Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
Related Articles: Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
- 3.1 The Geographical Canvas: Navigating the Mesopotamian Landscape
- 3.2 Mapping the Rise and Fall of Empires: A Glimpse into Mesopotamian History
- 3.3 Unveiling the Cultural Tapestry: Mapping Mesopotamian Achievements
- 3.4 The Legacy of Mesopotamia: Mapping an Enduring Influence
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Studying the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization

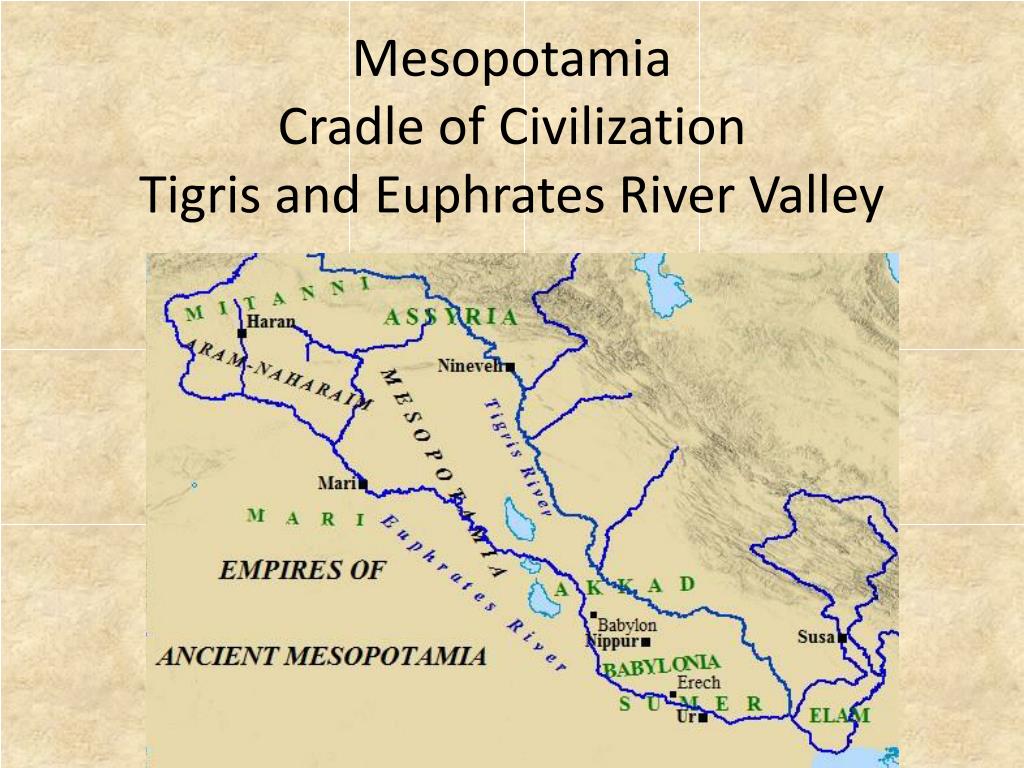
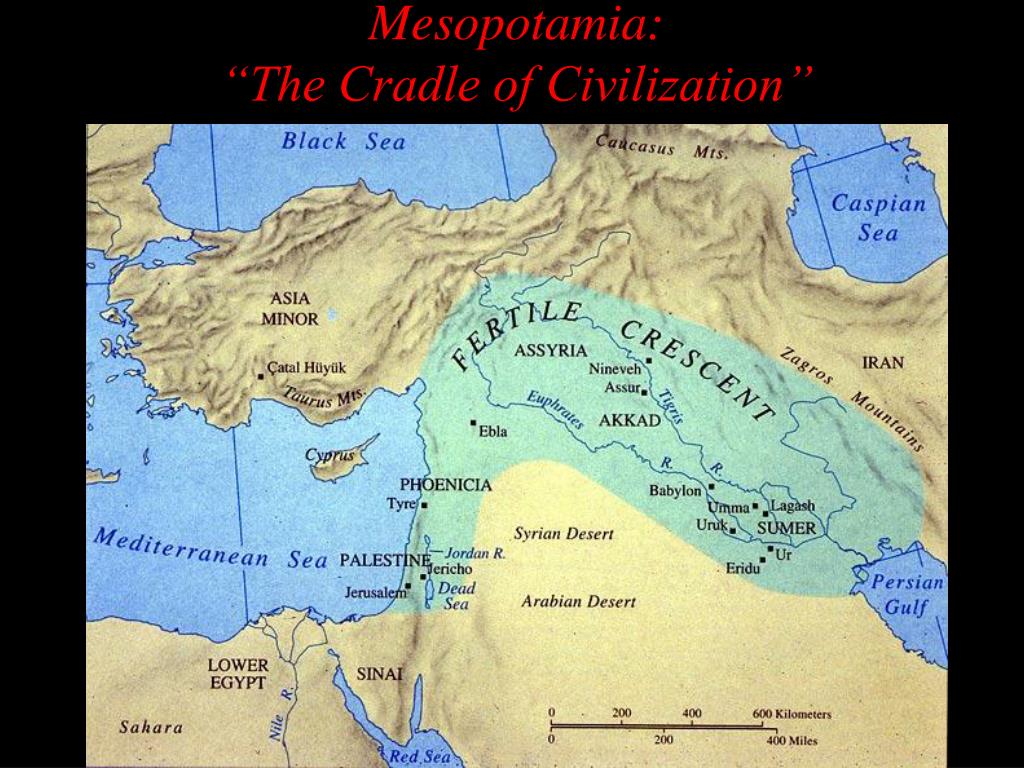
