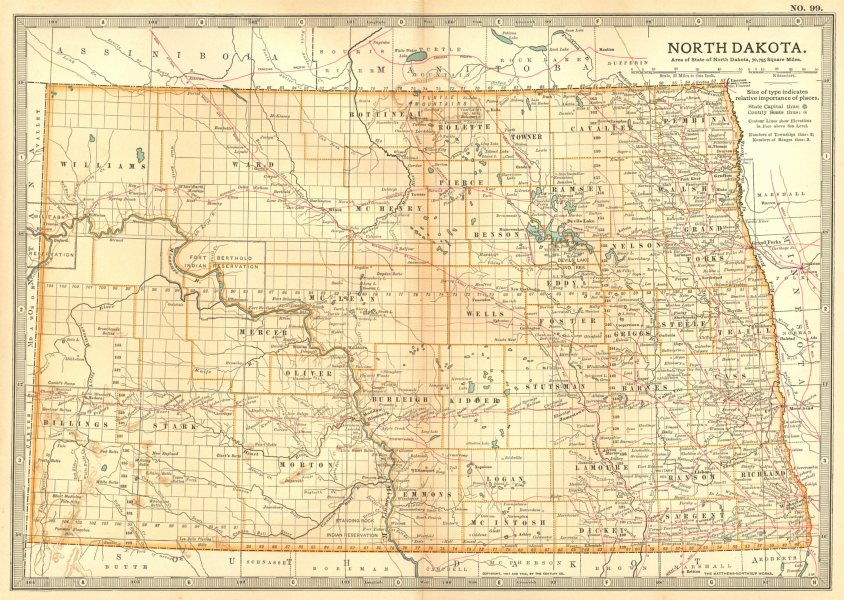
North Dakota, a state steeped in history and natural beauty, is also home to a significant Native American population. Within its borders lie seven federally recognized Indian reservations, each with its unique culture, traditions, and governance. Understanding the location and significance of these reservations is crucial for appreciating the rich tapestry of North Dakota’s history and present-day diversity.
A Geographical Overview
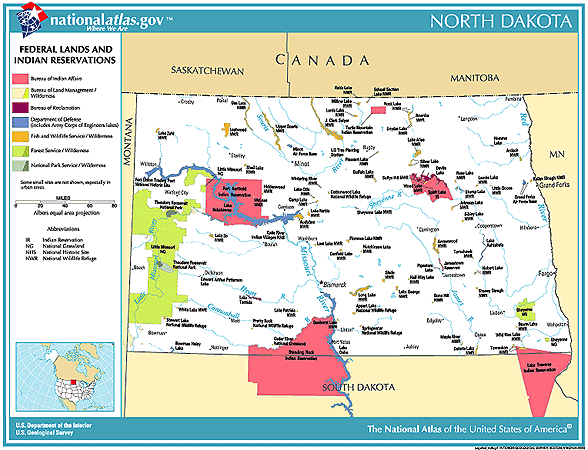
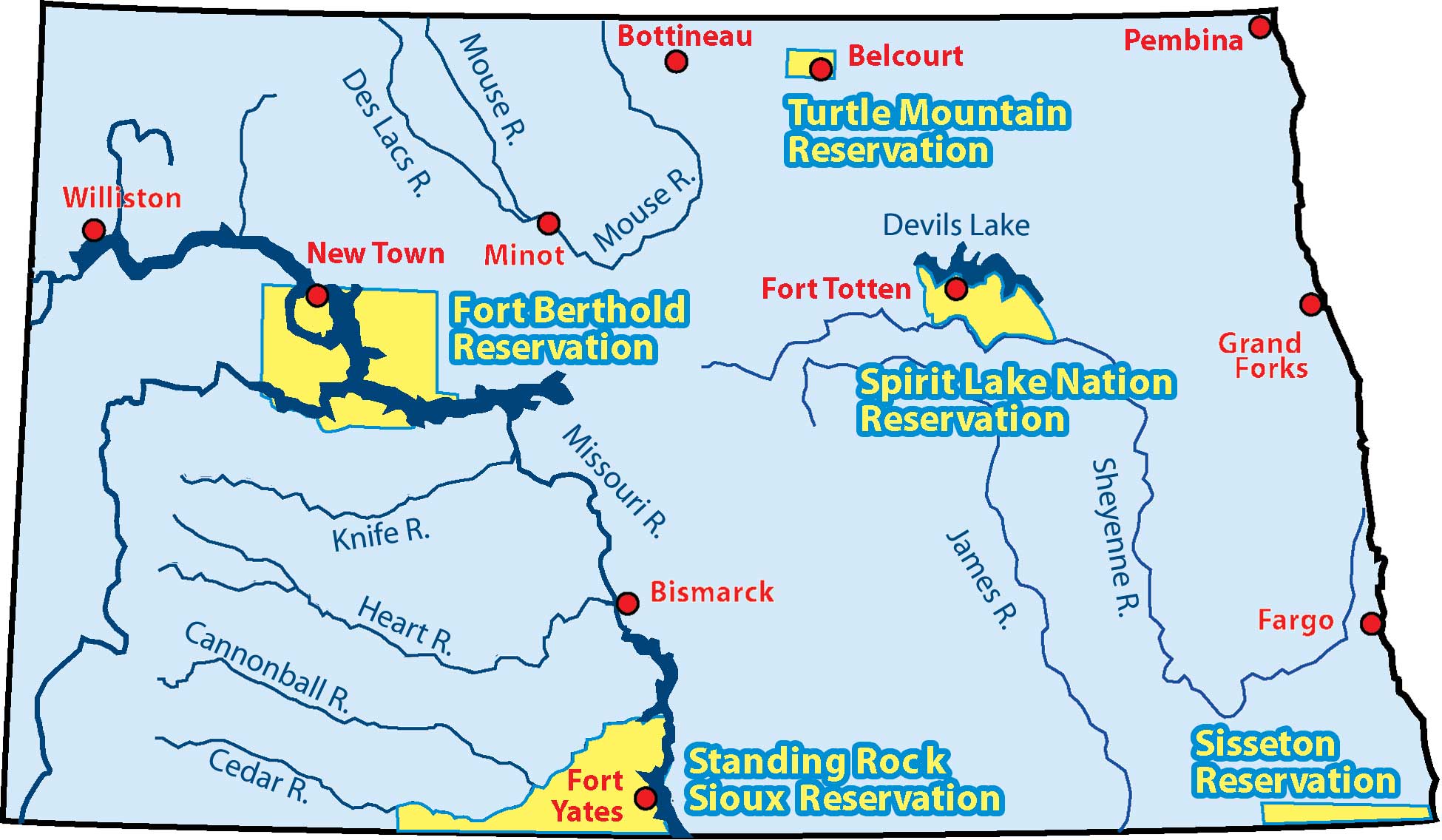
The seven reservations in North Dakota are:
- Fort Berthold Reservation: Located in the western part of the state, this reservation is home to the Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara (MHA) Nation. The reservation encompasses a vast area, including the Missouri River and Lake Sakakawea, a man-made lake created by the Garrison Dam.
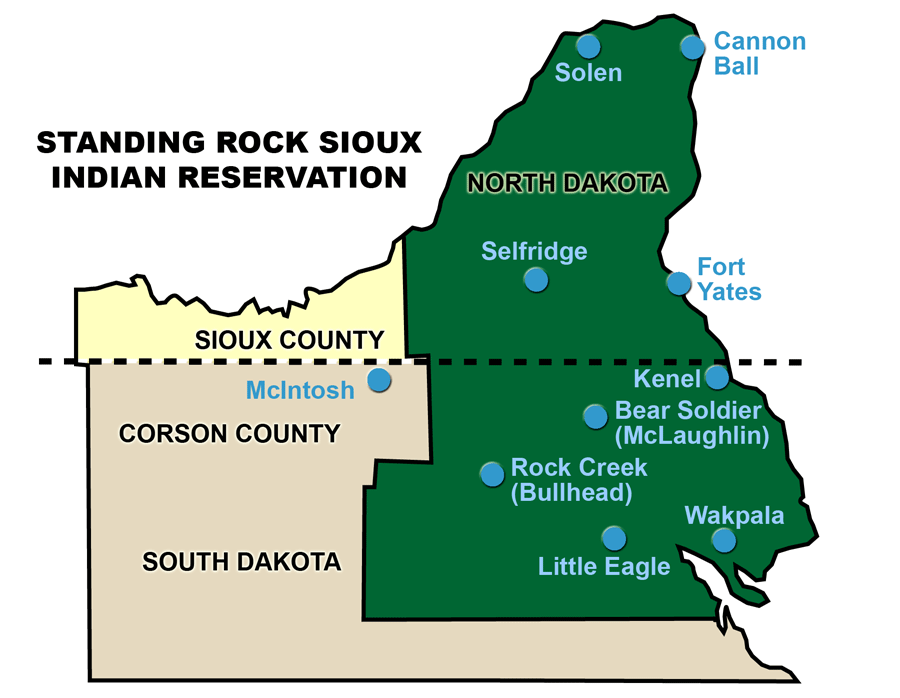
- Standing Rock Reservation: Situated along the Missouri River, this reservation is shared by the Sioux tribes of the Standing Rock Sioux Tribe. It is known for its historical significance, having been the site of the 1876 Battle of Little Bighorn.
