Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps
Related Articles: Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps
- 3.1 The Importance of Geographical Regions Maps
- 3.2 Types of Geographical Regions Maps
- 3.3 Key Features of Geographical Regions Maps
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Geographical Regions Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Geographical Regions Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps
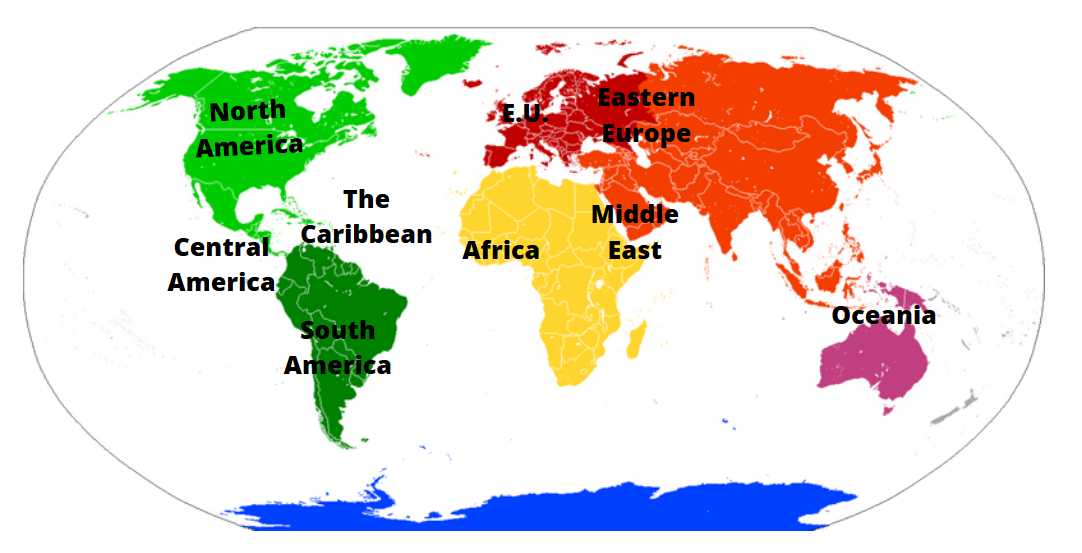
Geographical regions maps, often referred to as world maps, are fundamental tools for comprehending the Earth’s diverse landscapes, cultures, and populations. These maps provide a visual representation of the planet, dividing it into distinct regions based on various criteria, such as geographical features, political boundaries, climate, or cultural characteristics. They serve as invaluable resources for education, research, travel, and global understanding.
The Importance of Geographical Regions Maps
Geographical regions maps hold significant value in numerous fields:
1. Education: Maps are essential educational tools, fostering a deeper understanding of the world’s geography, history, and cultures. They help students visualize spatial relationships, comprehend the distribution of natural resources, and learn about different societies and their interactions.
2. Research: Researchers across disciplines, including geography, geology, environmental science, and social sciences, rely on geographical regions maps for data analysis, identifying patterns, and understanding spatial trends. They provide crucial insights into climate change, resource distribution, population dynamics, and economic development.
3. Travel and Tourism: Geographical regions maps are indispensable for travelers, enabling them to plan itineraries, navigate unfamiliar territories, and discover points of interest. They help travelers understand geographical distances, locate key cities and landmarks, and choose appropriate transportation options.
4. Global Awareness: By visually representing the Earth’s regions, geographical regions maps promote global awareness and understanding. They foster appreciation for diverse cultures, highlight environmental challenges, and emphasize the interconnectedness of our planet.
5. Political and Economic Analysis: Maps are crucial for understanding political boundaries, economic zones, and trade routes. They provide insights into global trade patterns, resource allocation, and geopolitical dynamics.
Types of Geographical Regions Maps
Geographical regions maps come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose:
1. Physical Maps: These maps emphasize Earth’s physical features, such as mountains, rivers, lakes, and oceans. They depict elevation, terrain, and hydrological systems, providing a detailed understanding of the planet’s natural landscape.
2. Political Maps: Political maps focus on human-defined boundaries, showcasing countries, states, provinces, and cities. They highlight political divisions, territorial disputes, and administrative structures.
3. Climate Maps: Climate maps illustrate global and regional climate patterns, depicting temperature zones, precipitation levels, and prevailing wind patterns. They provide insights into climatic variations and their impact on human activities.