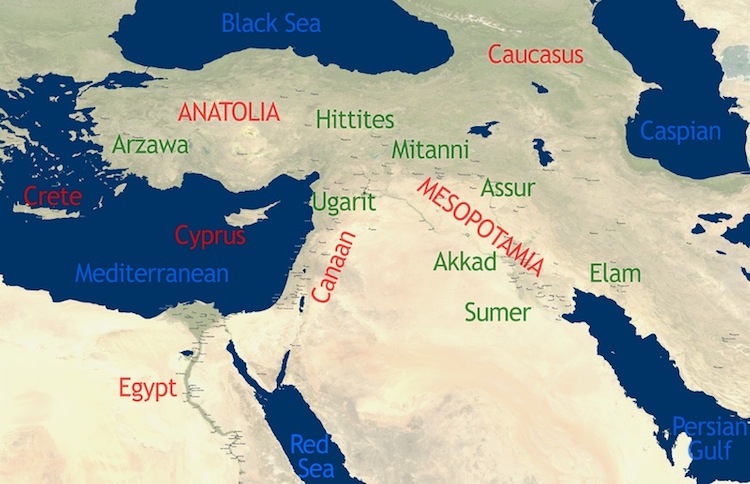
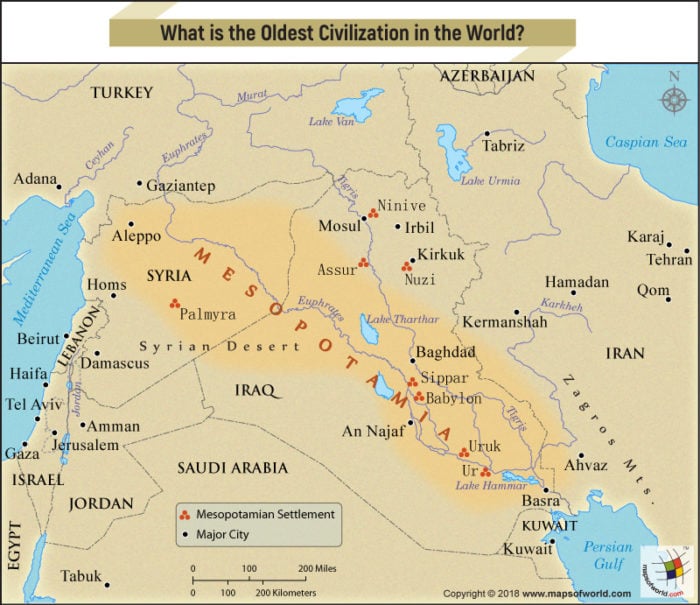
The Mesopotamian civilization, nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in present-day Iraq, Kuwait, and parts of Turkey and Syria, stands as a cornerstone of human history. Its contributions to civilization are vast and enduring, from the invention of writing to the development of sophisticated legal systems and architectural marvels. Understanding the geographical context of this civilization, as depicted on a map, is crucial for appreciating its cultural, social, and political complexities.