- Turtle Mountain Reservation: Located in the northwestern corner of the state, this reservation is home to the Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians. The reservation is characterized by its rolling hills and numerous lakes.
- Spirit Lake Reservation: Located in the northeast corner of the state, this reservation is home to the Spirit Lake Tribe, also known as the Dakota Tribe. The reservation is known for its beautiful natural landscapes, including Devils Lake, the largest natural lake in North Dakota.
- Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate Reservation: This reservation is located in the eastern part of the state, extending into South Dakota. It is home to the Sisseton Wahpeton Oyate, a Dakota tribe.
- Fort Totten Reservation: Located in the northeastern part of the state, this reservation is home to the Devils Lake Sioux Tribe. It is known for its rich history and cultural heritage.
- Three Affiliated Tribes Reservation: This reservation encompasses the Fort Berthold Reservation, and its name reflects the three tribes that share it: Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Significance
These reservations are not simply geographical entities; they are vibrant communities with a rich history and a strong cultural identity. They represent the enduring spirit of Native American resilience and the ongoing struggle for self-determination.
Economic Development and Self-Governance:
The reservations play a crucial role in the economic development of North Dakota. They are home to numerous businesses, including casinos, hotels, and agricultural operations. They also play a vital role in promoting tourism, attracting visitors interested in experiencing Native American culture and history.
The reservations are also governed by tribal governments, which are sovereign entities recognized by the federal government. Tribal governments have the authority to regulate various aspects of life on the reservations, including law enforcement, education, and healthcare. This self-governance is essential for preserving tribal sovereignty and promoting cultural identity.
Cultural Preservation and Heritage:
The reservations are vital centers for preserving Native American culture and heritage. They host traditional ceremonies, powwows, and cultural events that connect younger generations to their ancestral traditions. They also house museums and cultural centers that showcase the rich history and art of Native American communities.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite their importance, North Dakota’s reservations face numerous challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and limited access to healthcare and education. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort between tribal governments, state and federal agencies, and private organizations.
FAQs
Q: What are the main economic activities on North Dakota’s reservations?
A: The economies of North Dakota’s reservations are diverse, encompassing various sectors such as:
- Gaming: Casinos are a significant source of revenue for many reservations.
- Agriculture: Farming and ranching remain crucial economic activities on many reservations.
- Tourism: Reservations offer unique cultural experiences that attract visitors.
- Energy: Some reservations have significant energy resources, such as oil and gas, which contribute to their economies.
- Government Services: Tribal governments provide a range of services to residents, creating employment opportunities.
Q: How are the reservations governed?
A: Each reservation has its own tribal government, which is a sovereign entity recognized by the federal government. These governments have the authority to regulate various aspects of life on the reservations, including:
- Law Enforcement: Tribal police enforce laws on the reservations.
- Education: Tribal governments operate schools on the reservations.
- Healthcare: Tribal governments provide healthcare services to residents.
- Natural Resources: Tribal governments manage natural resources on the reservations.
- Economic Development: Tribal governments promote economic development on the reservations.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by North Dakota’s reservations?
A: North Dakota’s reservations face several challenges, including:
- Poverty: Poverty rates are significantly higher on reservations than in the surrounding communities.
- Unemployment: Unemployment rates on reservations are often higher than the national average.
- Limited Access to Healthcare: Access to healthcare services is limited on many reservations.
- Education Disparities: Educational attainment levels are often lower on reservations.
- Substance Abuse: Substance abuse rates are high on some reservations.
Q: How can I learn more about North Dakota’s reservations?
A: There are many resources available to learn more about North Dakota’s reservations:
- Visit Tribal Websites: Each reservation has its own website with information about its history, culture, and governance.
- Attend Cultural Events: Reservations host powwows, ceremonies, and other cultural events throughout the year.
- Visit Museums and Cultural Centers: Reservations have museums and cultural centers that showcase their history and art.
- Read Books and Articles: There are many books and articles available about the history and culture of North Dakota’s reservations.
Tips for Visiting North Dakota’s Reservations:
- Respect Tribal Customs: Be respectful of tribal customs and traditions when visiting a reservation.
- Obtain Permission: Obtain permission from the tribal government before filming or photographing on a reservation.
- Support Local Businesses: Support local businesses and artisans on the reservations.
- Learn About the History: Take the time to learn about the history and culture of the reservation you are visiting.
Conclusion
North Dakota’s Indian reservations are integral to the state’s cultural and economic landscape. They represent the resilience and spirit of Native American communities, while also highlighting the challenges they face. By understanding the location, history, and significance of these reservations, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the rich diversity of North Dakota and the enduring legacy of its Native American people.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: An Exploration of North Dakota’s Indian Reservations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!