4. Vegetation Maps: Vegetation maps depict the distribution of different plant communities, showcasing forests, grasslands, deserts, and other ecosystems. They provide valuable information about biodiversity, land use, and environmental conditions.
5. Population Maps: Population maps illustrate the distribution of human populations across the globe, highlighting population density, urban centers, and migration patterns. They offer insights into demographic trends and social dynamics.
6. Economic Maps: Economic maps focus on the distribution of economic activities, such as agriculture, industry, and trade. They depict resource extraction, production centers, and transportation networks, providing an understanding of global economic flows.
7. Thematic Maps: Thematic maps highlight specific themes, such as resource distribution, disease prevalence, or environmental pollution. They use various symbols, colors, and patterns to represent data and trends related to a particular subject.
Key Features of Geographical Regions Maps
Effective geographical regions maps share common features:
1. Projection: Maps are flat representations of a spherical Earth, requiring a projection system to translate three-dimensional data onto a two-dimensional surface. Different projections distort the shape, size, and relative distances of geographical features, each with its own advantages and limitations.
2. Scale: Scale refers to the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the Earth’s surface. Large-scale maps cover smaller areas with more detail, while small-scale maps cover larger areas with less detail.
3. Legend: A legend explains the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map, providing a key for interpreting the information presented.
4. Grid System: Many maps employ a grid system, such as latitude and longitude lines, for accurate location identification.
5. Data Representation: Geographical regions maps use various methods to represent data, including:
- Point Symbols: Used to represent specific locations, such as cities or natural features.
- Line Symbols: Used to depict linear features, such as roads, rivers, or boundaries.
- Area Symbols: Used to represent geographical regions, such as countries or continents.
- Choropleth Maps: Use color gradients or patterns to represent data values across geographical regions.
6. Map Projections: Maps utilize different projections to represent the Earth’s surface on a flat plane. Some commonly used projections include:
- Mercator Projection: Preserves shapes but distorts areas, particularly near the poles.
- Robinson Projection: A compromise projection that minimizes distortions but does not preserve shapes or areas accurately.
- Winkel Tripel Projection: A balanced projection that minimizes distortion in both shape and area.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Geographical Regions Maps
1. What are the main types of geographical regions maps?
Geographical regions maps are categorized into various types based on their focus, including physical maps, political maps, climate maps, vegetation maps, population maps, and economic maps.
2. What are the advantages of using different map projections?
Different map projections offer advantages depending on the purpose of the map. For example, the Mercator projection is suitable for navigation, while the Winkel Tripel projection minimizes distortion in both shape and area.
3. How can I use a geographical regions map for travel planning?
Geographical regions maps can help travelers plan itineraries, identify points of interest, and choose appropriate transportation options. They provide a visual representation of geographical distances, key cities, and landmarks.
4. What are some examples of thematic maps?
Thematic maps highlight specific themes, such as resource distribution, disease prevalence, or environmental pollution. They use various symbols, colors, and patterns to represent data and trends related to a particular subject.
5. How do I choose the right geographical regions map for my needs?
The choice of map depends on the specific purpose and intended use. Consider the type of information needed, the level of detail required, and the intended audience.
Tips for Using Geographical Regions Maps Effectively
1. Understand the Map’s Projection: Be aware of the projection used and its potential distortions.
2. Read the Legend: Carefully interpret the symbols, colors, and patterns used on the map.
3. Consider the Scale: Choose a map with an appropriate scale for the desired level of detail.
4. Use Multiple Maps: Combine different types of maps for a comprehensive understanding of the region.
5. Explore Interactive Maps: Utilize online mapping tools and interactive maps for dynamic visualization and data analysis.
6. Consult Multiple Sources: Verify information from different sources to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Conclusion
Geographical regions maps are essential tools for understanding the world’s geography, cultures, and societies. They provide a visual representation of the planet, highlighting key features, patterns, and trends. By understanding the different types of maps, their key features, and how to use them effectively, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the Earth’s diverse landscapes, human interactions, and global challenges. Geographical regions maps serve as valuable resources for education, research, travel, and global awareness, fostering a more informed and interconnected world.