The Geographical Canvas: Navigating the Mesopotamian Landscape
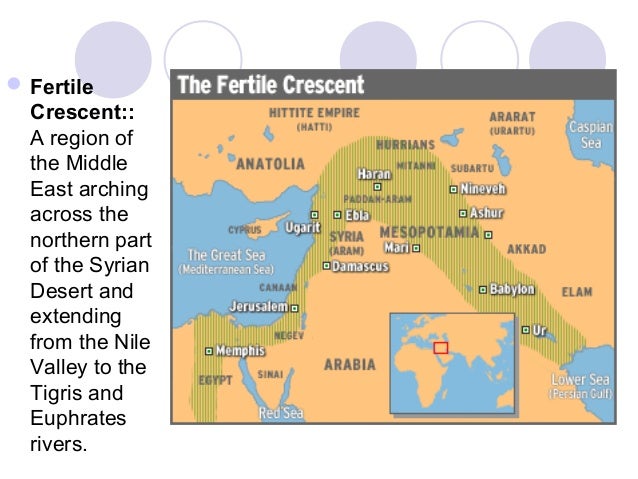
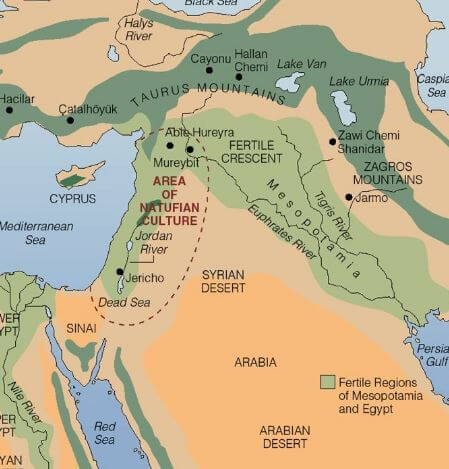
The map of Mesopotamia reveals a land shaped by the relentless flow of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. These rivers, acting as lifelines, provided fertile soil for agriculture, facilitated trade and communication, and shaped the very identity of the region. The land itself was a patchwork of diverse ecosystems: fertile plains, marshlands, arid steppes, and rolling hills. This geographical diversity fostered a variety of cultures and economies, enriching the tapestry of Mesopotamian life.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: These rivers served as the lifeblood of Mesopotamia, providing irrigation for agriculture, transportation routes for trade, and a source of freshwater.
- The Fertile Crescent: The region’s fertile soil, nurtured by the rivers, allowed for the development of agriculture, which was central to the rise of civilization.
- The Mesopotamian Plain: This vast plain, situated between the rivers, was the heartland of Mesopotamian civilization, home to its major cities and agricultural centers.
- The Zagros Mountains: These mountains, bordering the region to the east, provided natural barriers and resources, impacting trade routes and influencing the development of regional kingdoms.
Mapping the Rise and Fall of Empires: A Glimpse into Mesopotamian History
The map of Mesopotamia is not static. It tells a dynamic story of empires rising and falling, of cultural exchange and conflict, of innovation and adaptation. Examining the map through the lens of history reveals a captivating narrative:
Key Historical Periods:
- The Sumerian Civilization (c. 3500-2334 BCE): The Sumerians, known for their invention of cuneiform writing, established city-states like Ur, Uruk, and Kish. Their influence extended across the Mesopotamian plain, leaving a lasting legacy on subsequent civilizations.
- The Akkadian Empire (c. 2334-2154 BCE): Sargon the Great, the Akkadian king, unified Mesopotamia, establishing the first empire in the region. This period saw the expansion of trade and cultural influence, along with advancements in warfare and administration.
- The Babylonian Empire (c. 1894-1595 BCE): Hammurabi, the Babylonian king, codified the famous Code of Hammurabi, a landmark in legal history. The Babylonians also developed a sophisticated system of astronomy and mathematics.
- The Assyrian Empire (c. 911-609 BCE): Known for their military prowess, the Assyrians conquered a vast territory, extending their influence beyond Mesopotamia. Their empire was marked by a centralized bureaucracy and a focus on infrastructure development.
- The Neo-Babylonian Empire (c. 626-539 BCE): Nebuchadnezzar II, the Babylonian king, rebuilt Babylon into a magnificent city, known for its Hanging Gardens, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World.
- The Persian Empire (c. 539-330 BCE): The Persians, under Cyrus the Great, conquered Mesopotamia, integrating it into their vast empire. This period witnessed the rise of Zoroastrianism, a major religious influence in the region.
