Navigating the Flames: Understanding Fire Weather Zones Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Flames: Understanding Fire Weather Zones Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Flames: Understanding Fire Weather Zones Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Flames: Understanding Fire Weather Zones Maps
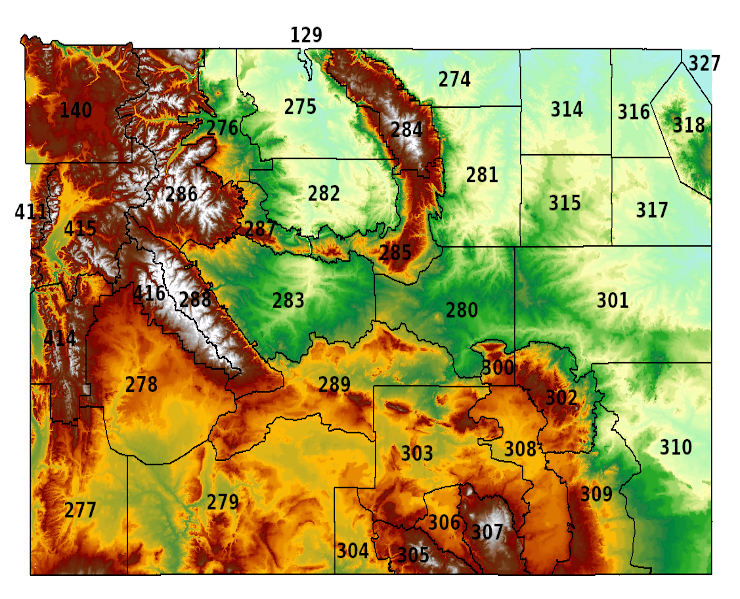
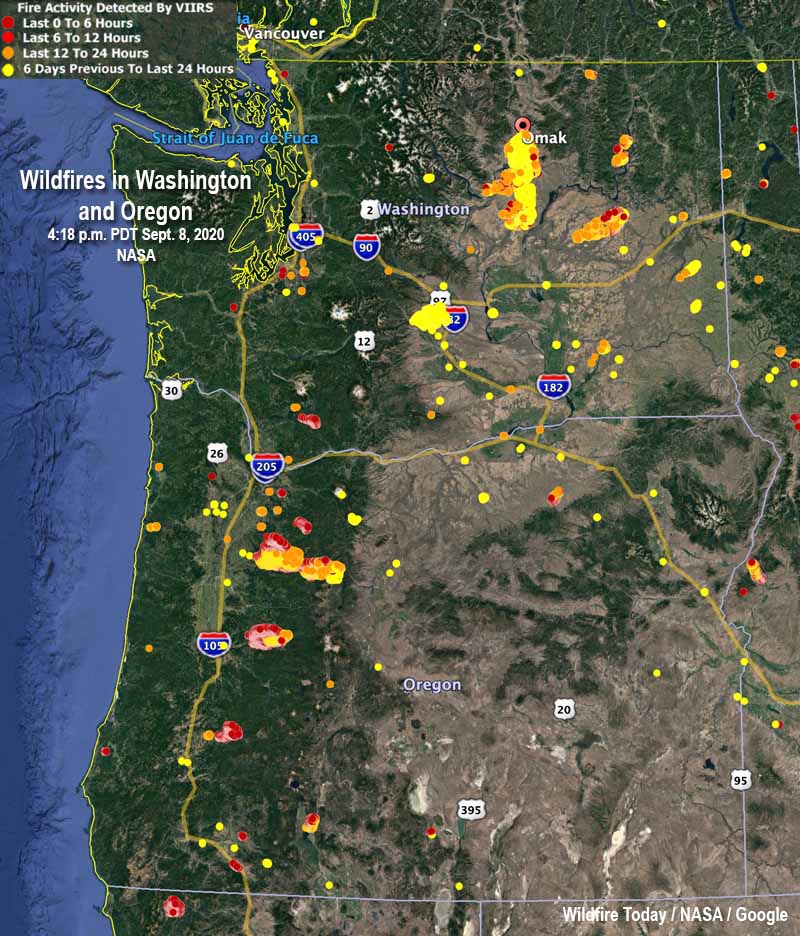
Wildfires, a devastating force of nature, pose a constant threat to communities and ecosystems worldwide. The unpredictable nature of these events necessitates proactive measures, and one vital tool in this fight is the fire weather zones map. These maps, often developed by meteorological agencies and fire management organizations, provide a crucial framework for understanding and predicting the risk of wildfire ignition and spread.