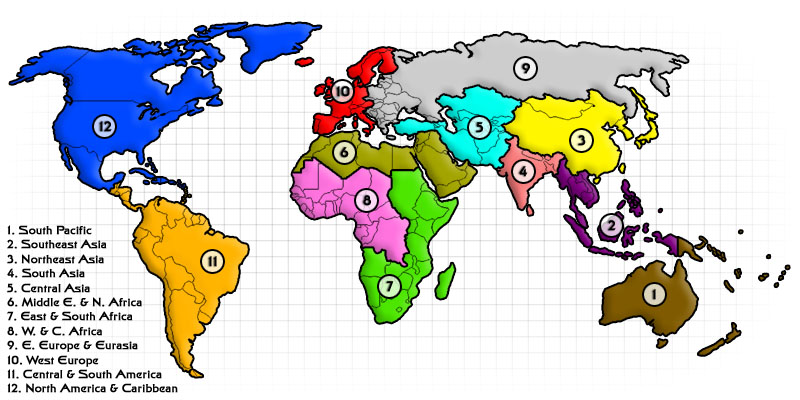
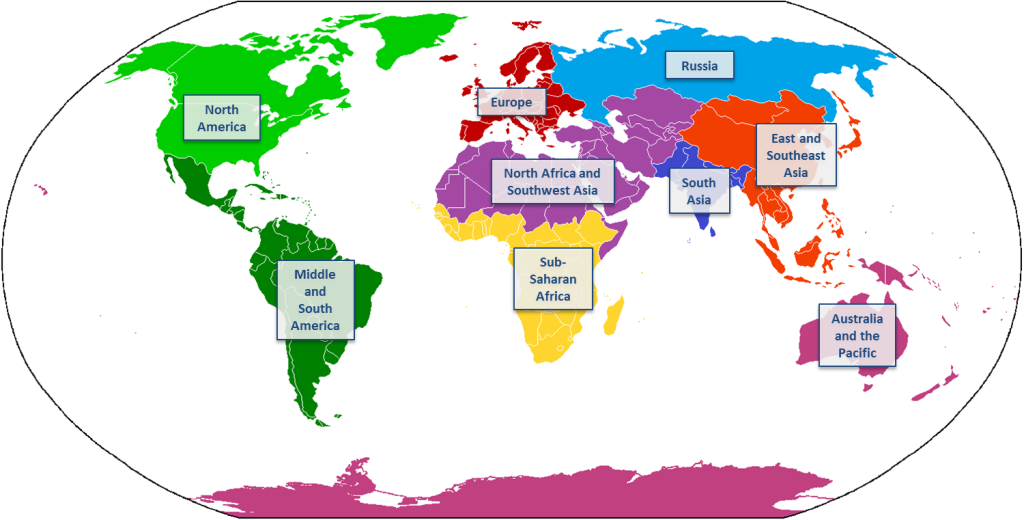
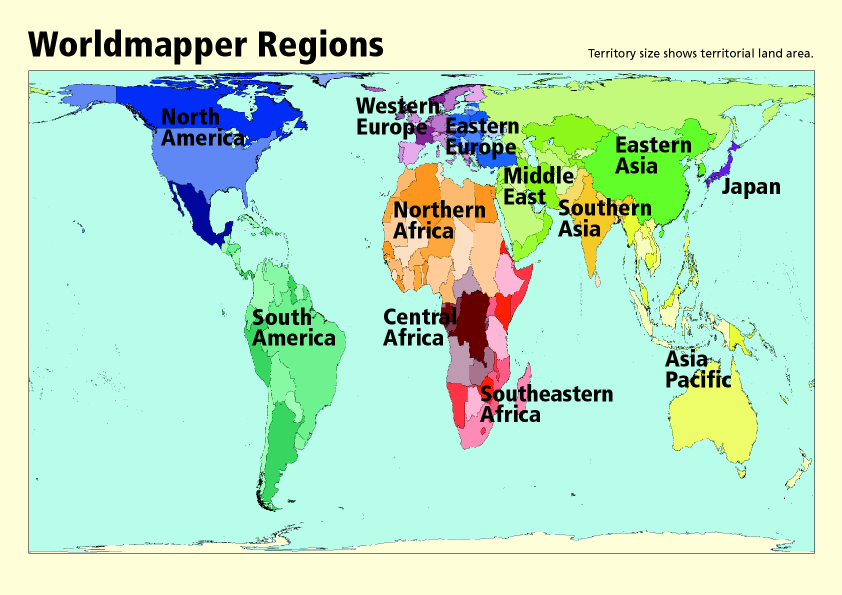

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the World: Understanding Geographical Regions Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!