Unveiling the Cultural Tapestry: Mapping Mesopotamian Achievements
The map of Mesopotamia is not just a geographical representation; it is a canvas on which the achievements of this civilization are vividly painted. From the invention of the wheel to the development of complex irrigation systems, Mesopotamia’s contributions to civilization are undeniable.
Key Cultural Achievements:
- Writing and Literature: The Sumerians invented cuneiform writing, a system of wedge-shaped symbols impressed on clay tablets. This invention paved the way for record-keeping, literature, and the transmission of knowledge. Mesopotamian literature includes epic poems like the Epic of Gilgamesh, which explores themes of mortality, heroism, and the human condition.
- Mathematics and Astronomy: The Mesopotamians developed a sophisticated system of mathematics, including the use of place-value notation and the concept of zero. They also made significant contributions to astronomy, charting the movement of celestial bodies and developing a calendar based on the lunar cycle.
- Architecture and Engineering: The Mesopotamians were skilled architects and engineers, building impressive ziggurats, temples, and palaces. They developed advanced irrigation systems to manage water resources and innovative techniques for constructing durable buildings.
- Law and Social Organization: The Code of Hammurabi, a comprehensive legal code, established a system of justice and social order. The Mesopotamian society was organized into complex social structures, with specialized roles and hierarchies.
The Legacy of Mesopotamia: Mapping an Enduring Influence
The map of Mesopotamia is not merely a historical artifact; it represents a living legacy that continues to influence our world today. The achievements of this civilization, from its advancements in agriculture and writing to its contributions to law and architecture, have shaped the course of human history.
Enduring Legacy:
- Foundation of Civilization: Mesopotamia laid the foundation for many aspects of civilization, including agriculture, writing, law, and urban planning. These innovations were adopted and adapted by subsequent civilizations, shaping the world we live in today.
- Inspiration for Art and Literature: Mesopotamian myths, legends, and epic poems have inspired artists and writers throughout history. The Epic of Gilgamesh, for instance, continues to resonate with readers today, exploring universal themes of human existence.
- Influence on Modern Science: Mesopotamian advancements in mathematics, astronomy, and medicine have contributed to the development of modern science. Their understanding of the celestial bodies and their observations of the natural world laid the groundwork for future scientific inquiry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the significance of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers to Mesopotamian civilization?
A: The Tigris and Euphrates rivers were the lifeblood of Mesopotamia, providing water for irrigation, transportation routes for trade, and a source of freshwater. Their fertile soil allowed for the development of agriculture, which was central to the rise of civilization.
Q: What are some of the major cities of Mesopotamia?
A: Some of the major cities of Mesopotamia include Ur, Uruk, Kish, Akkad, Babylon, Nineveh, and Assur. These cities were centers of trade, culture, and political power, playing a significant role in the development of the region.
Q: What are some of the key cultural achievements of Mesopotamia?
A: The Mesopotamians invented cuneiform writing, developed a sophisticated system of mathematics and astronomy, built impressive ziggurats and temples, and codified the Code of Hammurabi, a landmark in legal history.
Q: How did Mesopotamia influence subsequent civilizations?
A: Mesopotamia’s advancements in agriculture, writing, law, and architecture were adopted and adapted by subsequent civilizations, shaping the course of human history. Its cultural legacy continues to inspire artists, writers, and scholars today.
Tips for Studying the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization
- Use a detailed map: Utilize maps that highlight geographical features, major cities, and historical boundaries to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Connect the map to historical events: Relate the map to key historical periods, empires, and cultural achievements to understand the dynamic nature of Mesopotamian civilization.
- Explore primary sources: Consult ancient texts, archaeological evidence, and historical accounts to gain insights into the lives and experiences of Mesopotamian people.
- Compare and contrast different maps: Compare maps from different periods to observe changes in political boundaries, cultural influences, and the evolution of the Mesopotamian landscape.
Conclusion
The map of Mesopotamian civilization is a powerful tool for understanding the rise and fall of empires, the cultural achievements of this ancient society, and its lasting impact on the world. It provides a visual narrative of a civilization that laid the foundation for many aspects of human civilization, from the invention of writing to the development of sophisticated legal systems. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of Mesopotamian history, its enduring legacy, and its contribution to the tapestry of human civilization.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Cradle of Civilization: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Mesopotamian Civilization. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!