Decoding the Zones:
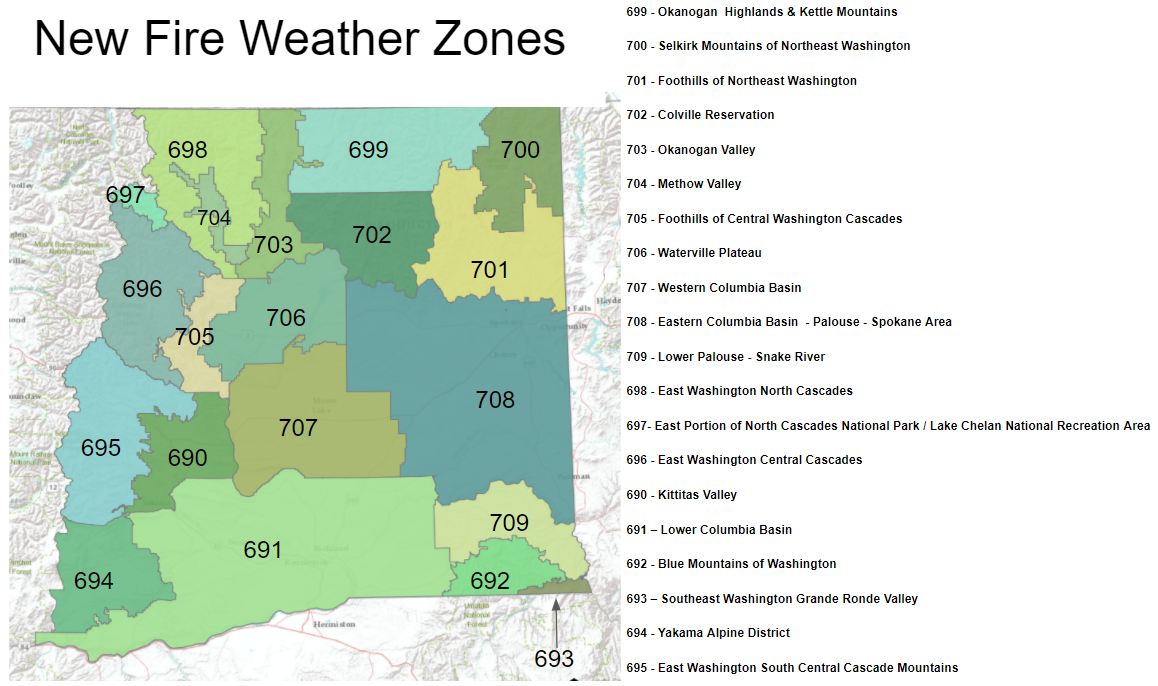
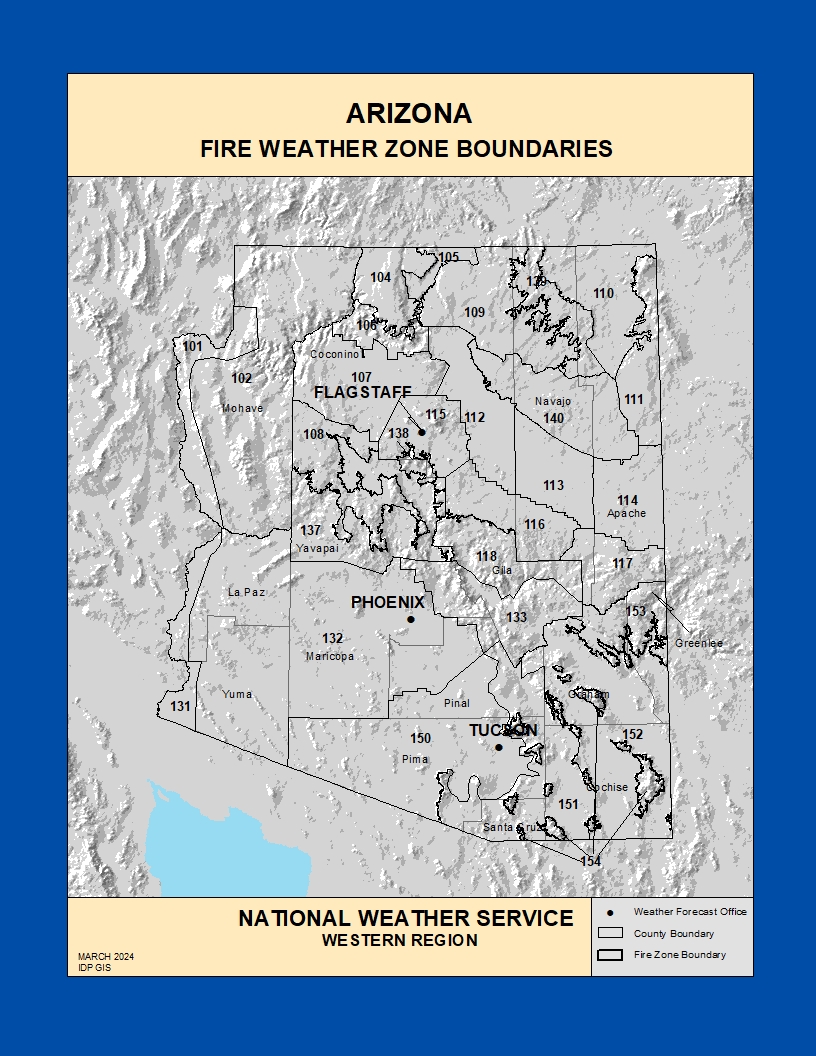
Fire weather zones maps typically divide a region into distinct zones, each characterized by specific weather conditions that influence fire behavior. These zones are not static, but rather dynamic, fluctuating with changes in weather patterns.
Key Elements of Fire Weather Zones Maps:
- Zone Boundaries: These boundaries are defined based on factors like topography, vegetation, and historical fire activity. They delineate areas with similar wildfire risks.
- Fire Danger Rating: Each zone is assigned a fire danger rating, typically using a standardized system like the Canadian Forest Fire Danger Rating System (CFFDRS). This rating, often represented by colors or numbers, indicates the potential for fire ignition and spread based on current weather conditions.
- Weather Parameters: Maps often incorporate data on key weather parameters like temperature, humidity, wind speed, and precipitation. These parameters directly influence the behavior of wildfires.
- Fuel Load and Type: The type and density of vegetation (fuel) present within a zone significantly impacts fire intensity and spread. Maps may incorporate information about fuel types and their flammability.
- Fire History: Historical fire records, including the frequency and intensity of past fires, provide valuable insights into the fire potential of a region.
The Importance of Fire Weather Zones Maps:
1. Enhanced Fire Prevention:
- Targeted Resource Allocation: Maps allow fire management agencies to prioritize resources and focus preventive efforts in areas with higher fire danger ratings.
- Prescribed Burning: By understanding the prevailing fire weather conditions, agencies can implement prescribed burns, a controlled fire management technique to reduce fuel loads and minimize the risk of uncontrolled wildfires.
- Public Education: Maps provide valuable information for the public, raising awareness about fire risks and promoting fire safety practices.
2. Improved Wildfire Response:
- Strategic Deployment: Firefighting resources, including personnel and equipment, can be strategically deployed based on the fire danger rating and location of active fires.
- Evacuation Planning: Maps provide critical information for evacuation planning, allowing authorities to identify areas at high risk and implement timely evacuations.
- Suppression Strategies: Understanding the fire weather conditions within a specific zone helps firefighters tailor their suppression strategies to effectively combat the fire.
3. Enhanced Research and Monitoring:
- Fire Behavior Modeling: Fire weather zones maps provide valuable input for developing and refining fire behavior models, which predict fire spread and intensity.
- Climate Change Impact: Maps can be used to analyze the long-term impact of climate change on fire risk, enabling researchers and policymakers to develop adaptation strategies.
- Ecosystem Management: Understanding fire weather patterns is crucial for managing ecosystems susceptible to wildfire, balancing the need for fire for ecological renewal with the need for protection.
Beyond the Map: Utilizing Fire Weather Information:
Fire weather zones maps are just one component of a comprehensive wildfire risk management strategy. Other important factors include:
- Real-time Weather Monitoring: Continuously monitoring weather conditions, especially changes in wind direction and speed, is crucial for effective fire response.
- Fuel Management: Reducing fuel loads through prescribed burns, mechanical thinning, and other methods can significantly decrease the risk of intense wildfires.
- Public Awareness and Education: Engaging the public in fire prevention and response efforts is crucial for building community resilience.
FAQs on Fire Weather Zones Maps:
1. How are fire weather zones defined?
Fire weather zones are defined based on a combination of factors, including:
- Topography: Elevation, slope, and aspect influence wind patterns and fuel moisture.
- Vegetation: The type and density of vegetation determine fuel load and flammability.
- Historical Fire Activity: Past fire events provide valuable data on fire behavior and risk.
- Weather Patterns: Long-term weather data, including average temperatures, humidity, and precipitation, contribute to zone delineation.
2. Who develops and maintains fire weather zones maps?
Fire weather zones maps are typically developed and maintained by:
- Meteorological Agencies: National weather services often provide fire weather forecasts and maps.
- Fire Management Agencies: Federal, state, and local fire management organizations create and maintain maps specific to their jurisdictions.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research centers conduct research on fire weather and contribute to map development.
3. How frequently are fire weather zones maps updated?
Fire weather zones maps are updated regularly, often daily or even more frequently, to reflect changes in weather conditions.
4. How accurate are fire weather zones maps?
The accuracy of fire weather zones maps depends on the quality of data used and the sophistication of the modeling techniques employed. While these maps provide valuable guidance, they should be used in conjunction with other data sources and expert judgment.
5. Are fire weather zones maps only used for wildfires?
While fire weather zones maps are primarily used for wildfire management, the information they provide is also relevant for other purposes, including:
- Air Quality Management: Smoke from wildfires can significantly impact air quality, and fire weather zones maps help identify areas at risk.
- Agricultural Practices: Farmers can use fire weather information to make informed decisions about burning practices.
- Emergency Planning: Fire weather zones maps provide valuable data for emergency planning and response, including evacuations and resource allocation.
Tips for Using Fire Weather Zones Maps:
- Consult the Most Recent Maps: Ensure you are using the most up-to-date fire weather zones map, as conditions can change rapidly.
- Understand the Fire Danger Rating: Familiarize yourself with the fire danger rating system used in your region and its implications for fire behavior.
- Check for Weather Alerts: Pay attention to weather alerts and warnings issued by relevant authorities.
- Be Aware of Local Conditions: Even within a specific fire weather zone, local conditions can vary, so be mindful of your immediate surroundings.
- Follow Fire Safety Guidelines: Adhere to fire safety guidelines and regulations, especially during periods of high fire danger.
Conclusion:
Fire weather zones maps serve as a vital tool for managing the ever-present threat of wildfires. By providing a clear framework for understanding fire risk and behavior, these maps empower fire management agencies, researchers, and the public to make informed decisions and take proactive steps to mitigate the devastating impacts of wildfires. As climate change intensifies and fuels the frequency and intensity of wildfires, the importance of fire weather zones maps will only grow, playing a crucial role in protecting communities, ecosystems, and the future of our planet.
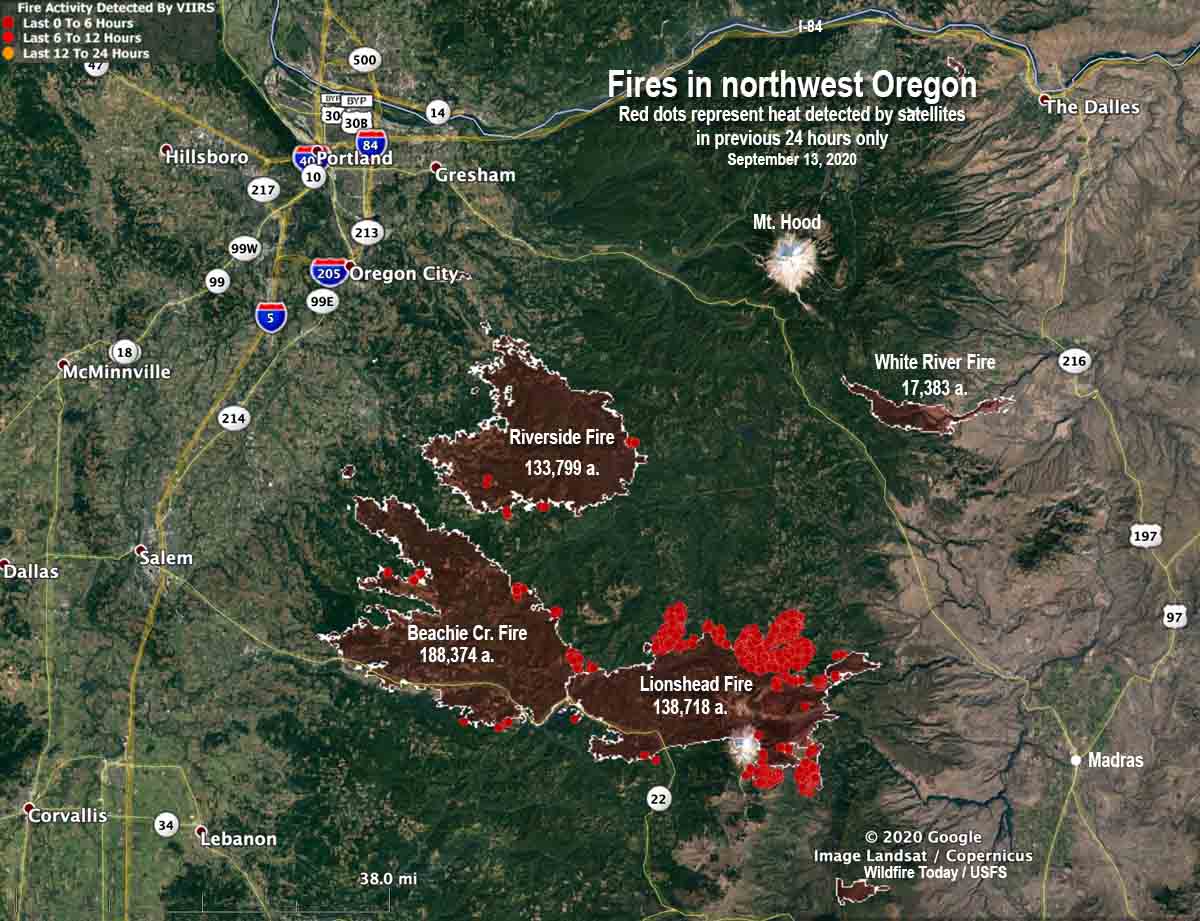
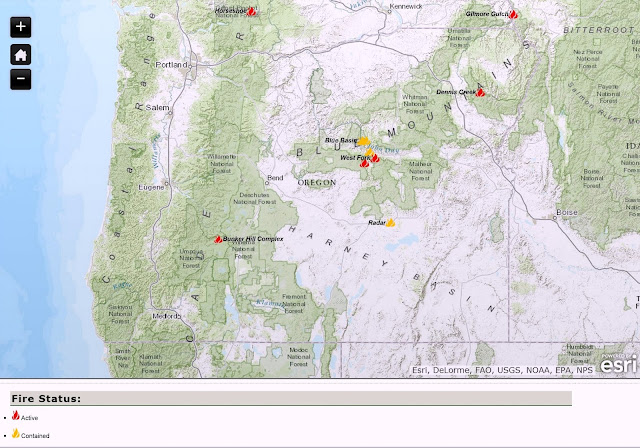
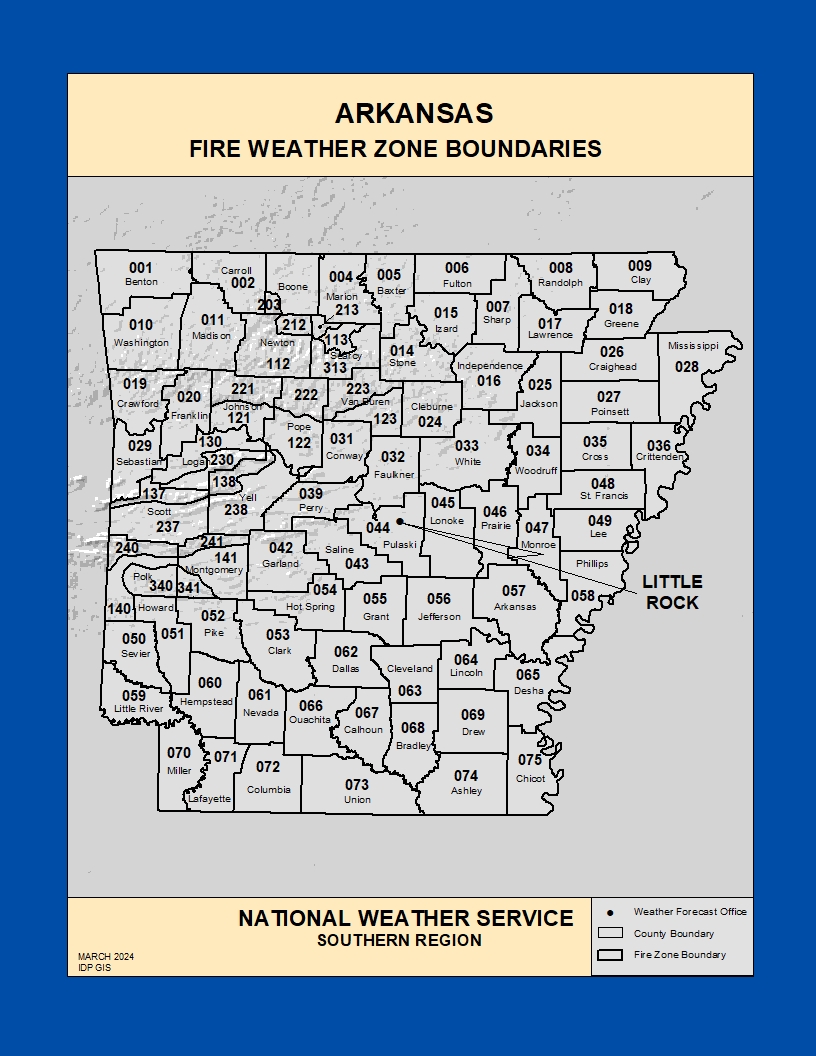

.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Flames: Understanding Fire Weather Zones Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!